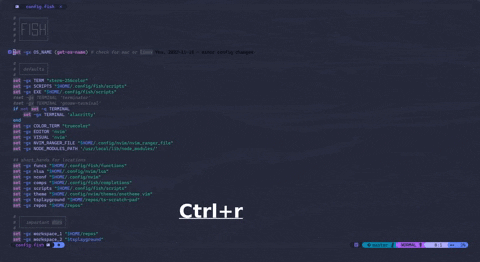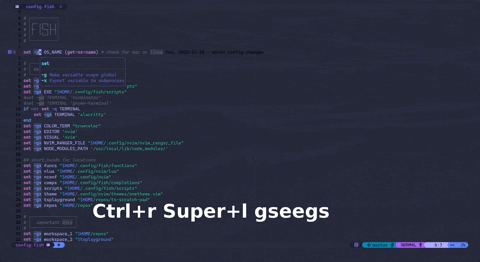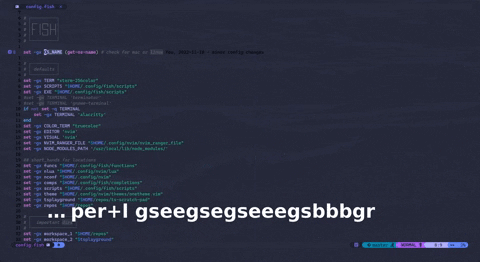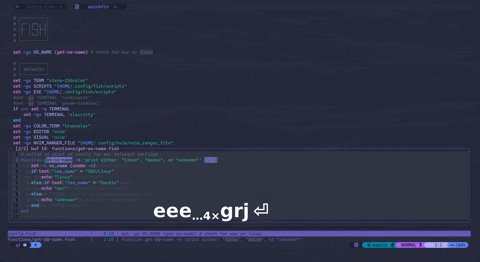
A feature-rich, extensible, and blazingly fast language-server for the fish-shell. Uses tree-sitter, tree-sitter-fish, yarn and typescript. Implements both standard & non-standard features from the language-server-protocol, to be connected to a language-client (neovim,coc.nvim, vscode, etc.). More info on the wiki.
-
Create the
fish-lspcommand via one of the following methods (building from source is recommended)Build from source
-
clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/ndonfris/fish-lsp.git
-
enter the directory
cd ./fish-lsp -
run the install commands:
yarn install # install dependencies
Using release binaries (UNTESTED)
Currently is not recommended for use as the release binaries are error prone and not fully tested. Future
tsupbuilds, should provide stability across different installation enviornments.-
navigate to the releases, and download the file for your OS
-
Rename file to fish-lsp (make sure the binary is executable as well)
# cd to downloaded location mv fish-lsp-linux fish-lsp chmod +x ./fish-lsp
-
move the binary to your $PATH:
mv ./fish-lsp ~/.local/bin/fish-lsp
-
-
Provide the
fish-lspcommand to start the server from a language client{ "languageserver": { "fish-lsp": { "command": "fish-lsp", "args": ["start"], "filetypes": ["fish"] } } }configuration shown for "coc.nvim" lua and other language-client configuration syntax's can be built by fish-lsp startup-configuration . Demo shows different hover documentation, go-to definition, go-to references and some other features.
| Feature | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Completion | Provides completions for commands, variables, and functions | ✅ |
| Hover | Shows documentation for commands, variables, and functions. Has special handlers for --flag, commands, functions, variables
|
✅ |
| Signature Help | Shows the signature of a command or function | ✖ |
| Goto Definition | Jumps to the definition of a command, variable, or function | ✅ |
| Find References | Shows all references to a command, variable, or function | ✅ |
| Rename | Rename within matching global && local scope | ✅ |
| Document Symbols | Shows all commands, variables, and functions in a document | ✅ |
| Workspace Symbols | Shows all commands, variables, and functions in a workspace | ✅ |
| Document Formatting | Formats a document, full & selection | ✅ |
| Document Highlight / Semantic Token | Highlights all references to a command, variable, or function. | ✖ |
| Command Execution | Executes a server command from the client | ✖ |
| Code Action | Shows all available code actions | ✖ |
| Code Lens | Shows all available code lenses | ✖ |
| Logger | Logs all server activity | ✅ |
| Diagnostic | Shows all diagnostics | ✖ |
| Telescope Integration | Integrates with the telescope.nvim plugin | ✅ |
| CLI Interactivity | Provides a CLI for server interaction. Built by fish-lsp complete <option>
|
✅ |
| Client Tree | Shows the defined scope as a Tree | ✅ |
| Indexing | Indexes all commands, variables, and functions | ✅ |
The wiki Contains more information on the project. Project is still in it's early releases, so the wiki information is subject to change. Contains 'minimal' client submodules, useful snippets, and bleeding edge feature documentation.
This project aims to be a more feature rich alternative to some of it's predecessors, while maintaining an editor agnostic server implantation. The following sources were major influences on the project's overall design and structure.
-
Official Documentation
-
Related/Similiar projects
-
Important Packages
-
Default Implementation Git Repos