simple-lambda-api-router
From v 1.5.4 the package is the same. For some reason NPM is not publishing the readme I had to do some workarounds on it.
Simple and lightweight lambda api router.
After version 1.2. the router initialization is asynchronous. Why? Async is better, async is love, you think in async and the day goes better, and you won't pay large AWS bills, why? because IT is async and you will use what you saved in bills for coffee or even better: PIZZA
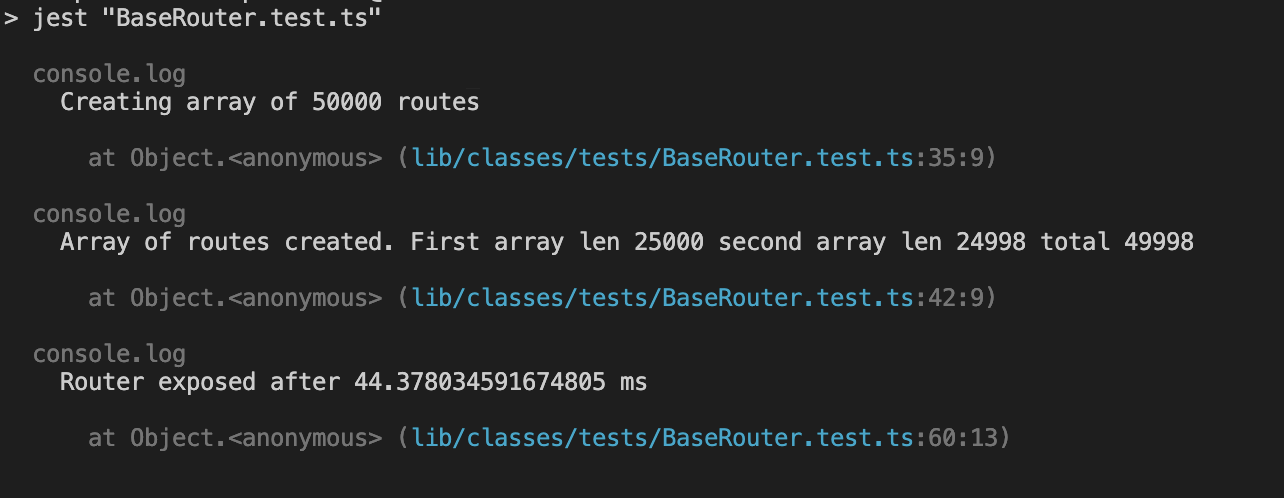
This is intended to won't mess with your lambda coldstart. It's lightning-fast, even with 50K routes, it'll be ready to roll in less than 50ms! And the best part? It can reach your routes in under 2ms.
However, it won't save you of doing bad controllers. So please stay warm, drink water and do exercise.
Happy Coding!
Example Projects:
Visit the examples to get started
- https://github.com/alphonse92/AwsProxyRouterExample
- https://github.com/alphonse92/AwsSamRouterExample
CommonJS
const { createController } = require('simple-lambda-api-router/dist/utils/controller');
const { AwsSamRouter } = require('simple-lambda-api-router/dist/classes');
// Use the SAM router
const router = new AwsSamRouter();
router.use(
// Resources should match with the template.yml api paths
'/user/{type}/clients/{id+}',
createController({
// should each be a HTTP method in lower case
get: async (event, context) => {
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'hello world' };
},
}),
);
/**
* Expose and export the lambda handler
*/
export const lambdaHandler = router.expose();Usage with AWS SAM
import { Context, APIGatewayProxyEvent, APIGatewayProxyResult } from 'aws-lambda';
import AwsSamRouter, { HandlerType } from 'simple-lambda-api-router/dist/classes/AwsSamRouter';
import { createController } from 'simple-lambda-api-router/dist/utils/controller';
// Use the SAM router
const router = new AwsSamRouter();
router.use(
// Resources should match with the template.yml api paths
'/user/{type}/clients/{id+}',
createController<HandlerType>({
// should each be a HTTP method in lower case
get: async (event: APIGatewayProxyEvent, context: Context): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> => {
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'hello world' };
},
}),
);
/**
* Expose and export the lambda handler
*/
export const lambdaHandler = router.expose();Usage with AWS Url Lambda
import { Context, APIGatewayProxyEvent, APIGatewayProxyResult } from 'aws-lambda';
import { NotImplementedControllerError, NotImplementedHandler } from 'simple-lambda-api-router/dist/errors/http';
import { createController } from 'simple-lambda-api-router/dist//utils/controller';
import AwsProxyRouter, { HandlerType } from 'simple-lambda-api-router/dist/classes/AwsProxyRouter';
// Instance of AwsProxyRouter
const router = new AwsProxyRouter();
router.use(
// It supports express-like paths
'/resource/:type/user/:id?',
createController<HandlerType>({
get: async (event: APIGatewayProxyEvent, context: Context): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> => {
return { statusCode: 200, body: faker.datatype.string() };
},
}),
);
export const lambdaHandler = router.expose();Using decorators
Decorators are a great option to the people who want to do more writing less. Since decorators are not supported natively on JS it's only supported by typescript.
The only thing you should worry about is your business logic implementation. One class and one decorator are enough to start routing. The following examples shows how it works:
Using the AwsProxyRouter
The paths are express-like. So, you may be familiar with that.
See example here: https://github.com/alphonse92/AwsProxyRouterExample
// replace the types according with the handler schema you are using. In this example we are using AWS
// so the event schema will be APIGatewayProxyEvent
import { APIGatewayProxyResult, APIGatewayProxyEvent, Context } from 'aws-lambda';
import Route from 'simple-lambda-api-router/dist/decorators/Route';
import AwsProxyRouter from 'simple-lambda-api-router/dist/classes/AwsProxyRouter';
import userService from '../services/UserService/';
class UserController {
@Route('get', '/user/:id')
async getUser(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.getUser();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
@Route('get', '/user')
async getUsers(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.getUsers();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
@Route('post', '/user')
async createUser(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.createUser();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
@Route('delete', '/user/:id')
async deleteUser(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.deleteUser();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
}
class ClientsController {
@Route('get', '/user/clients/:id')
async getClient(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.getClient();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
@Route('get', '/user/clients')
async getClients(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.getClients();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
@Route('post', '/user/clients')
async createClient(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.createClient();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
@Route('delete', '/user/clients/:id')
async deleteClient(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.deleteClient();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
}
const router = new AwsProxyRouter();
const userController = new UserController();
const clientsController = new ClientsController();
router.use(clientsController.getClient);
router.use(clientsController.getClients);
router.use(clientsController.createClient);
router.use(clientsController.deleteClient);
router.use(userController.getUser);
router.use(userController.getUsers);
router.use(userController.createUser);
router.use(userController.deleteUser);
export const lambdaHandler = router.expose();Using the sam router
Take in mind your route paths MUST match with your paths in your template.yaml
See example here: https://github.com/alphonse92/AwsSamRouterExample
import { APIGatewayProxyResult, APIGatewayProxyEvent, Context } from 'aws-lambda';
import Route from 'simple-lambda-api-router/dist/decorators/Route';
import AwsProxyRouter from 'simple-lambda-api-router/dist/classes/AwsProxyRouter';
import userService from '../services/UserService/';
class UserController {
@Route('get', '/user/{id}/')
async getUser(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.getUser();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
@Route('get', '/user/')
async getUsers(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.getUsers();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
@Route('post', '/user/')
async createUser(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.createUser();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
@Route('delete', '/user/{id}/')
async deleteUser(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.deleteUser();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
}
class ClientsController {
@Route('get', '/user/clients/{id}/')
async getClient(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.getClient();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
@Route('get', '/user/clients/')
async getClients(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.getClients();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
@Route('post', '/user/clients/')
async createClient(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.createClient();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
@Route('delete', '/user/clients/{id}/')
async deleteClient(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
userService.deleteClient();
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'ok' };
}
}
const router = new AwsSamRouter();
const userController = new UserController();
const clientsController = new ClientsController();
router.use(clientsController.getClient);
router.use(clientsController.getClients);
router.use(clientsController.createClient);
router.use(clientsController.deleteClient);
router.use(userController.getUser);
router.use(userController.getUsers);
router.use(userController.createUser);
router.use(userController.deleteUser);
export const handler = router.expose();Setting middy middlewares
Sometimes you need middlewares capabilites. For that instance you might want to use middy. Middlewares works for both routers: AwsProxyRouter and AwsSamRouter
import { APIGatewayProxyEvent, APIGatewayProxyResult, Context } from 'aws-lambda';
import middy from '@middy/core';
import httpErrorHandler from '@middy/http-error-handler';
import httpEventNormalizer from '@middy/http-event-normalizer';
import httpJsonBodyParser from '@middy/http-json-body-parser';
import { HandlerType } from 'simple-lambda-api-router/dist/classes/AwsSamRouter';
import { createController } from 'simple-lambda-api-router/dist/utils/controller';
async function get(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent, context: Context): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
return { statusCode: 200, body: JSON.stringify({ event }) };
}
async function post(event: APIGatewayProxyEvent, context: Context): Promise<APIGatewayProxyResult> {
return { statusCode: 200, body: JSON.stringify({ event }) };
}
const middlewares = [httpErrorHandler(), httpEventNormalizer(), httpJsonBodyParser()];
const controller = createController<HandlerType>({
get: middy(get).use(middlewares) as HandlerType,
post: middy(post).use(middlewares) as HandlerType,
});
export default controller;If you dont want to use middy you are free to use the library of your preference, but you should pass that function to the controller configuration object.
Setting middlewares to decorators-based controllers
If you are using decorators to build your controllers, you might use a middleware of your preference. To use middlewares on the controllers handlers, you should wrap that function inside the middleware of your preference
import { APIGatewayProxyResult, APIGatewayProxyEvent, Context } from 'aws-lambda';
import AwsSamRouter from 'simple-lambda-api-router/dist/classes/AwsSamRouter';
import middy from '@middy/core';
import httpErrorHandler from '@middy/http-error-handler';
import httpEventNormalizer from '@middy/http-event-normalizer';
import httpJsonBodyParser from '@middy/http-json-body-parser';
import userController from '../controllers/user';
const router = new AwsSamRouter();
const middlewares = [httpErrorHandler(), httpEventNormalizer(), httpJsonBodyParser()];
router.use(middy(userController.getUser).use(middlewares));
export const lambdaHandler = router.expose();Feedback
I would appreciate any feedback you may have. If you encounter a bug or issue, please don't hesitate to post it in the GitHub repository. Additionally, you can reach me at my email address, alejandromover92@gmail.com, at any time.