Simple algorithmic stock and option trading for Node.js.
Features
- Extensive broker library
- Easily place orders
- Retrieve past orders
- Query a users portfolio
- Supported brokers:
- Robinhood
- TDAmeritrade (in progress)
- Oanda (in progress)
- If you'd like to have another broker supported, submit an issue or a pull request
- Data library
- Real time quote data streaming for cryptocurrency, forex, equities
- Get data on bids, asks, last price, and more from the Yahoo Finance API
- Stream news headlines along with quotes
- Up-to-date options data
- Easily find stocks for various queries
- Retrieve the day's top gainers
- Retrieve the day's top losers
- Get stocks by highest (abnormal) volume
- Get options contracts by highest open interest
- And more
- Get up to the minute breaking headlines
- Get technical indicators from AlphaVantage
- SMA, EMA, RSI, etc.
- Get fundamentals and balance sheet data (in progress)
- Assets, debt, liabilities, revenue, earnings, etc.
- Real time quote data streaming for cryptocurrency, forex, equities
- Algorithm library (in progress)
- Create algorithms that will automatically place trades based on your criteria
- Backtest algorithms on past market data
- Paper (simulated) trade your algorithm to see how it performs in real time
- Support for many third-party APIs
Table of Contents
- Getting Started
- Broker Library
- Algorithm Library
- Data Library
- Further Notes
Support
- Join our Discord: https://discord.gg/DWFWBPn
- Get answers to questions or help us deal with open issues.
- Tell us about how you're using Algotrader!
Getting started
Using NPM, you can install Algotrader using the following console command: npm i algotrader --save
Once Algotrader is installed, you can import it into your Node.js project.
const algotrader = ;After, you can instantiate any Algotrader library like so:
const Robinhood = algotraderRobinhood;const Data = algotraderData;const Algorithm = algotraderAlgorithm; // in progressRobinhood
First, you'll need to create a new User instance and authenticate them.
const robinhood = Robinhood;const User = robinhoodUser; const options = doNotSaveToDisk: false // If the `save` method should not store the user login info to disk (file) serializedUserFile: null // File to where the serialized user login info can be saved; const myUser = "username" "password" options;myUser Personally, I either store user data as an array in a .json file, then require it into the class, (insecure) or ask for the user's credentials in the console. You should handle this sensitive data in a way that you're comfortable with.
Note: providing a password in the User constructor is optional. You can also pass it to User.authenticate() as the first parameter like so:
const myUser = "username";// Or with options:// const myUser = new User("username", null, options);myUser ;If it is not provided at all, you will be prompted via CLI.
MFA
Algotrader now supports multi-factor authentication. So, if you have this enabled on your account (which is a good idea by the way), you'll be prompted to enter the six-digit code after login. If you run a trading script with this library automatically and have MFA enabled, it may be worth your while to utilize a telecom API (possible through Twilio?) to have the code programmatically retrieved (see below).
The MFA prompt will appear like so:

To enter the code programmatically, you can pass a function to User.authenticate() that returns a promise containing the MFA code in a six-character string. For example:
{ return { // Get the code here const mfa = "123456" ; }}// Note: the first parameter here is 'password' and is only required if you are re-authenticating// an expired user or if you did not provide a password in the User constructor.myUser Saving & loading a user
In order to reduce time logging in, you can save an authenticated user to disk and load it into memory for subsequent requests. If you're using multi-factor authentication, I definitely recommend this- it really saves a lot of time and energy.
After you've logged in (see above), you can run the following:
const authenticatedUser;authenticatedUser ;Note that your password will never be saved to disk. Keep this in mind when having to re-authenticate.
Once saved, you can easily login like so:
const robinhood = Robinhood;const User = robinhoodUser; User ;However, authentication tokens issued by Robinhood expire after 24 hours. Version 1.4.5 takes this into account and User.isAuthenticated() will return false if the token has expired. Make sure to check for this and re-authenticate if necessary. When re-authenticating, you will need to provide a password either through CLI or when calling User.authenticate() as the first parameter.
If you need to save and retrieve the user login info to somewhere else (like a Database, specially useful to keep your service stateless), you can use:
const options = doNotSaveToDisk: true ;const authenticatedUser = "username" "password" options;// ...authenticatedUser ; // ...const serializedUser = ''; // Get this value from your storageUser ;Get a user's portfolio
There are a good amount of query functions that you can run on the user's portfolio. Using your User instance, you can grab the portfolio using User.getPortfolio which returns a new Portfolio object.
myUser For documentation on all portfolio functions, visit the Robinhood Library Docs.
Note: the portfolio object does not return a user's open option positions. See the options section below for details.
Placing an order
Placing an order will require instances of the User, Instrument, Quote, and Order classes.
All orders first require that you grab a new Instrument object which represents, in most cases, a stock or ETF. You can also grab the object from your Portfolio. Then, Robinhood requires that you also submit the stock's market price in the order, so you should retrieve a Quote from them on via Instrument object (the origin of the quote doesn't matter, as long as it contains accurate pricing information- so, the quote returned from the Stream class would also work). You'll then create an object with this and other necessary information to pass as a parameter to a new Order.
The object should contain the following:
Instrument- The Robinhood instrument you would like to place an order for.Quote- An updated quote containing the last sale price for the given instrument.typelimit- The lowest price to accept in a buy, the highest price in a sellmarket- Order executes at the current bid/ask price
timeInForceGFD- Good for the day (cancels at market close)GTC- Good-til-cancelled (active until you cancel it)IOC- Immediate or cancel (possibly deprecated by Robinhood)OPG- Market/limit on open (possibly deprecated by Robinhood)
triggerimmediate- The order is active as soon as it's placedstop- The order won't be active until the market price crossed your stop price
stopPrice- If
trigger = stop, this must be specified
- If
quantity- How many shares should be bought / sold
sidebuysell
extendedHoursboolean- Whether the order should be allowed to execute when exchanges are closed
overrideDayTradeCheckboolean- Whether to override Pattern Day Trader protection (this should definitely be false)
With this in mind, you can place a simple market order for ten shares of Twitter like so:
// ES6Instrument;For documentation on all order functions, visit the Robinhood Library Docs.
Options
Receiving open option positions and placing option orders varies slightly from stocks. These actions will require the OptionInstrument and OptionOrder classes.
Here is an example for how to query an option chain and place an order for an individual option. See OptionOrder documentation for details on new order parameters.
const Instrument = algotraderRobinhoodInstrument;const OptionInstrument = algotraderRobinhoodOptionInstrument;const OptionOrder = algotraderRobinhoodOptionOrder; { // First, we'll get the instrument that corresponds to the symbol TLRY. const tlry = await Instrument; // Next, we'll fetch an option chain containing puts for the upcoming expiration date. // This will return an array of OptionInstruments. See the example in the next section below. const chain = await OptionInstrument; // Now that we have the option chain, we'll need to find which OptionInstrument to trade // based on its strike price and expiration date. See the example below for how to sort them. // For now, we'll just take the first option contract in the array. const optionToBuy = chain0; // Finally, we can create and place an order like so: let order = user side: 'buy' type: 'limit' // Note: Robinhood does not allow market buy orders price: '' timeInForce: 'gtc' quantity: 1 option: optionToBuy ; order;}Option chains
Represented as an array of OptionInstruments, option chains provide you with all of the tradable contracts for a specific option instrument and expiration date. They are fetched using OptionInstrument.getChain and used for an OptionOrder.
Below is an example of a single element from within the array:
OptionInstrument url: 'https://api.robinhood.com' tradability: 'tradable' strikePrice: 121 state: 'active' type: 'put' symbol: 'TLRY' minTicks: cutoff_price: '3.00' below_tick: '0.01' above_tick: '0.05' instrumentURL: 'https://api.robinhood.com/options/instruments/28c3224d-3aa3-428c-aa78-7e0f5a4d01a0/' ids: chain: 'c49063f0-557b-44b7-aeef-11fbc6a51243' option: '28c3224d-3aa3-428c-aa78-7e0f5a4d01a0' dates: expiration: 2019-02-01T00:00:00000Z created: 2019-01-18T03:08:31325Z updated: 2019-01-18T03:08:31325Z ...Here is an example of how you would sort an option chain by strike price and expiration date. For this example, we'll get a quote, the options chain, and option expiration dates and use that data buy the nearest in-the-money call.
const moment = ; const qqq = await Instrument;const quote = await qqq;const chain = await OptionInstrument;const expirations = await OptionInstrument;// Returns an array of expiration dates [ 2019-02-01T00:00:00.000Z, 2019-02-08T00:00:00.000Z, ... const nextExpiration = ; let optionsExpiringNext = ; chain;Algorithm Library
For scheduling tasks, running backtests, and paper-trading, the algorithm library should be more than useful.
Scheduler
Using the Scheduler class, you'll be able to define exactly when you want a function to run using the following methods:
Scheduler.onMarketOpen(offset, f)- Runs every morning when the NYSE opens. (Typically 9:30 AM EST)
- Offset is in milliseconds and can be positive (after) or negative (before).
Scheduler.onMarketClose(offset, f)- Runs every afternoon when the NYSE closes. (Typically 4:00 PM EST)
- Offset is in milliseconds and can be positive (after) or negative (before).
Scheduler.every(minutes, extended, f)- Runs every
xminutes during market hours or during typical extended trading hours. (9 AM EST - 6 PM EST)
- Runs every
Here's an easy example that runs a function 5 minutes before the market opens and another one every 30 minutes during regular trading hours:
const Scheduler = algotraderAlgorithmScheduler; Scheduler; Scheduler;For documentation on all Scheduler functions, visit the Algorithm Library Docs.
Data Library
The data library allows you to retrieve a ton of data on the market as a whole and individual stocks or options. This uses the Yahoo Finance and Alpha Vantage APIs and additional support for other free API's will be added in the future.
I'll only add a few examples here, but for the full documentation visit the Data Library Docs.
Real time streaming
To stream live quotes from Yahoo Finance, you'll need an array of symbols that you want to monitor. If you only need data on one, just fill the array with that single symbol. The Stream class is an extension of the Node EventEmitter, so you can either use .on() or .pipe() like other events.
Once the stream starts, a data object for each symbol is immediately received. You will then begin to get real time updates. Note that the data objects streamed by Yahoo aren't always of the same format, so make sure to have a check for undefined each time you access a key in the object.
const Stream = algotraderDataStream; const myStream = "PG" "DPS" "ULTA" "DIN" "ETSY";myStreamstart; myStream ;For documentation on Quotes, visit the Global Docs.
Not only can you stream quotes, but you can include news articles using the built-in News Library. This is useful for reacting to breaking headlines with pre-determined trades (for example, earnings reports or FOMC results). To do this, just add a second parameter (an object) to new Stream() as shown below.
const myStreamWithNews = "JPM" "COST" "FDX" news: true // Tells the streamer to also include news allHeadlines: true // If true, all U.S. headlines will be sent in the stream. If false, only news pertaining to the given symbols will be outputted. newsApiKey: "newsApiKeyGoesHere" // Your API key from NewsAPI.org. See the link below for documentation on News.;myStreamWithNewsstart; myStreamWithNews ;For documentation on News, visit the Data Library Docs.
You can also instruct the stream class to fire events from IEX. You'll first want to find the streaming endpoint that contains the data you want to query. For the most part, you'll want to use tops, deep, and last. Find them all here.
const streamWithIEX = "PG" "DIN" "ULTA" iex: true iexType: "tops";streamWithIEX;For documentation on IEX, visit the Data Library Docs.
Alpha Vantage
Providing free access to real time and historical market data along with advanced technical analysis, Alpha Vantage has proven to be very helpful when it comes to analyzing stock activity. The only caveat is that, during market hours, their servers can occasionally take a while to respond. But aside from that, you won't find a more well equipped API for free.
To use Algotrader's built-in Alpha Vantage library, you'll first need to grab a free API key here. After the key is displayed on the page, you can copy it to your program and instantiate a new AlphaVantage object like so:
const AlphaVantage = algotraderDataAlphaVantage;const av = "myApiKey";After, you can access any of the information provided in their documentation easily.
// Get real time intraday price informationav;// Get relative strength indexav;For documentation on all Alpha Vantage functions, visit the Data Library Docs.
IEX
IEX is a stock exchange founded in 2012 with the goal of creating "fairer markets." True to this goal, they've created a public API for use by everyone, not just institutions that can afford a massive monthly payment for data. Thanks to many factors, such as trading arbitrage, their quotes are the same (if not off by a fraction of a basis point) as the NYSE's and Nasdaq's nearly 100% of the time, even with their low volume comparatively. With that being said, below are a few examples of ways you can access their quote data and corporate financial information. For a full list of IEX queries, visit the Data Library Docs.
const IEX = algotraderDataIEX; // Returns a quote objectIEX; // Returns an array of fiscal reports dating back 5 yearsIEX; // Returns company name, EPS, divided, short interest, 52-week high/low, percent change, EBITDA, and more.IEX; You can even grab a company's logo with:
IEX;Output:

For documentation on IEX queries, visit the Data Library Docs.
Nasdaq
By market cap, the Nasdaq is the second largest global stock exchange behind only the NYSE. They offer a paid subscription for real time streaming, but Algotrader makes use of their public data repository via FTP. Below is an example of how to retrieve an array of all securities listed on their exchange. For a full list of Nasdaq queries, visit the Data Library Docs.
const Nasdaq = algotraderDataNasdaq; Nasdaq;For documentation on Nasdaq queries, visit the Data Library Docs.
Query
Using the Yahoo Finance and Robinhood APIs, you can easily find stocks based on certain criteria.
Here are a few examples:
const Query = algotraderDataQuery; Query; Query; Query; Query;For documentation on all functions of the Query class, visit the Data Library Docs.
News
Thanks to both News API and Yahoo Finance, you can get breaking news headlines and various articles on either specific companies or the market or world as a whole.
First you'll want to create a reference to the News class: const News = algotrader.Data.News;
You can then use either Yahoo Finance or News API to retrieve news articles, but it's easier to find exactly what you're looking for with the latter.
For Yahoo Finance, simply do the following:
News;You'll notice that Yahoo Finance does not provide the author or the source and only links back to their website.
With News API, you'll get many more options on what articles to return. However, you'll need a free API key in order to use their service. Register for one here. You can then get either breaking/recent headlines or search for all articles matching your query.
Each News API query must contain an object with at least one query option. Possible parameters for the two functions are:
getHeadlines(apiKey, object)q- Keywords or phrases to search for.category- Possible options: business, entertainment, general, health, science, sports, technology (Cannot be mixed with sources parameter)country- The 2-letter ISO 3166-1 code of the country you want to get headlines for. (Cannot be mixed with sources parameter)sources- A comma-separated string of identifiers (maximum 20) for the news sources or blogs you want headlines from. (Cannot be mixed with country parameter)pageSize- The number of results to return per page. 20 is the default, 100 is the maximum.page- Use this to page through the results.
getAll(apiKey, object)q- Keywords or phrases to search for.sources- A comma-separated string of identifiers (maximum 20) for the news sources or blogs you want headlines from.domains- A comma-separated string of domains (eg bbc.co.uk, techcrunch.com, engadget.com) to restrict the search to.from- A date object for the oldest allowed article.to- A date object for the newest allowed article.language- Possible options: ar, de, en, es, fr, he, it, nl, no, pt, ru, se, ud, zhsortBy- Possible options: relevancy, popularity, publishedAt (newest)pageSize- The number of results to return per page. 20 is the default, 100 is the maximum.page- Use this to page through the results.
Here is an example query for U.S. articles relating to using getHeadlines(apiKey, object):
News;The News Class provides a few functions that you can run to easily retrieve information you need, such as news.getTitle(), news.getDate(), and news.getDescription(). You can also download the full article from the source:
news;For documentation on all News functions, visit the Data Library Docs.
Notes
Dealing with errors
You should ensure that all promises are provided a catch function in case they are rejected. In order to help with debugging, the Error.toString() method is modified in Algotrader's library. If you don't choose to use this you can continue to simply print the error.
For example:
myOrder;This would print something similar to the image below, providing the response code and error message(s) from Robinhood. This is a larger error, so keep in mind that most of these would be on one line.
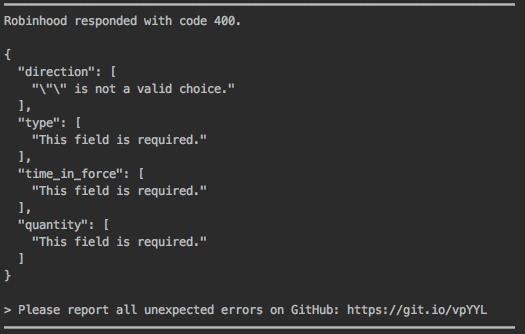
However, if you don't like this and want to keep your errors uniform, you can simply use console.error(error) without toString().
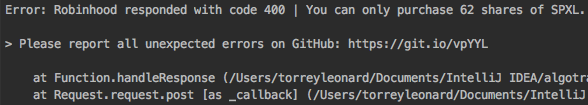
As you can probably see from the images, it's much appreciated if you report unexpected errors as a new Issue on GitHub. Not only can you get help resolving the error if it's an isolated incident, but it also helps fix bugs in future updates.
You can report errors here.