coap-node
Client node of lightweight M2M (LWM2M).
Documentation
Please visit the Wiki.
Overview
OMA Lightweight M2M (LWM2M) is a resource constrained device management protocol relies on CoAP. And CoAP is an application layer protocol that allows devices to communicate with each other RESTfully over the Internet.
coap-shepherd, coap-node and lwm2m-bs-server modules aim to provide a simple way to build and manage a LWM2M machine network.
- Server-side library: coap-shepherd
- Client-side library: coap-node (this module)
- Bootstrap server library: lwm2m-bs-server
- A simple demo webapp
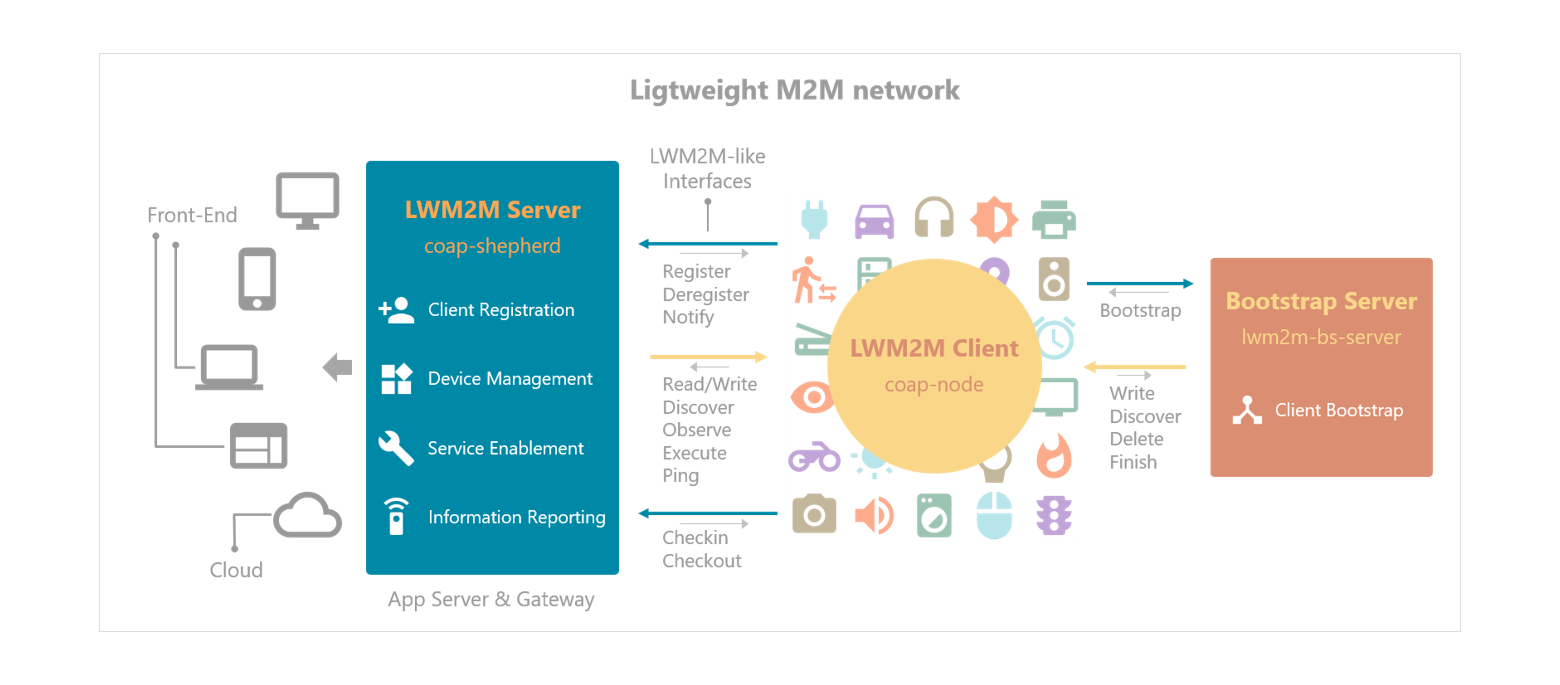
LWM2M Client: coap-node
- It is an implementation of LWM2M Client managed by a coap-shepherd Server.
- It follows most parts of LWM2M specification to meet the requirements of a machine network and devices management.
- It works well with Leshan.
- Support mulitple servers, factory bootstrap and client initiated bootstrap.
- It uses smartobject as its fundamental of resource organizing on devices. smartobject can help you create smart objects with IPSO data model, and it also provides a scheme to help you abstract your hardware into smart objects. You may like to use smartobject to create many plugins for your own hardware or modules, i.e., temperature sensor, humidity sensor, light control. Here is a tutorual of how to plan resources with smartobject.
Installation
$ npm install coap-node --save
Usage
Client-side example (the following example is how you use coap-node on a machine node):
- Step 1: Resources initialzation.
var SmartObject = ; // initialize Resources that follow IPSO definitionvar so = ; // initialize your Resources// oid = 'temperature', iid = 0so; // oid = 'lightCtrl', iid = 0so;- Step 2: Client device initialzation.
var CoapNode = ; // Instantiate a machine node with a client name and your smart objectvar cnode = 'my_first_node' so; cnode; // register to a Server with its ip and portcnode;Server-side example (please go to coap-shepherd document for details):
var cnode = cserver; cnode; cnode;License
Licensed under MIT.