A lexical analyzer and longest common shared sequence finder between a list of JS files.
Suppose, you have two files with the same function but different function calls:
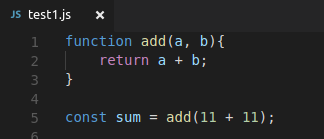
test1.js
function add(a, b){
return a + b;
}
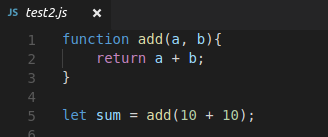
const sum = add(11 + 11);test2.js
function add(a, b){
return a + b;
}
let sum = add(11 + 11);The longest common shared sequence between these two files is the entire function definition.
LCSS
function add(a, b){
return a + b;
}You can download the module via npm. (To install npm, which ships with node.js, you can download node from nodejs.org for your OS.) node.js > 6.x
$ npm install -g lexer.jsOr, if you prefer yarn
$ yarn global add lexer.jsThat's it. 🎉
In your application:
const lexerJS = require('lexer.js');
const result = lexerJS(files, options);files: An array of files.
options: See options This parameter is (ironically) optional.
To run it on your own set of files, you can either provide the files in CSV/JSON, or as command line arguments like this:
lexer.js test1.js test2.jsThe JSON must have a key named files and it's value should be an array of the paths of files you want to test on.
{
"files": [
"./example/test1.js",
"./example/test2.js",
]
}The CSV config file only has one header (or column) and is called filename. Each new line should contain the path of a source code file.
filename,
./example/test1.js,
./example/test2.js
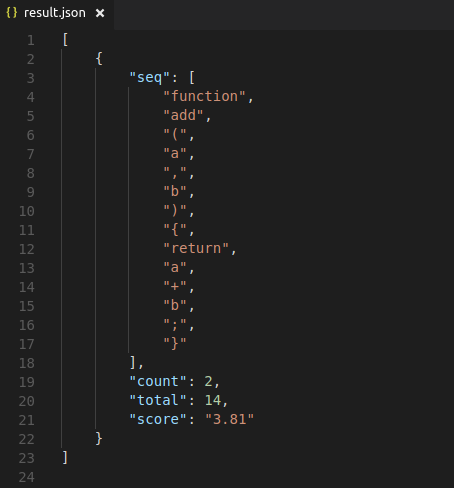
The result contains the longest common shared sequence found between the set of files. The default format is JSON, but can be configured. (See options below.)
It also asssigns a score to each subsequnce using the following formula:
score = log2(count) * log2(total)count: Total number of occurences of the subsequence
total: Total number of tokens in the subsequence
lexer.js supports JSON as well as CSV output. JSON is the defualt output format if you do not specify any during invocation.
lexer.js test.json -o csvOutput would now be a
CSVfile. To know what that file would contain, check out result.
This is a boolean option, which when set, saves the tokens for each test file.
lexer.js test.json -sIt will generate a tokens folder, and save individual
tokensfor each file in that directory.
lexer.js test.json -f YayTheResultsYay
Note: If you provide a file name with extension, such as art.json, then the output mode will be determined from the fileName and the output mode flag ( if passed) will be overriden.
The examples directory contains a minimal example set that you can run lexer.js on. To do so, clone the repo, fire a terminal, and run:
npm installThis will downdload the dependencies. Then, run:
lexer.js test.jsonThis assumes that you already have lexer.js installed. If you don't, you can directly invoke the node script as follows:
node index.js test.jsonAs always, you must have node installed.
The repo also contains a script to test lexer.js on any GitHub project. The script does the following:
- Find all JS files in a project.
- Select a file which has more than n commits. n is configurable.
- Downloads the file at that point in time (when that commit was made).
- Generates a configuration file for lexer.js.
- Run lexer.js with that config file.
To run it, fire a terminal and run (assuming you are inside the project directory):
node runGitHubExamples.js --owner OWNERNAME --repo REPONAME -n 20OWNERNAME: Owner of the repo [default: prettier]
REPONAME: Name of the repo [default: prettier]
n: Minimum commits the selected file must have [default: 10]
The results are saved in result.json. The command line options for lexer.js can also be passed.
To run tests, clone the repo (That green button above the repo contents) and run the following command:
npm install && npm run testThis will first download the dependencies, and then run the tests (using mocha) and output the result.