English | 中文
vue-condition-watcher 
Introduction
Vue composition API for automatic data fetching. With conditions as the core. Easily control and sync to URL query string by conditions
requires Node.js 12.0.0 or higher.
Features
conditions changes
null undefined [] '' will be automatically filtered out before sending the request
conditions according to the query string of the URL, and will automatically correspond to the type ( string, number, array, date )
conditions changes, the URL query string will be automatically synchronized, and the previous page and next page will work normally
race condition, ensure requests are first in, first out, and can also avoid repeated requests
data
data to make the user experience better
Navigation
- Installation
- Quick Start
- Configs
- Return Values
- Execute Fetch
- Prevent Request
- Manually Trigger Request
- Intercepting Request
- Mutations data
- Conditions Change Event
- Fetch Event
- Polling
- Cache
- History Mode
- Lifecycle
- Pagination
- Changelog
Demo
cd examples/vue3
yarn
yarn servecd examples/vue2
yarn
yarn serve👉 Online demo
Getting Started
Installation
In your project
yarn add vue-condition-watcherOr with npm
npm install vue-condition-watcherCDN
https://unpkg.com/vue-condition-watcher/dist/index.jsQuick Start
This is a simple example for vue-next and vue-router-next
First you need to create a fetcher function, use the native fetch or libs like Axios. Then import useConditionWatcher and start using it.
createApp({
template: `
<div class="filter">
<input v-model="conditions.name">
<button @click="execute">Refetch</button>
</div>
<div class="container">
{{ !loading ? data : 'Loading...' }}
</div>
<div v-if="error">{{ error }}</div>
`,
setup() {
const fetcher = params => axios.get('/user/', {params})
const router = useRouter()
const { conditions, data, loading, error } = useConditionWatcher(
{
fetcher,
conditions: {
name: ''
},
history: {
sync: router
}
}
)
return { conditions, data, loading, error }
},
})
.use(router)
.mount(document.createElement('div'))You can use the value of data, error, and loading to determine the current state of the request.
When the conditions.name value changes, will fire the lifecycle to fetching data again.
Use config.history of sync to sync: router. Will store the conditions within the URL query string every time conditions change.
Basic Usage
const { conditions, data, error, loading, execute, resetConditions, onConditionsChange } = useConditionWatcher(config)Configs
-
fetcher: (⚠️ Required) promise function for data fetching. -
conditions: (⚠️ Required)conditionsdefault value. -
defaultParams: The parameters that will be preset with each request and cannot be modified. -
initialData:datareturns null by default. If you want to define the initial data, you can use this parameter setting. -
immediate: If you don't want to automatically fetch data in the first time, you can set this parameter tofalse, and the request will not be executed untilconditionsis changed orexecuteis executed. -
manual: Instead manually executeexecutefunction to trigger the request, even ifconditionschanges, it will not be automatically requested. -
history: Based on vue-router (v3 & v4), enables synchronization ofconditionsto URL's Query String. Synchronize Query String toconditionswhen the page is refreshed -
pollingInterval: Enable polling, can benumberorref(number)in milliseconds -
pollingWhenHidden: Continue polling whenever you leave the focused screen, the default isfalse. -
pollingWhenOffline: continue polling whenever the network is disconnected, the default isfalse. -
revalidateOnFocus: After re-focusing the screen, re-request once, the default isfalse. -
cacheProvider:vue-condition-watchwill cache data behind, you can pass this parameter to customizecacheProvider -
beforeFetch: You can last modify theconditionsbefore the request, or you can terminate the request at this stage. -
afterFetch: you can adjust the result ofdatabeforedatais updated -
onFetchError: Triggered when an error occurs in the request, you can adjusterror&databeforedataanderrorare updated
Return Values
-
conditions:
Type:reactive
Reactive objects (conditions based on config) are the main core ofvue-conditions-watcher. Wheneverconditionschanges, the lifecycle will be triggered.
-
data:
Type:👁🗨 readonly & ref
Default Value:undefined
The return result ofconfig.fetcher, will beundefinedagain when conditions changed.
-
error:
Type:👁🗨 readonly & ref
Default Value:undefined
config.fetchererror return result
-
isFetching:
Type:👁🗨 readonly & ref
Default Value:false
The status of the request being processed
-
loading: When!data.value & !error.valuewill betrue. -
execute: Trigger the request again based on the currentconditionsanddefaultParams.
-
mutate:datacan be modified using this method
🔒 (datadefault is only unmodifiable )
-
resetConditions: Resetconditionsback to their initial values -
onConditionsChange: Fires whenconditionschanges, returning new and old values -
onFetchSuccess: The request is successfully triggered and the original request result is returned -
onFetchError: Triggered by request failure, returning the original request failure result -
onFetchFinally: Fired when the request ends
Execute Fetch
conditions is reactive proxy, easy execute fetch when conditions value changed
const { conditions } = useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
conditions: {
page: 0
},
defaultParams: {
opt_expand: 'date'
}
})
conditions.page = 1 // fetch data with payload { page: 1, opt_expand: 'date' }
conditions.page = 2 // fetch data with payload { page: 2, opt_expand: 'date' }Just call execute function to send a request if you need.
const { conditions, execute: refetch } = useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
conditions: {
page: 0
},
defaultParams: {
opt_expand: 'date'
}
})
refetch() // fetch data with payload { page: 0, opt_expand: 'date' }Force update conditions in time.
const { conditions, resetConditions } = useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
immediate: false,
conditions: {
page: 0,
name: '',
date: []
},
})
// initial conditions then fire onConditionsChange event
resetConditions({
name: 'runkids',
date: ['2022-01-01', '2022-01-02']
})
// Reset conditions
function reset () {
// You can just use `resetConditions` function to initial value.
resetConditions()
}Prevent Request
Setting the immediate to false will prevent the request until the execute
function called or conditions changed.
const { execute } = useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
conditions,
immediate: false,
})
execute()Manually Trigger Request
By default, vue-condition-watcher will automatically trigger fetch data. You can pass manual to disable the default fetch and then use execute() to trigger fetch data.
const { execute } = useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
conditions,
manual: true,
})
execute()Intercepting Request
The beforeFetch let you modify conditions before fetch.
Receive two params:
- Object of clone deep conditions.
- Function called to stop fetch.
useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
conditions: {
date: ['2022/01/01', '2022/01/02']
},
initialData: [],
async beforeFetch(conds, cancel) {
// await to check token before fetch
await checkToken ()
// conds is an object clone copy from config.conditions
const {date, ...baseConditions} = conds
const [after, before] = date
baseConditions.created_at_after = after
baseConditions.created_at_before = before
return baseConditions
}
})The afterFetch can intercept the response before data updated, also your can requests depend on each other
const { data } = useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
conditions,
async afterFetch(response) {
//response.data = {id: 1, name: 'runkids'}
if(response.data === null) {
return []
}
// requests depend on each other
// the loading is still be true until fire `onFetchFinally`
const finalResponse = await otherAPIById(response.data.id)
return finalResponse // [{message: 'Hello', sender: 'runkids'}]
}
})
console.log(data) //[{message: 'Hello', sender: 'runkids'}]The onFetchError can intercept the response before data and error updated
const { data, error } = useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
conditions,
async onFetchError({data, error}) {
if(error.code === 401) {
await doSomething()
}
return {
data: [],
error: 'Error Message'
}
}
})
console.log(data) //[]
console.log(error) //'Error Message'Mutations data
In some cases, mutations to data is a good way to make the user experience better, you don't need wait for the remote data.
Use mutate function, you can update data. While onFetchSuccess will replace data again.
Two way to use mutate function:
- First way, force update current data.
mutate(newData)- Second way, use function will receive deep clone data, and return updated data.
const finalData = mutate((currentData) => {
currentData[0].name = 'runkids'
return currentData
})
console.log(finalData[0]name === data.value[0].name) //true🏄♂️ Example for update a part of your data based on the current data
POST API will just return the updated data directly, so we don’t need to fetch list data again.
const { conditions, data, mutate } = useConditionWatcher({
fetcher: api.userInfo,
conditions,
initialData: []
})
async function updateUserName (userId, newName, rowIndex = 0) {
console.log(data.value) //before: [{ id: 1, name: 'runkids' }, { id: 2, name: 'vuejs' }]
const response = await api.updateUer(userId, newName)
// 🚫 `data.value[0] = response.data`
// Not work! Because `data` is read only.
// Easy to use function will receive deep clone data, and return updated data.
mutate(currentData => {
currentData[rowIndex] = response.data
return currentData
})
console.log(data.value) //after: [{ id: 1, name: 'mutate name' }, { id: 2, name: 'vuejs' }]
}Conditions Change Event
onConditionsChange can help you handle conditions changed.
Will return new value and old value.
const { conditions, onConditionsChange } = useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
conditions: {
page: 0
},
})
conditions.page = 1
onConditionsChange((conditions, preConditions)=> {
console.log(conditions) // { page: 1}
console.log(preConditions) // { page: 0}
})Fetch Event
The onFetchResponse, onFetchError and onFetchFinally will fire on fetch request.
const { onFetchResponse, onFetchError, onFetchFinally } = useConditionWatcher(config)
onFetchResponse((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
onFetchError((error) => {
console.error(error)
})
onFetchFinally(() => {
//todo
})Polling
You can use pollingInterval to automatically refetch data. Just enable it by setting pollingInterval value.
useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
conditions,
pollingInterval: 1000
})And also you can use ref, it's will be reactivity.
const pollingInterval = ref(0)
useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
conditions,
pollingInterval: pollingInterval
})
function startPolling () {
pollingInterval.value = 1000
}
onMounted(startPolling)The vue-condition-watcher default will disable polling when you leave the screen in focus or when the network is disconnected.
You can turn off the default behavior by setting:
-
pollingWhenHidden=trueto continue polling after leaving focus -
pollingWhenOffline=truewill continue polling if the network is disconnected
You can also retry the request after enabling the focus screen to make sure the data is up to date.
revalidateOnFocus=true
useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
conditions,
pollingInterval: 1000,
pollingWhenHidden: true, // pollingWhenHidden default is false
pollingWhenOffline: true, // pollingWhenOffline default is false
revalidateOnFocus: true // revalidateOnFocus default is false
})Cache
The vue-condition-watcher preset will cache your first data in the current component. Then the following requests will use the cached data first, silently request new data behind, wait for the latest return result and compare whether the cached data is the same to achieve a similar preloading effect.
You can also set cacheProvider by function to share globally or cache data in localStorage, and with polling, it can achieve the effect of paging and synchronizing data.
Global Based
// App.vue
<script lang="ts">
const cache = new Map()
export default {
name: 'App',
provide: {
cacheProvider: () => cache
}
}
//Other.vue
useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
conditions,
cacheProvider: inject('cacheProvider')
})
</script>LocalStorage Based
function localStorageProvider() {
const map = new Map(JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('your-cache-key') || '[]'))
window.addEventListener('beforeunload', () => {
const appCache = JSON.stringify(Array.from(map.entries()))
localStorage.setItem('your-cache-key', appCache)
})
return map
}
useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
conditions,
cacheProvider: localStorageProvider
})History Mode
You can enable History mode by setting config.history, which is based on vue-router and supports v3 and v4 versions
const router = useRouter()
useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
conditions,
history: {
sync: router
}
})You can also set history.ignore to exclude the key&value in the conditions section from being synced to the URL query string.
const router = useRouter()
useConditionWatcher({
fetcher,
conditions: {
users: ['runkids', 'hello']
limit: 20,
offset: 0
},
history: {
sync: router,
ignore: ['limit']
}
})
// the query string will be ?offset=0&users=runkids,helloHistory mode will convert the corresponding types of conditions default values to query strings and will filter out undefined, null, '', [] values.
conditions: {
users: ['runkids', 'hello']
company: ''
limit: 20,
offset: 0
}
// the query string will be ?offset=0&limit=20&users=runkids,helloAlso automatically syncs the query string to conditions whenever you refresh the page
URL query string: ?offset=0&limit=10&users=runkids,hello&company=vue
conditions will become
{
users: ['runkids', 'hello']
company: 'vue'
limit: 10,
offset: 0
}Lifecycle
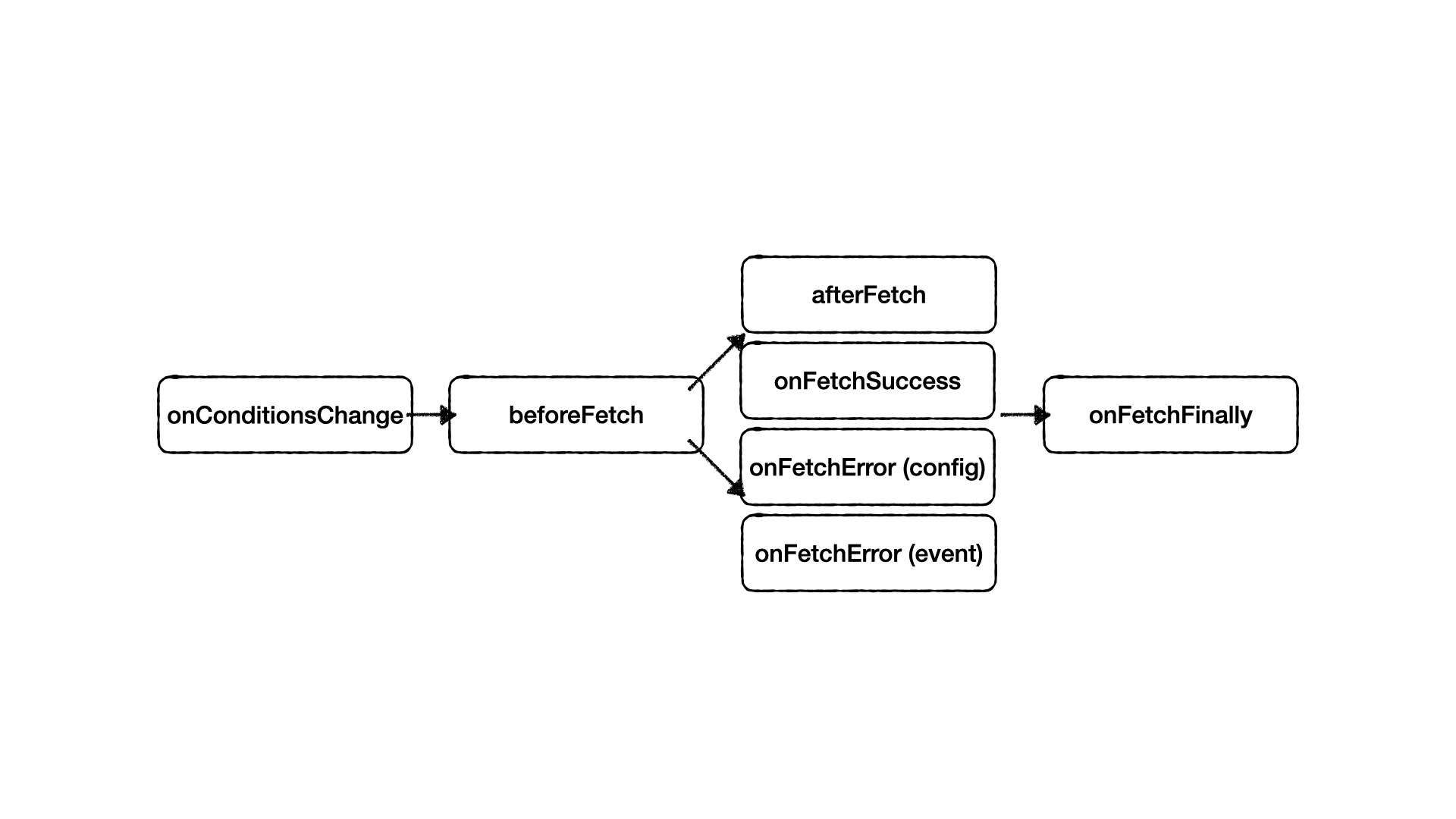
-
onConditionsChangeFire new conditions value and old conditions value.
onConditionsChange((cond, preCond)=> { console.log(cond) console.log(preCond) })
-
beforeFetchYou can modify conditions before fetch, or you can call second of arguments to stop fetch this time.
const { conditions } = useConditionWatcher({ fetcher, conditions, beforeFetch }) async function beforeFetch(cond, cancel){ if(!cond.token) { // stop fetch cancel() // will fire onConditionsChange again conditions.token = await fetchToken() } return cond })
-
afterFetch&onFetchSuccessafterFetchfire beforeonFetchSuccess
afterFetchcan modify data before update.Type Modify data before update Dependent request afterFetch config ⭕️ ⭕️ onFetchSuccess event ❌ ❌ <template> {{ data?.detail }} <!-- 'xxx' --> </template>
const { data, onFetchSuccess } = useConditionWatcher({ fetcher, conditions, async afterFetch(response){ //response = { id: 1 } const detail = await fetchDataById(response.id) return detail // { id: 1, detail: 'xxx' } }) }) onFetchSuccess((response)=> { console.log(response) // { id: 1, detail: 'xxx' } })
-
onFetchError(config)&onFetchError(event)config.onFetchErrorfire beforeevent.onFetchError
config.onFetchErrorcan modify data and error before update.Type Modify data before update Modify error before update onFetchError config ⭕️ ⭕️ onFetchError event ❌ ❌ const { onFetchError } = useConditionWatcher({ fetcher, conditions, onFetchError(ctx){ return { data: [], error: 'Error message.' } }) }) onFetchError((error)=> { console.log(error) // origin error data })
-
onFetchFinallyWill fire on fetch finished.
onFetchFinally(async ()=> { //do something })
Make It Reusable
You might need to reuse the data in many places. It is incredibly easy to create reusable hooks of vue-condition-watcher :
function useUserExpensesHistory (id) {
const { conditions, data, error, loading } = useConditionWatcher({
fetcher: params => api.user(id, { params }),
defaultParams: {
opt_expand: 'amount,place'
},
conditions: {
daterange: []
}
immediate: false,
initialData: [],
beforeFetch(cond, cancel) {
if(!id) {
cancel()
}
const { daterange, ...baseCond } = cond
if(daterange.length) {
[baseCond.created_at_after, baseCond.created_at_before] = [
daterange[0],
daterange[1]
]
}
return baseCond
}
})
return {
histories: data,
isFetching: loading,
isError: error,
daterange: conditions.daterange
}
}And use it in your components:
<script setup>
const {
daterange,
histories,
isFetching,
isError
} = useUserExpensesHistory(route.params.id)
onMounted(() => {
//start first time data fetching after initial date range
daterange = [new Date(), new Date()]
})
</script><template>
<el-date-picker
v-model="daterange"
:disabled="isFetching"
type="daterange"
/>
<div v-for="history in histories" :key="history.id">
{{ `${history.created_at}: ${history.amount}` }}
</div>
</template>Congratulations! vue-condition-watcher.
Now we can manage the paging information use vue-condition-watcher .
Pagination
Here is an example use Django the limit and offset functions and Element UI.
Create usePagination
function usePagination () {
let cancelFlag = false // check this to cancel fetch
const { startLoading, stopLoading } = useLoading()
const router = useRouter()
const { conditions, data, execute, resetConditions, onConditionsChange, onFetchFinally } = useConditionWatcher(
{
fetcher: api.list,
conditions: {
daterange: [],
limit: 20,
offset: 0
}
immediate: true,
initialData: [],
history: {
sync: router,
// You can ignore the key of URL query string, prevent users from entering unreasonable numbers by themselves.
// The URL will look like ?offset=0 not show `limit`
ignore: ['limit']
},
beforeFetch
},
)
// use on pagination component
const currentPage = computed({
get: () => conditions.offset / conditions.limit + 1,
set: (page) => {
conditions.offset = (page - 1) * conditions.limit
}
})
// onConditionsChange -> beforeFetch -> onFetchFinally
onConditionsChange((newCond, oldCond) => {
// When conditions changed, reset offset to 0 and then will fire beforeEach again.
if (newCond.offset !== 0 && newCond.offset === oldCond.offset) {
cancelFlag = true
conditions.offset = 0
}
})
async function beforeFetch(cond, cancel) {
if (cancelFlag) {
// cancel fetch when cancelFlag be true
cancel()
cancelFlag = false // reset cancelFlag
return cond
}
// start loading
await nextTick()
startLoading()
const { daterange, ...baseCond } = cond
if(daterange.length) {
[baseCond.created_at_after, baseCond.created_at_before] = [
daterange[0],
daterange[1]
]
}
return baseCond
}
onFetchFinally(async () => {
await nextTick()
// stop loading
stopLoading()
window.scrollTo(0, 0)
})
return {
data,
conditions,
currentPage,
resetConditions,
refetch: execute
}
}And use it in your components:
<script setup>
const { data, conditions, currentPage, resetConditions, refetch } = usePagination()
</script><template>
<el-button @click="refetch">Refetch Data</el-button>
<el-button @click="resetConditions">Reset Offset</el-button>
<el-date-picker
v-model="conditions.daterange"
type="daterange"
/>
<div v-for="info in data" :key="info.id">
{{ info }}
</div>
<el-pagination
v-model:currentPage="currentPage"
v-model:page-size="conditions.limit"
:total="data.length"
/>
</template>When daterange or limit changed, will reset offset to 0 and only fetch data again after reset offset.
TDOD List
- [ ] Error Retry
- [ ] Nuxt SSR SSG Support
Thanks
This project is heavily inspired by the following awesome projects.
📄 License
MIT License © 2020-PRESENT Runkids