flowpipe is installable via:
- npm:
npm install flowpipe --save
- v0.5.0 is based on
PromiseObject, so not support previous version. - for using older version,
let flowpipe = require('flowpipe').older
'use strict';
const Flowpipe = require('flowpipe');
let myWork = (args)=> new Promise((resolve)=>{
args.data2.push(Math.random());
setTimeout(resolve, 5);
});
let flowpipe = Flowpipe.instance('MyWork');
flowpipe
// set arguments
.init((args)=> args.index = 0)
.init((args)=> args.data1 = [])
.init((args)=> args.data2 = [])
.init((args)=> args.data3 = [])
// set work, name as work-1
.then('work-1', (args)=> new Promise((resolve)=> {
args.data1.push(Math.random());
setTimeout(resolve, 5);
}))
// set work, set name as myWork
.then(myWork)
// set work, set auto created name
.then((args)=> new Promise((resolve)=> {
args.data3.push(Math.random());
setTimeout(resolve, 5);
}))
// loop back to work-1 if args.index < 100 and increase args.index
.loop('work-1', (args)=> ++args.index < 100)
// print something
.log((args)=> `data1 data2 data3 / ${args.data1.length} ${args.data2.length} ${args.data3.length}`)
// set parallel max thread
.maxThread(30)
// set parallel
.parallel((args)=> args.data1, (args, data, idx)=> new Promise((resolve)=> {
setTimeout(()=> {
resolve();
}, data * 1000);
}))
// print timestamp
.timestamp((total, premodule)=> `total: ${total}ms, parallel ${premodule}ms`)
// run
.run();- Flowpipe.instance(name)
-
returnFlowpipe instance - such as
let myjob = require('flowpipe').instance('myJob')
-
- instance.init(setterFn)
- set instance's local variables
-
setterFn(args): must sync function, not async.- such as
instance.init((args)=> args.data = [])
- such as
- instance.log(printFn)
- print log
-
printFn(args): must have return string
- instance.timestamp(printFn)
- print timestamp
-
printFn(total, preModule): must have return string
- instance.then(name, work)
- add some work
- also,
then, add, pipe -
name(optional): work name for loop back -
work: work function,
- instance.loop(workname, condition)
- also,
loop, for, loopback -
workname: target to loopback -
condition: must have return boolean
- also,
- instance.maxThread(number)
- set parallel max thread
- instance.parallel(which, work)
-
which: must have return array -
work: work function (args, data, idx)
-
var flowpipe = require('flowpipe').older;
flowpipe
.init(function (next) {
// init before start
var page = 1;
next(null, page);
})
.pipe('start', function (next, page) {
// page is that previous next function's variable
setTimeout(function (err) {
// next is function that proceed next pipe, parallel or loopback
next(err, page);
}, 1000);
})
.pipe('list', function (next, page) {
console.log('start page: ' + page);
// preparing list for parallel
var list = [{no: 1}, {no: 2}, {no: 3}];
for (var i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
list[i].page = page;
list[i].delay = 3 - i; // delay time in parallel process
}
// next before parallel, pass only second parameter to parallel process.
// second parameter must be array.
// other parameters pass to next pipe or loopback.
next(null, list, page);
})
.parallel('parallel process', function (next, data) {
// data is indicating each of list items.
setTimeout(function () {
data.title = 'title-' + data.no;
next(null, data);
}, data.delay * 1000);
})
.parallel('parallel process 2', function (next, data) {
// data is indicating each of list items.
setTimeout(function () {
data.title = 'title-' + data.no;
next(null, data);
}, data.delay * 1000);
})
.parallel('multi-thread', function (next, data) {
// this option {multiThread: true} makes your function async.
// in node.js's single thread, navie logic is processing by single thread.
// if you use this, all of logics are processing in multi thread.
// ***WARNING: use only local variables or parameters from previous pipe.
// do not use global, or functional objects from previous pipe.
for(var i=0;i<100000000;i++) ;
next(null, data);
}, {multiThread: true})
.pipe('pass-1', function (next, parallel, page) {
console.log('pass-1');
next(null, parallel, page);
})
.pipe('pass-else', function (next, parallel, page) {
console.log('pass-else');
next(null, parallel, page);
})
.loopback('pipe-list', function (loop, next, instance, parallel, page) {
// loopback(process_type-process_name, fn)
// - process_type: pipe, parallel
// - process_name: must defined
// - fn(loop, next, instance, others...)
// - loop(err, variables...): passing variable to target process
// - next(err, variables...): proceeding if loop ended
// - instance: maintainable variable in loop, object type {}
// - others: passed from before process
if (!instance.data) instance.data = [];
for (var i = 0; i < parallel.length; i++)
instance.data.push(parallel[i]);
if (page < 5) loop(null, page + 1);
else next(null, instance.data);
})
.pipe('finalize', function (next, data) {
next(null, data);
})
.end(function (err, test) {
// end(callback) or end()
// this must be declared, if not all function don't working.
// proceed in the end or occured error in process
})
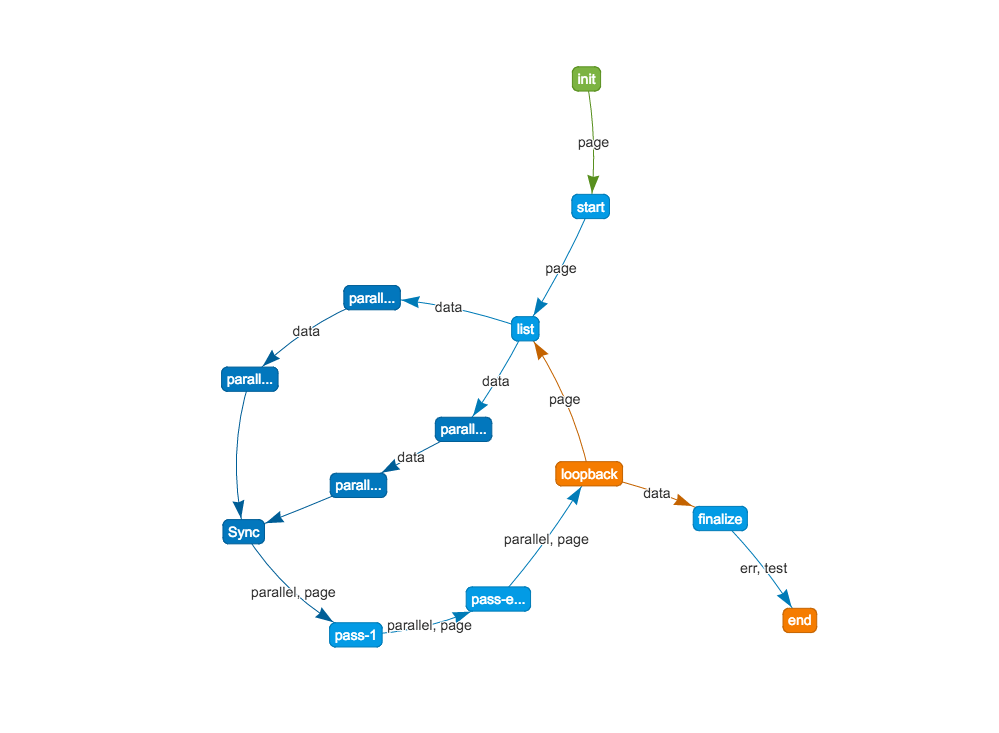
.graph('./basic-example-graph.html');- flowpipe.init(work)
- initialize variables
- params
-
work: function(next)-
next: function(err, arg1, arg2 ...)- callback for next work. must be execute this function in callback.
-
-
- flowpipe.pipe(name, work)
- params
-
name: current work's name -
work: function(next, arg1, arg2 ...)-
next: function(err, arg1, arg2 ...) -
args: previous work's results
-
-
- params
- flowpipe.parallel(name, work, opts)
- processing work in parallel.
- params
-
name: current work's name -
work: function(next, list_item, args ...)-
next: function(err, item)-
item: sync items to list
-
-
list_item: parameter in previous work's first variable. must be array in previous. -
args: previous work's results, not array
-
-
opts:- multiThread: default
false
- multiThread: default
-
- flowpipe.loopback(target, work)
- params
-
target: jump to,function-name -
work: function(loop, next, instance, args ...)-
loop: function(err, args ...), when loop continue -
next: function(err, args ...), when loop end -
instance: maintenance variable in loop
-
-
- params
- flowpipe.end(work)
- this function must be added in last.
- params
- work: function(err, args ...)
- flowpipe.graph(savePath)
- save graph
- must be proceed after end