A Bitcoin SV (BSV) data protocol for effortless reads, writes and updates. Write any arbitrary javascript class value to the blockchain and easily update it, leaving an immutable audit trail.
Each class instance that is written to chain is called a link and the class definition is the template.
Features
- Full control over your data
- Fast - A single link with any number of changes can be loaded in the time it takes to make one network call
- BSV 2 library
- First class data transaction management
- Link templates enforce data contracts
- Node and browser compatible
-
FileandBuffersupport; write any type of file to chain - NPM package
- Works with modern build tools such as Babel and Typescript
- No restrictions placed on what can be inside your link classes - use native code,
for inloops,Math.random()etc. - Optional template ownership enforces co-signing to validate links are authentic
- Back-to-genesis problem is irrelevant as only your trusted apps control templates and their data; Link SV is not a layer 2 token protocol (though it would be possible to build a layer 2 token on Link SV)
How fast is it?
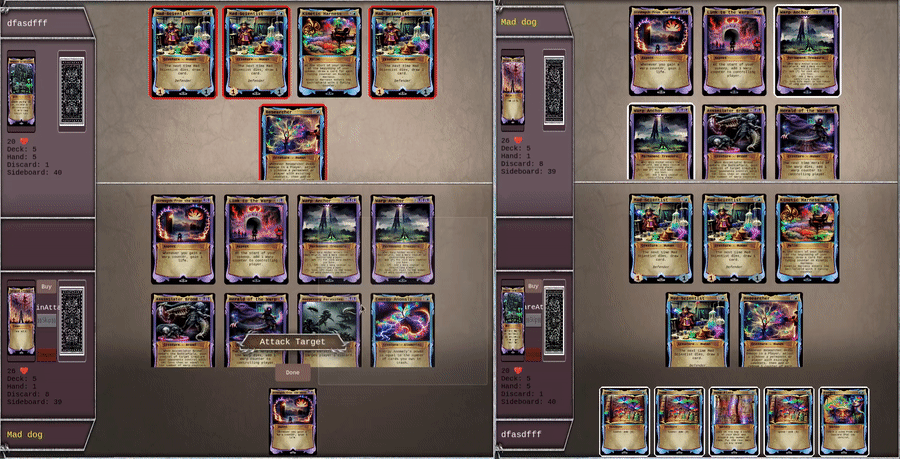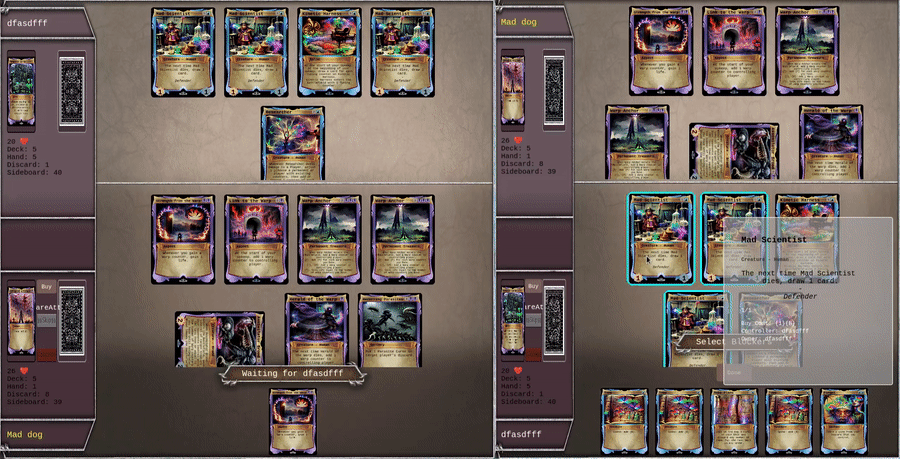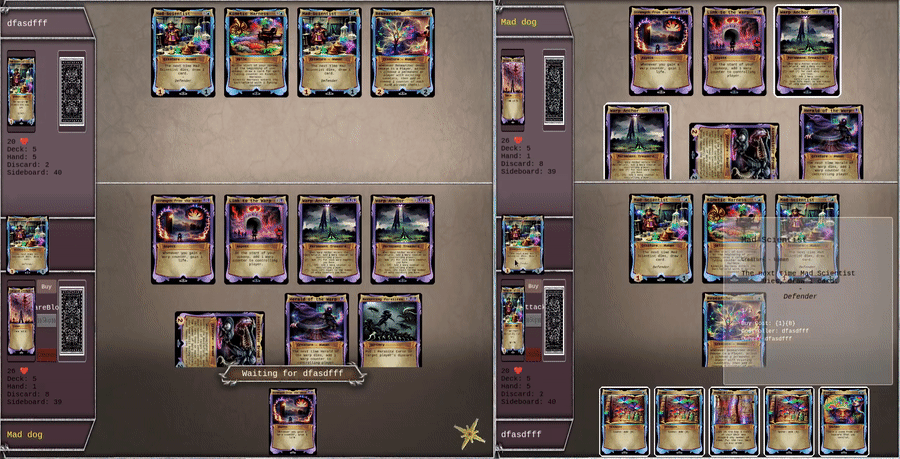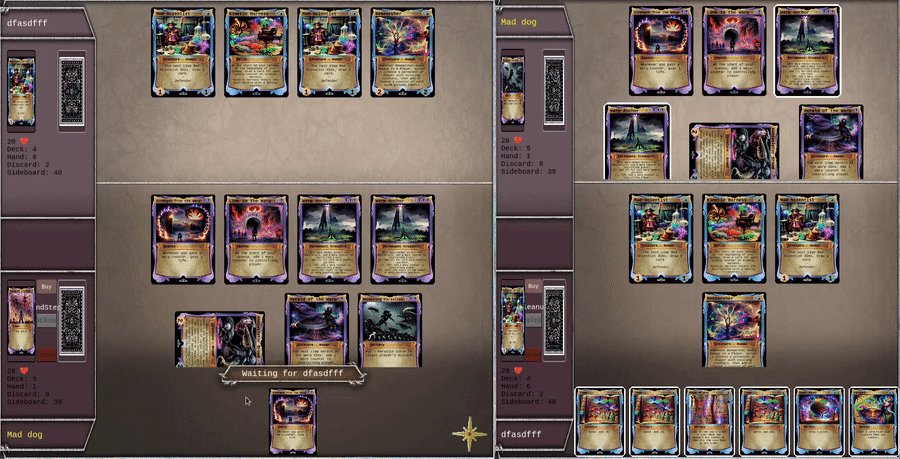
Here is linksv used in a real world video game, showing 2 client battling each other in a PvP card game. All actions are written to chain in the lowest latency way possible, while still enabling backend validation.
Installation
npm install linksv axios axios-rate-limit axios-retry bsv pako
Or
yarn add linksv axios axios-rate-limit axios-retry bsv pako
If using in the browser also add crypto-js and buffer npm packages and modify your webpack config like so:
module.exports = {
...
resolve: {
alias:{
bsv: require.resolve("bsv/dist/bsv.bundle"),
},
fallback: {
crypto: require.resolve("crypto-js"),
buffer: require.resolve("buffer/")
}
},
...
plugins: [
...
new webpack.ProvidePlugin({
process: "process/browser",
Buffer: ["buffer", "Buffer"]
})
]
}Use
import { PrivKey, Address, PubKey, Constants } from "bsv";
import { LinkTemplate, Link, LinkTransaction, LinkContext, BackendLinkProvider } from "linksv";
// uncomment to use testnet
// Constants.Default = Constants.Testnet;
const pursePk = PrivKey.fromRandom();
const ownerPk = PrivKey.fromRandom();
const ownerAddr = Address.fromPubKey(PubKey.fromPrivKey(ownerPk));
const ctx = new LinkContext({
purse: pursePk.toString(),
owner: ownerPk.toString(),
logger: console,
provider: new BackendLinkProvider("https://<your_provider_host_url>[:port]"),
app: "appName",
});
@LinkTemplate("Sword")
export class Sword extends Link {
name: string;
owner: string;
constructor(name: string) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
changeName(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
}
// if your environment doesn't allow class decorators,
// you can use LinkTemplate like this:
// Sword = LinkTemplate("Sword")(Sword);
const tx = new LinkTransaction()
const swordInstance = tx.update(() => new Sword("sword"));
tx.update(() => swordInstance.changeName("cool sword"));
expect(swordInstance.name).toEqual("cool sword");
expect(swordInstance.owner).toEqual(ownerAddr);
expect(tx.outputs.length).toEqual(1);
const txid = await tx.publish();
console.log(swordInstance.location);To load a location from chain:
const swordInstance = await ctx.load(Sword, locationToLoadStr);
expect(swordInstance.name).toEqual("cool sword");Files
To save a file to chain, create a link with any property that stores a javascript File object. Then, publish that link like any other. In node js, use Buffer instead of File.
@LinkTemplate("LinkWithFile")
class LinkWithFile extends Link {
myFile: File;
constructor(file: File) {
super();
this.myFile = file;
}
}
const filebuf = await loadFile();
const inst = tx.update(() => new LinkWithFile(new File([filebuf], "image.png", { type: "image/png" })));
await tx.publish();
const location = inst.location;
//then to load the file...
const fileLink: LinkWithFile = await ctx.load(LinkWithFile, location)
console.log(fileLink.myFile);For best practices with files, it is recommended to wrap them in a link, then store that link in your main link class. This is because any nested links are serialized to chain as a pointer, so changes you make to
your parent link won't result in the file being written to chain more than once. You can use the built in FileLink to wrap your files and buffers for this purpose.
Template Owner
To give a template an owner, requiring that owner to sign whenever a new instance of a link is constructed, call tx.deploy(LinkClass, ownerAddrStr) then tx.publish(). See template owner tests for more info.
Backend
You will need to run a provider backend to store link locations. Clone this repo onto your server and start it with docker-compose:
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/zpxp/linksv.git
cd linksv
mkdir .data
sudo chown -R 5678 .data
docker-compose up -d --build --force-recreateThis will run a instance of the provider backend and store the links in a sqlite database located in .data/link.db.
If you wish to use a database other than sqlite, you may change the UseSqlite in src/provider/Program.cs to another provider. You may need to install the nuget packages for your relevant database. See ef core database providers. After setting up the backend, point your client's link provider to it when creating the LinkContext.
In production apps it is highly recommended to extend the backend to include authentication, so only trusted parties can write link locations. You may also implement the provider functionality in your own application backend and include authentication.
Swagger
To see what endpoints are provided by the backend, run in debug mode and visit the url http://localhost:5000/swagger/index.html.
How it works
Link SV tracks changes to link instances and serializes those changes to chain on tx.publish(). Data is compressed so large amounts of data can be written while maintaining cheap transaction fees. New link locations are automatically recorded in the backend provider so blockchain indexing is not required.
Compression
Compression modes supported are:
- ZLib
- GZip
- ECIES (private encrypted data written to chain)
- Raw json (no compression)
Note
The LinkContext.utxoStore in the browser defaults to indexed DB, but defaults to an in memory only implementation in nodejs. If you need to persist your purse utxos across sessions, implement a persistent IUtxoStore and pass to LinkContext constructor.