Defer and recover for JavaScript and TypeScript, inspired by Golang. defer lets you schedule cleanup functions to run after a parent function exits, ensuring efficient resource management. recover helps handle errors gracefully, making them ideal for robust error handling and resource cleanup in complex workflows.
npm i defer-node-js
In go, the defer keyword schedules a function call to be run when the parent exit. Weather by reaching the end of the funciton or by a panic. The recover function in go stops the panic and returns the error value inside the defered block.
Javascript doesn't have built-in language feature for defer or recover. Instead, developers often rely on try/finally to construct or explicit cleanup calls.
This library emulates Go's defer and recover for blocking and non-blocking functions.
- Resource management: Provide a simpler pattern for resource cleanup without scattering finally blocks trhoughout your code.
- Error handling: Allow centeral point to catch and " recover " from error that happened in the main function.
-
Defer stack (LIFO): We maintain a stack of deferred functions. When .defer(fn) is called, fn is pushed into the stack.
-
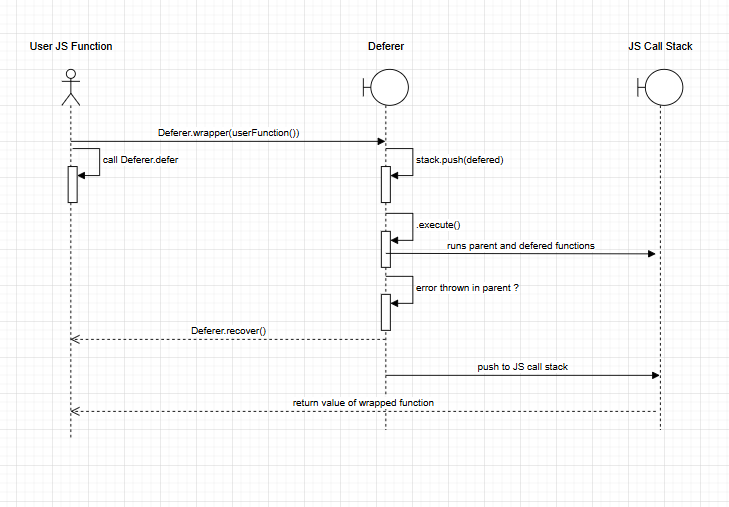
.wrapper:
- The wrapper method returns a new function that when invoked setups the ( deferr environment) which is managed stack within js stack.
- it calls the original function capturing any errors.
- It then executes all the defered functions LIFO.
- If no defered funcations calls recover, the original error is rethrown.
- Recover: if a defered function calls .recover() and the parent function thrown an error, the bottom defered function will nullifies the error, the error is swallowed and returns with the recover() method.
- File handling
import fs from 'fs';
import { SyncDeferer } from 'defer';
const readFileSafely = SyncDeferer.wrapper((filePath: string) => {
// open file
const fd = fs.openSync(filePath, 'r');
// always close file when the function returns or throws
SyncDeferer.defer(() => fs.closeSync(fd));
const content = fs.readFileSync(fd, 'utf-8');
return content;
});
try {
const data = readFileSafely('/path/to/file.txt');
console.log('File data:', data);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to read file:', error);
}
- Networking and socket cleanup
import net from 'net';
import { AsyncDeferer } from 'defer';
const defer = new AsyncDeferer();
const handleConnection = defer.wrapper((socket: net.Socket) => {
// schedule a cleanup
defer.defer(() => socket.end());
// do some I/O
socket.write('Hello from server!');
// possibly more code ...
});
- Error recovery handling example :
import { SyncDeferer } from 'defer';
const faultyFunction = SyncDeferer.wrapper(() => {
// schedule a deferred function that recovers from error
SyncDeferer.defer(() => {
const err = Deferer.recover();
if (err) {
console.log('Recovered from error:', err);
}
});
// Now deliberately throw an error
throw new Error('Something went wrong...');
});
// This call will NOT crash the program; it recovers inside the deferred function
faultyFunction();
console.log("Program continues after recovered error!");