ngx-envconfig
Configuration utility for Angular app based on the environment variables.
Using JSON files configure your Angular app like a BOSS!
Specify a list of API endpoints in the JSON and get them in your code with ease.
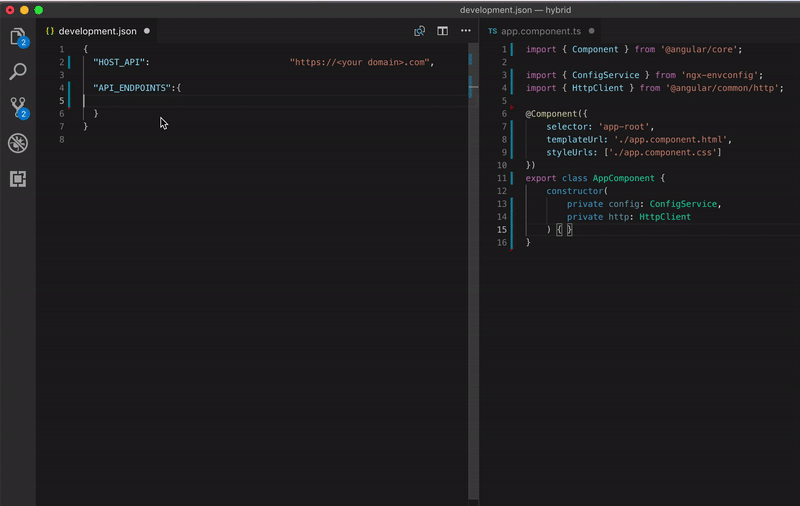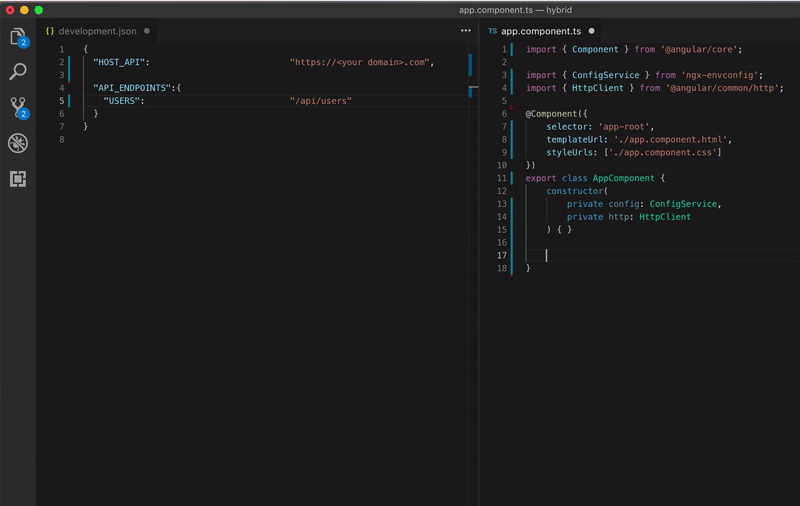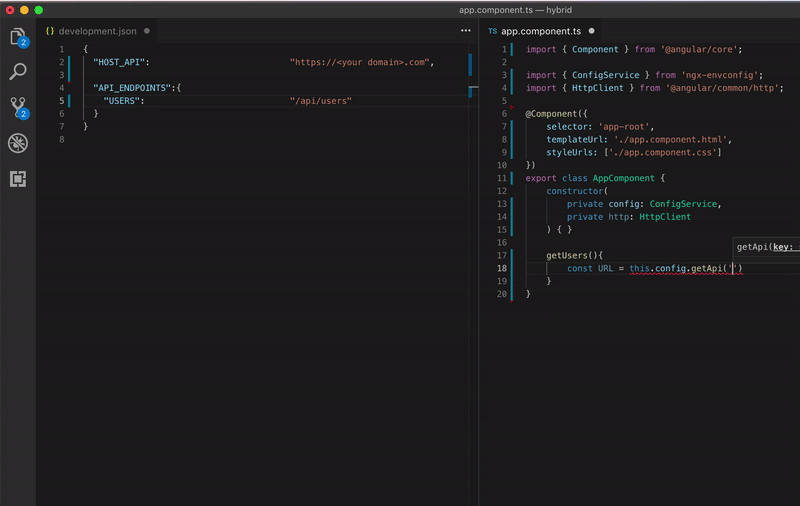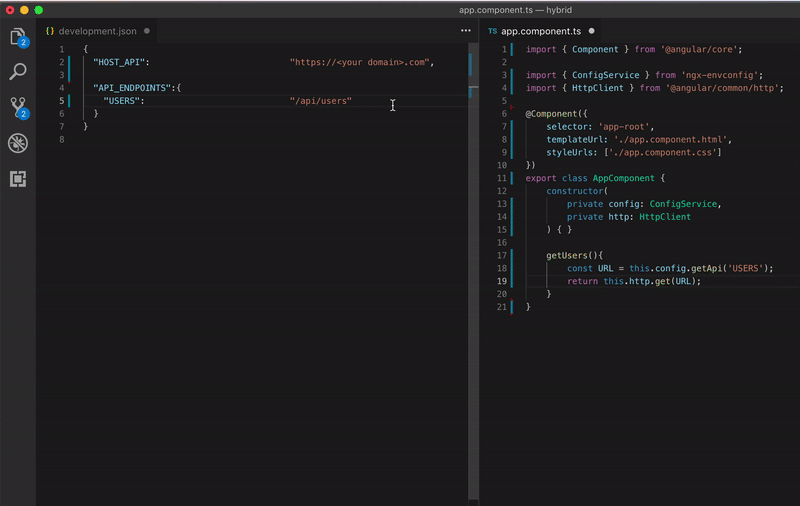
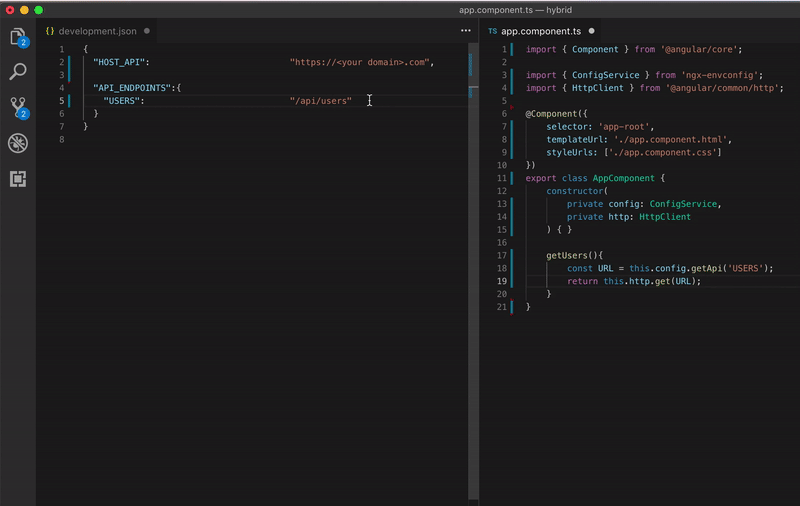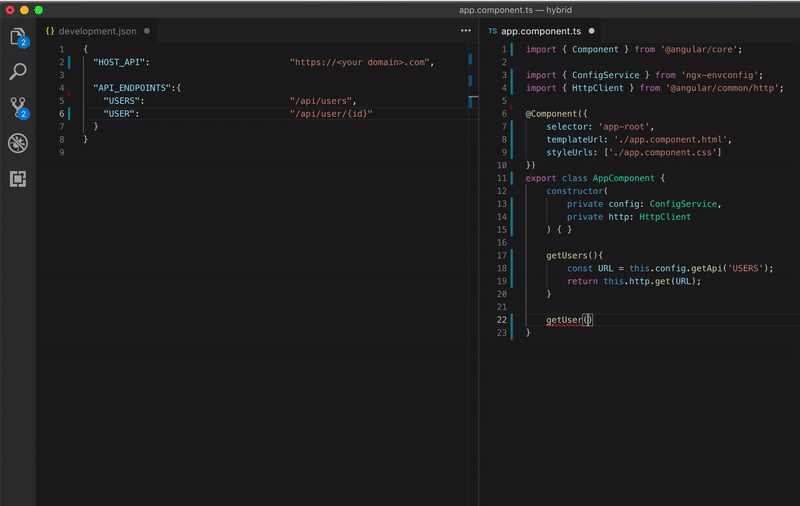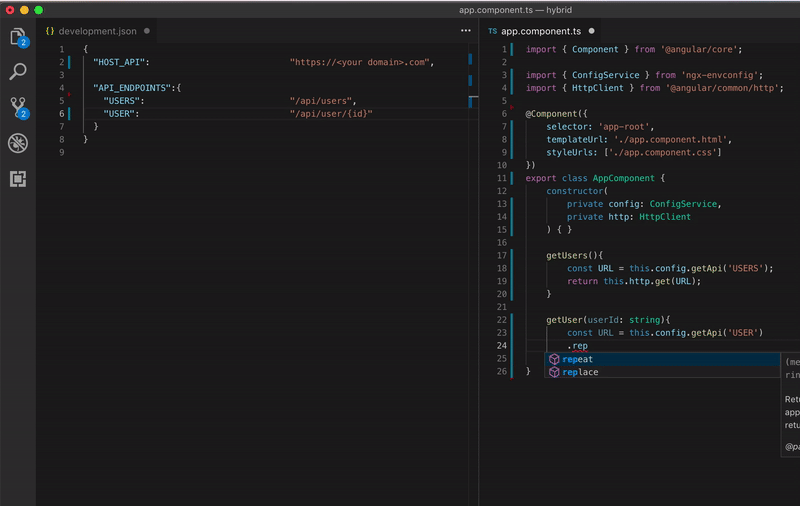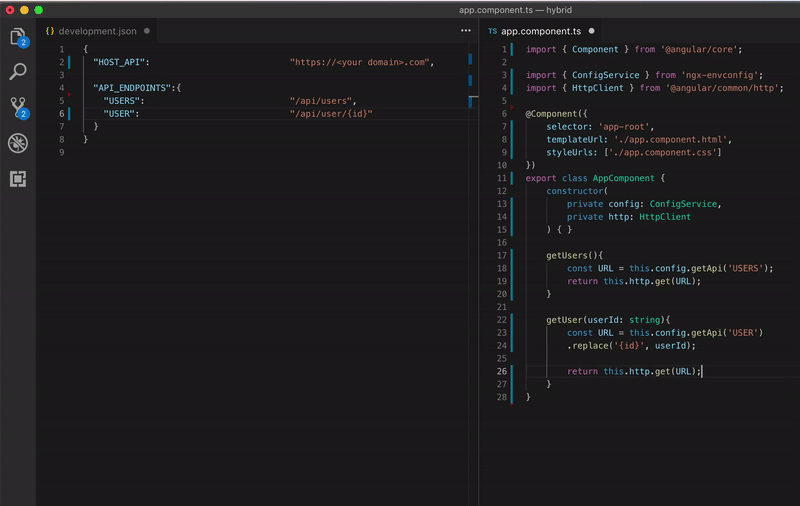
Look how beautiful is your code
Configuring your app for each environment be like:
Did you like it? Please put a Github star to support.
Table of contents:
-
4.1 ConfigModule
4.2 ConfigService
-
5.1 Setting up configuration files
Features
- Configure the project for staging, development and production environments, by taking advantage of Angular environment variables.
- Fallback to default (development.json) configuration if there is no match in production/staging configuration.
- Initializ configuration, before whole application initialization process complete
- Simplified methods for getting back-end API endpoints
Installation
npm install ngx-envconfig --save
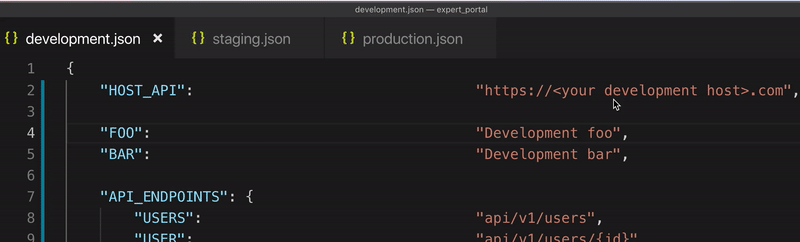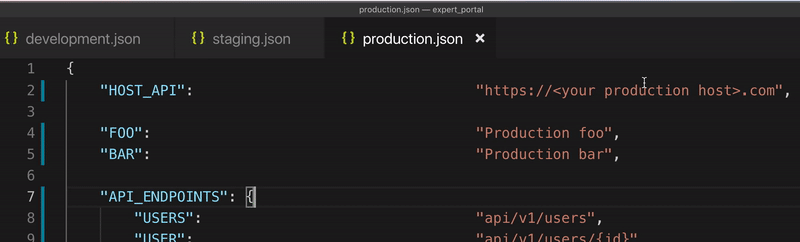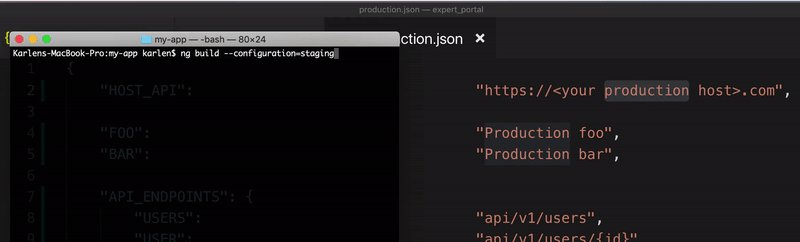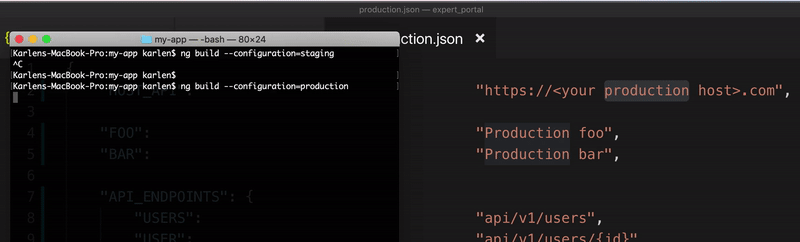
Build Environments
-
ng build --configuration=stagingbuilds for staging environment. For older versionsng build --env=staging -
ng build --configuration=productionbuilds for production environment. For older versionsng build --env=prod
Getting Started
Setting up configuration files
- Create
/configfolder under/assetsdirectory - Create the following config files for the appropriate environment under
/assets/configfolder.
// src/assets/config/development.json
{
"HOST_API": "http://development.server.com",
"API_ENDPOINTS": {
"USER": "/api/v1/user"
},
"TOKEN": "development token"
}// src/assets/config/staging.json
{
"HOST_API": "http://staging.server.com",
"TOKEN": "staging token"
}// src/assets/config/production.json
{
"HOST_API": "http://production.server.com",
"TOKEN": "production token"
}Usage without Angular environment variables
// src/app/app.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { ConfigModule } from 'ngx-envconfig';
@NgModule({
imports: [
ConfigModule.forRoot({state: 'development'})
...
],
providers: [
...
Your Providers
...
]
})
export class AppModule { }// src/app/app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { ConfigService } from 'ngx-envconfig';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
constructor(private configService: ConfigService){
console.log(configService.get('HOST_API'))
// prints: http://development.server.com
console.log(configService.getApi('USERS'))
// prints: http://development.server.com/api/v1/users
// prints: http://production.server.com/api/v1/users if the state is production
}
}Usage with Angular environment variables
-
Add staging configurations in
angular.jsonfile. Make sure production configuration is added. Default one we assume is the development configuration, which is points toenvironment.tsfile.... "projects": { "YOUR APP NAME": { "root": "", ... "architect": { "build": { ... "configurations": { "production": { "fileReplacements": [ { "replace": "src/environments/environment.ts", "with": "src/environments/environment.prod.ts" } ], ... }, "staging": { "fileReplacements": [ { "replace": "src/environments/environment.ts", "with": "src/environments/environment.staging.ts" } ] } ... }
-
If you have older version of Anuglar then make the updates in
.angular-cli.jsonfile as follows:"environmentSource": "environments/environment.ts", "environments": { "dev": "environments/environment.ts", "prod": "environments/environment.prod.ts", "staging": "environments/environment.staging.ts" }
-
Create the following files under
/environmentsfolder.// ./environments/environment.prod.ts export const environment = { state: 'production' };
// ./environments/environment.staging.ts export const environment = { state: 'staging' };
// ./environments/environment.ts export const environment = { state: 'development' };
-
Then you can add environment value to
ConfigModulelike this:// src/app/app.module.ts import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'; import { ConfigModule } from 'ngx-envconfig'; import { environment } from '../src/environments/environment'; // <-- add this line @NgModule({ imports: [ ConfigModule.forRoot(environment) // <-- pass environment variable ... ], providers: [ ... Your Providers ... ] }) export class AppModule { }
// src/app/app.component.ts import { Component } from '@angular/core'; import { ConfigService } from 'ngx-envconfig'; @Component({ selector: 'app-root', templateUrl: './app.component.html', styleUrls: ['./app.component.css'] }) export class AppComponent { constructor(private configService: ConfigService){ console.log(configService.get('HOST_API')) // prints: http://development.server.com // prints: http://production.server.com if the state is production console.log(configService.getApi('USERS')) // prints: http://development.server.com/api/v1/users // prints: http://production.server.com/api/v1/users if the state is production } }
API Reference
ConfigModule
-
.forRoot(envConfig: EnvConfig) Based on the provided
envConfig.statevalue, it will load the approprate*.jsonconfig file. It assumes that configuration json files are located under./src/assets/configfolder. Angular will bootstrap the app, only after the configuration*.jsonfile is loaded.
EnvConfig
-
.state: string Specifies the environment. For instane if it's equalt to
'development'then will loaddevelopment.jsonfile from./src/assets/configfolder -
.fallbackDev: boolean = false Indicates whether to get the value from
development.jsonconfiguration if there is no match in the specified environment. For instance if"SOME_KEY"does not exist inproduction.jsonthen it will return the value of"SOME_KEY"fromdevelopment.json, if"SOME_KEY"value does existdevelopment.jsonfile.
ConfigService
-
.get(propertyName: string): any. Returns the corresponding value of the provided property
propertyNameconfig file.constructor(private config: ConfigService){ console.log(this.config.get('HOST_API')) // prints: 'http://development.server.com' in development mode }
-
.getEnv(): string. Returns the current environment
constructor(private config: ConfigService){ console.log(this.config.getEnv()) // prints: 'development' in development mode }
-
.isDevMode(): boolean. Returns
trueif environment is development, otherwhisefalseconstructor(private config: ConfigService){ console.log(this.config.isDevMode()) // prints: true in development mode }
-
.getApi(endpoint: string): string. This function will only work if you have provided
"API_ENDPOINTS"object in cofig file, which provides the list of available API endpoints and"HOST_API"which is the API's host URL. Returns API endpoint from"API_ENDPOINTS"by concatenating it with"HOST_API".constructor(private config: ConfigService){ console.log(this.config.getApi('USER')) // prints: 'http://development.server.com/api/v1/user' in development mode }
-
.onLoad: AsyncSubject boolean. Async subject to be subscribed. Emits when the config file is already loaded.
constructor(private config: ConfigService){ this.config.onLoad.subscribe(()=>{ console.log('Config file is loaded'); }) }