sequel.ai
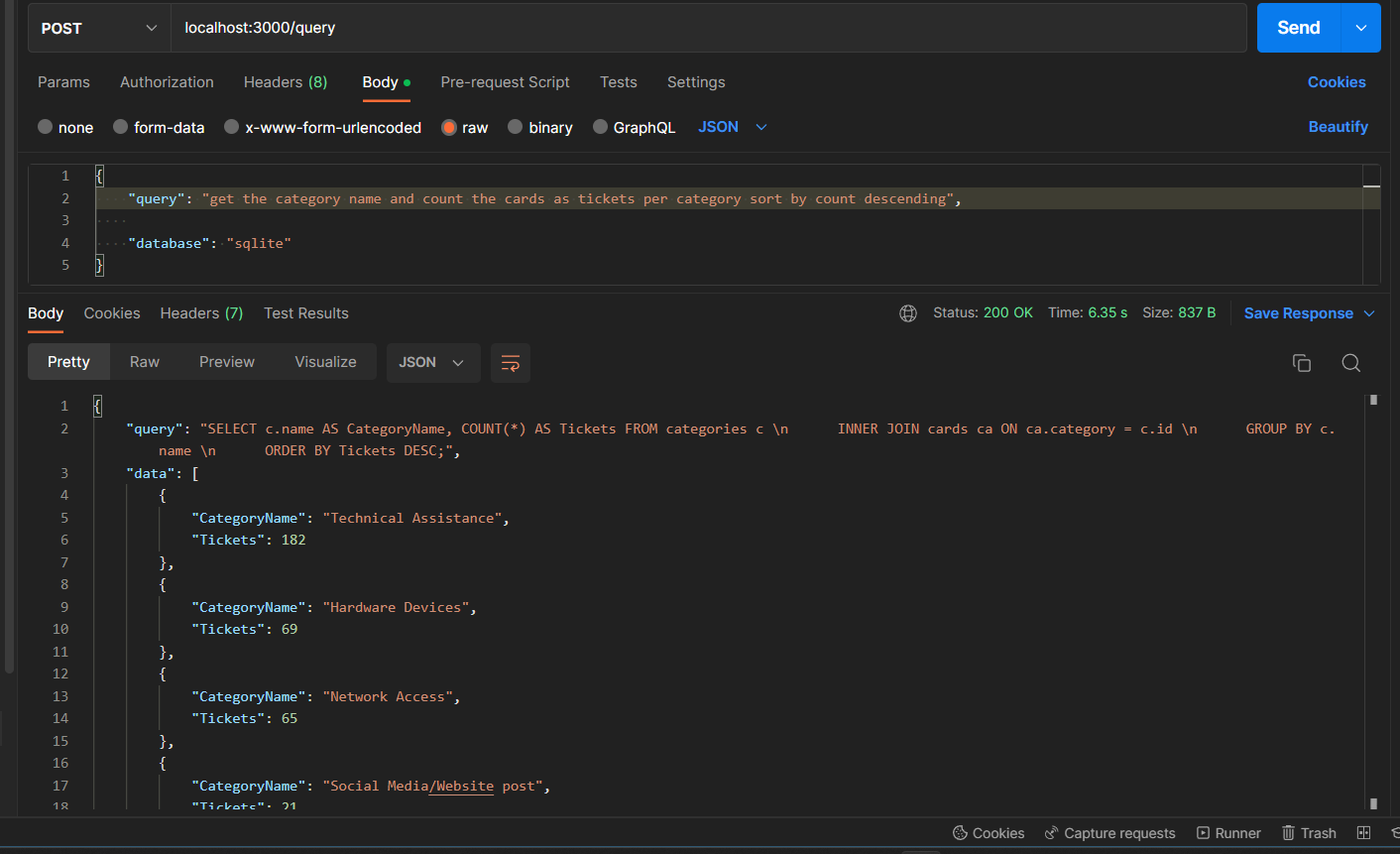 Natural Language to Database Query Result! Say goodbye to the frustration of writing complex SQL queries - with sequel.ai, you can simply input your query in any Language (English, Cebuano, you name it!), get accurate, speedy results. Seamlessly converting natural language into SQL queries and executing them on your specified database. Need to change databases? No problem - our app is fully customizable and can be configured to work with any database engine. Try it today and experience the future of query building!
Natural Language to Database Query Result! Say goodbye to the frustration of writing complex SQL queries - with sequel.ai, you can simply input your query in any Language (English, Cebuano, you name it!), get accurate, speedy results. Seamlessly converting natural language into SQL queries and executing them on your specified database. Need to change databases? No problem - our app is fully customizable and can be configured to work with any database engine. Try it today and experience the future of query building!
facebook.com/Trinwhocode
linkedin.com/in/trinmar
Environment Variables
The .env file is used to define the environment variables used in the application. The .env file should be located in the root directory of the application.
DB_ENGINE=sqlite
OPENAI_API_KEY=<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>Variables
DB_ENGINE
This variable is used to specify the database engine that the application will connect to. examples:sqlite3, mysql, postgre.
OPENAI_API_KEY
This variable is used to specify the API key for OpenAI. You can obtain an API key by creating an account at https://beta.openai.com/signup/. Once you have an account, you can find your API key on the dashboard page. The API key is required for the natural language processing part of the application.
Using the sequelAIze.js Library
The sequelAIze.js library exports a single function, sequelAIze(prompt). This function takes a natural language prompt as its only argument, and returns a Promise that resolves to an object with two properties: query and data.
Here's an example of how to use the sequelAIze function:
const { sequelAIze } = require('sequel.ai');
async function asyncQuery(query) {
// your SQL code execution here
// it should returns the rows (result)
// you can create a Promise (resolve/reject) or normal async/await
let rows = []
return rows;
}
const prompt = 'Show me all the customers from Los Angeles';
const model = 'gpt-3.5-turbo';
sequelAIze(prompt, asyncQuery, model).then(result => {
console.log(result);
}).catch(error => {
console.error(error);
});This example will execute the natural language prompt, generate an appropriate SQL query, and execute that query on the database. The resulting data will be returned in the data property of the object, and the SQL query will be returned in the query property.
asyncQuery Function
The asyncQuery function is a key component of the App. It is responsible for executing SQL queries on the connected database based on the natural language input provided by the user.
To use this function, you should first ensure that the database is properly configured and connected to the application. You can modify the asyncQuery function to work with different databases by updating the SQL code execution logic.
The asyncQuery function takes a single parameter, query, which is the SQL query to be executed. It should return the rows (result) of the executed query. You can create a Promise (resolve/reject) or use the normal async/await syntax for this purpose.
Configuring the Database Connection
The example application index.js using the imported database.js is configured to connect to a SQLite database by default. To configure the database connection, you will need to modify the database.js file to use the appropriate database driver for your database engine.
Here's an example of how to modify database.js to use MySQL instead of SQLite:
javascriptCopy code
const mysql = require('mysql');
// Create a connection pool
const pool = mysql.createPool({
host: 'localhost',
user: 'your_username',
password: 'your_password',
database: 'your_database'
});
/**
* Executes an asynchronous SQL query
*
* @param {String} query The SQL query string to execute
* @param {Array} data An optional array of data values to pass into the query
* @returns {Promise<Array>} A promise that resolves with the resulting rows if the query is successful, or rejects with an error if it fails
*/
async function asyncQuery(query, data = []) {
return await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// Get a connection from the pool
pool.getConnection((error, connection) => {
if (error) {
reject(error);
} else {
// Execute the query using the connection
connection.query(query, data, (error, rows) => {
// Release the connection back to the pool
connection.release();
if (error) {
reject(error);
} else {
resolve(rows);
}
});
}
});
});
}
// Export the asyncQuery function
module.exports = {
asyncQuery
}This example uses the mysql package to create a connection pool and execute SQL queries. You will need to modify the host, user, password, and database properties of the configuration object to match your MySQL database.