sudo-fn
Call a node function with sudo privileges (prompts the user for admin privileges with a native OS X dialog).
Note: OS X Only
Uses sudo-prompt and cmd-fn.
Installation
npm install sudo-fn
Usage
// To use something other than process.title as the app name.// Must be alphanumeric (may contain spaces).sudoFn// To call a function with admin (sudo) privileges.sudoFn;Options (also see cmd-fn):
module module name e.g.: 'fs'
function function name
params function arguments specified as an array e.g.: ["foo", "bar"]
type the type of target function, can be:
'node-callback' or
'promise'
cwd change working directory context
After calling sudoFn an authentication dialog will display (see below). If challenge is successful then the requested function will be called with admin privileges. The requested function is called in a child process, use absolute paths for non-core modules.
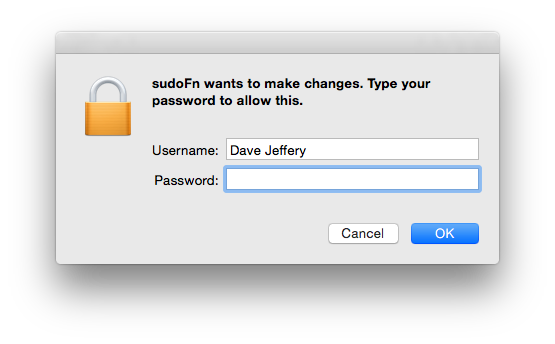
Examples
Simple Local Module Example
If I wanted to do the equivalent of:
;Then I could do:
;Node Callback Example
If I wanted to read a privileged admin directory:
;Then I could do:
;Author
Dave Jeffery (@DaveJ)