swagger-typed-express-docs keep you simple document your endpoints with just one single source of truth which
this project generates OpenAPI 3.0.0, not swagger!
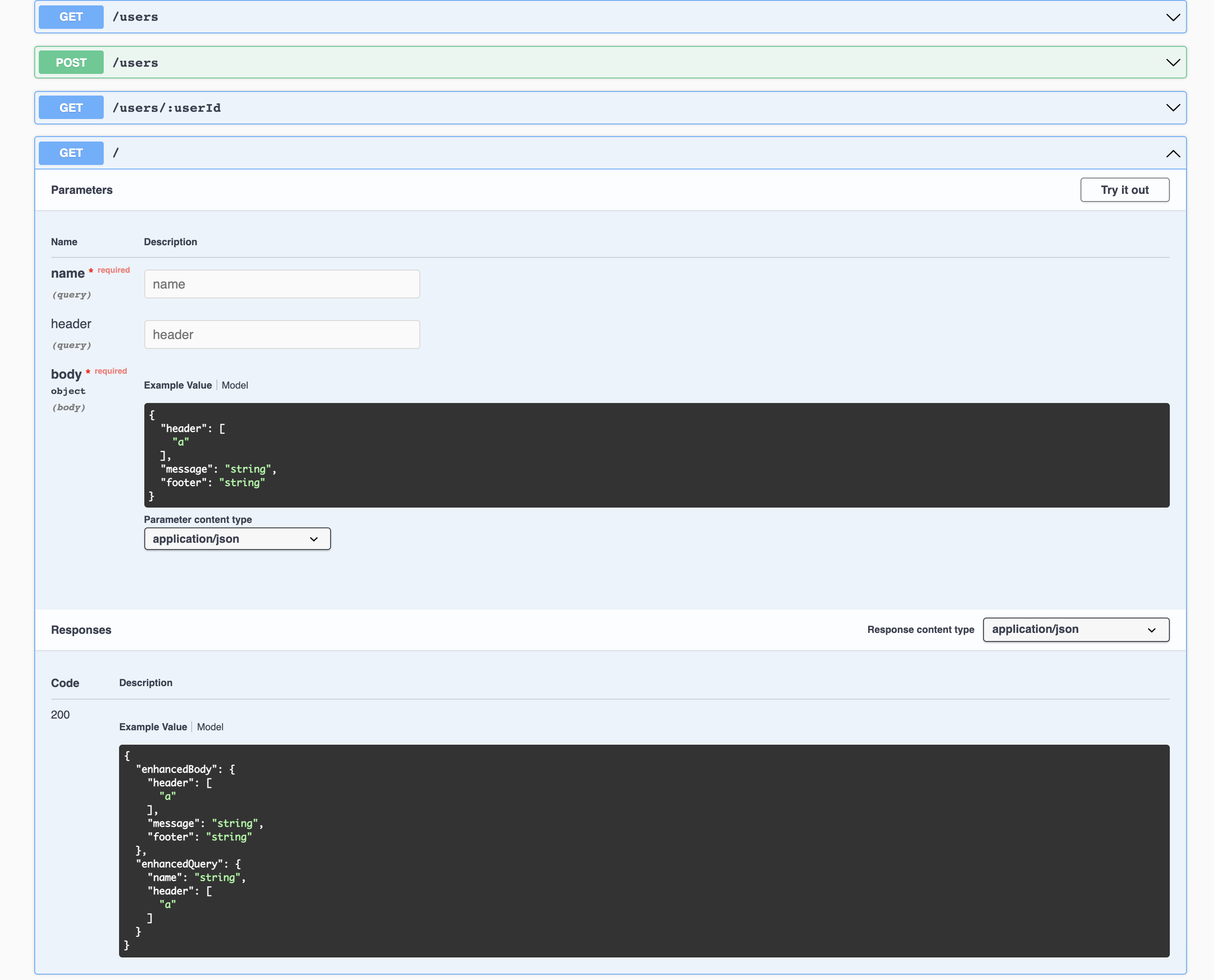
- Generate OpenAPI API documentation
- Compile time validations - Infer Typescript static types out of the box
- Runtime validate each of your HTTP request with user-friendly error messages
To do that there is just a simple high-order-function API.
So you can just simply wrap your endpoint with the apiDoc(...) and initialize project via initApiDocs()
You can see full app example in the repository:
import express from 'express'
import { apiDoc, initApiDocs, T } from 'swagger-typed-express-docs'
import swaggerUi from 'swagger-ui-express'
const app = express()
const port = 3000
app.get(
'/user/:userId',
/**
* adding metadata for handlers where we want to have
* - runtime checks
* - compile-time checks
* - generate swagger documentation
*/
apiDoc({
params: {
userId: T.string,
},
query: {
name: T.string,
header: T.list(T.enum(['a', 'b', 'c'] as const)),
},
body: {
header: T.list(T.enum(['a', 'b', 'c'] as const)),
message: T.string,
footer: T.string,
},
returns: T.object({
enhancedBody: T.object({
data: T.enum(['a', 'b', 'c'] as const),
}),
}),
})((req, res) => {
const body = req.body
const query = req.query
// res.send is typed by typescript, but it do not transform values by tSchema, so
// you may use tSend instead
res.tSend({
body,
query,
})
})
)
/**
* before you start the server you have to setup library
*/
const swaggerJSON = initApiDocs(app, { info: { title: 'my application' } })
app.use('/api-docs', swaggerUi.serve, swaggerUi.setup(swaggerJSON))The whole library expose 2 main functions: initApiDocs(...) and & apiDoc(...)
This method takes a swagger metadata which will be deeply merged into generated documentation.
initApiDocs() returns generated Swagger JSON which you can use to document your API.
const swaggerJSON = initApiDocs(app, { info: { title: 'my application' } })to make the application work you have to call initApiDocs() at the end of routes definition
and before you start app.listen(...)
apiDoc(...) is high-order-function which you use to wrap express endpoint handler
and define a meta-information about inputs & outputs of each API handler.
example usage:
import { T } from 'swagger-typed-express-docs'
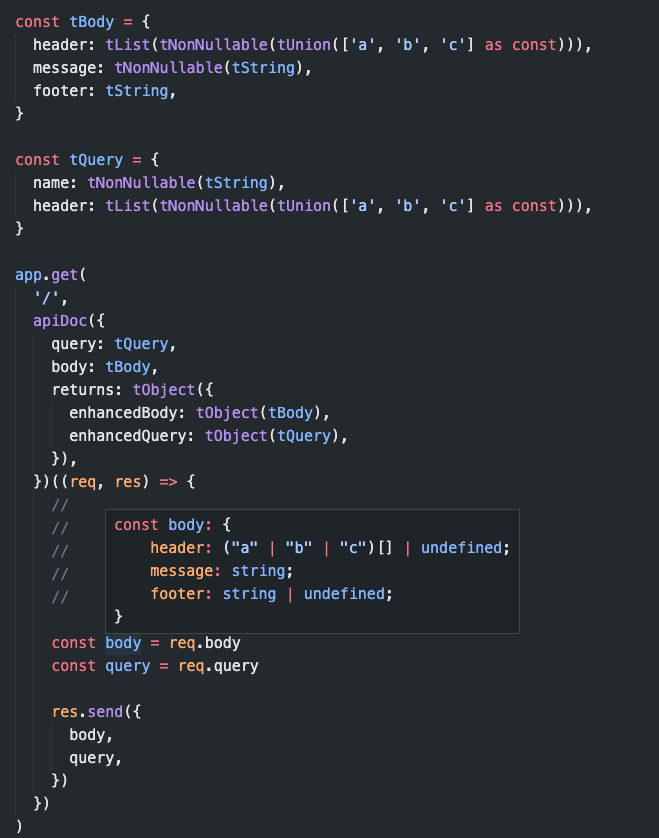
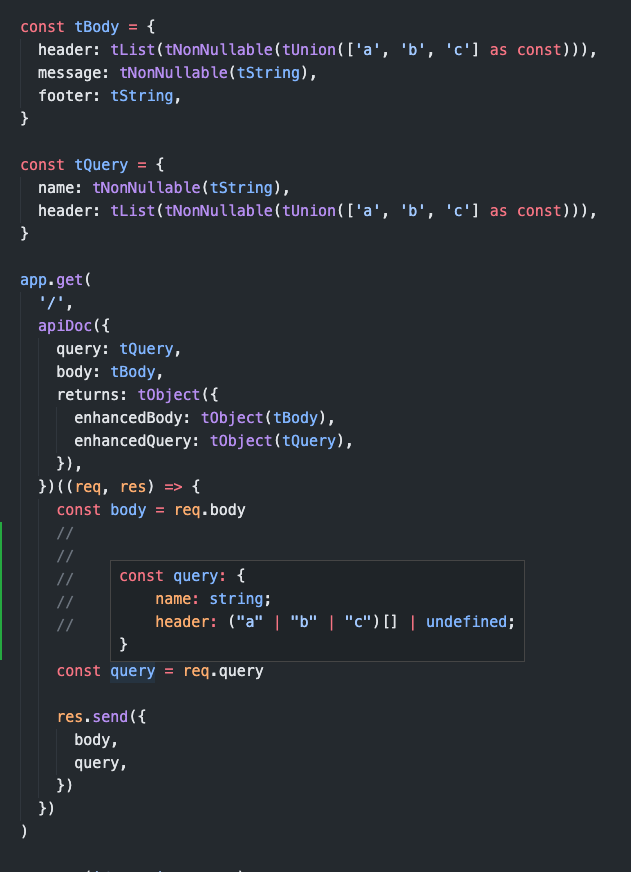
app.get(
'/',
apiDoc({
query: {
name: T.string
header: T.list(T.enum(['a', 'b', 'c'] as const))),
},
body: {
header: T.list(T.enum(['a', 'b', 'c'] as const))),
message: T.null_list,
footer: T.string,
},
returns: T.null_object({
data: T.null_object({
nestedData: T.enum(['a', 'b', 'c'] as const),
}),
}),
})((req, res) => {
const body = req.body
const query = req.query
res.send({
body,
query,
})
})
)The library exposes many functions and objects which help you to create schema as you want.
T.string(...)T.null_string(...)T.boolean(...)T.null_boolean(...)T.number(...)T.null_number(...)T.enum(...)T.null_enum(...)T.oneOf(...)T.null_oneOf(...)T.any(...)T.null_any(...)T.object(...)T.null_object(...)T.list(...)T.null_list(...)T.nonNullable(...)
if you want to see more examples on how to build schema structure by function compositions you can check the tests
if you want to parser body, you have to setup body parser express middleware.
app.use(express.json())to make fully work tNonNullable you have to setup tsconfig.json properly.
{
...
"compilerOptions": {
...
"strictNullChecks": true,
}
}if some field in the object is nullable null_ key may not be required, but in TS types, only value is of type | undefined
so the non existed keys are nullable as well, thanks to this, the schema is simplier for the writter, because there is less edge cases to think about
if you define one of apiDoc objects like query, body, params or headers it'll strip all unknown object attributes so omit potential security data injections
By default, if you do not define some of the tSchema, nothing is validate or parsed for current object
You can parse query thanks to express-query-parser library.
We parser to keep parsing only undefined and null values and the rest may be done by transform types.
Many transform types is predefined in the T.cast. object.
import { queryParser } from 'express-query-parser'
app.use(
queryParser({
parseNumber: false,
parseBoolean: false,
// turn on only null & undefined values, to use T.cast. utils
parseNull: true,
parseUndefined: true,
})
)
app.get(
'/',
apiDoc({
query: {
name: T.cast.number,
ids: T.extra.null_toListIfNot(T.cast.number),
},
})((req, res) => {
const body = req.body
const query = req.query
res.send({
body,
query,
})
})
)if you want to parse string 'null' by yourself, you need to create a custom T.transform data type which will handle this edge case
The library automatically injects the tSend function into res.tSend. This function takes data and sends a 200 success status response.
However, before sending, it verifies if the schema matches the apiDoc({ returns: ... }) schema definition and sanitizes the data.
Therefore, if you send more data than what is defined (for example, an object with additional attributes),
the surplus data will be stripped. This mechanism enhances the function's reliability.
After defining T.transform types, encoders are applied, and the data is transformed accordingly.
Data Transformation Flow: User -> HTTP -> Encoded -> Decoded -> Express Handler Express Handler -> Decoded -> Encoded -> HTTP -> User
- Users interact exclusively with encoded types.
- Express handlers interact solely with decoded types.
Null Handling:
- If a data type is nullable,
nullandundefinedvalues are automatically handled, and the encoder/decoder functions will not be invoked. - If
nullis not explicitly defined, encoder and decoder functions may still be called withnullorundefinedvalues. In such cases, handling must be implemented manually within the parser/serializer functions.
- T.deepNullable
decoder = parser encoder = serializer transform = encoder + decoder
- remove async validations
- do porting to zod
- make smarter union object matching