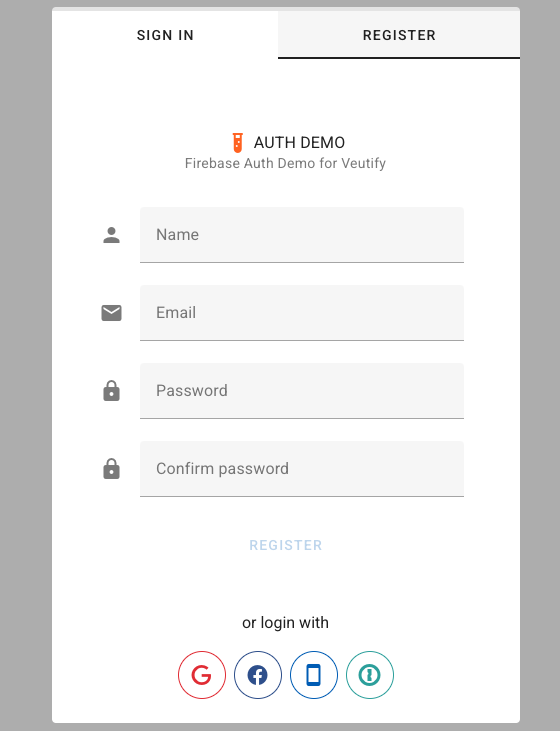
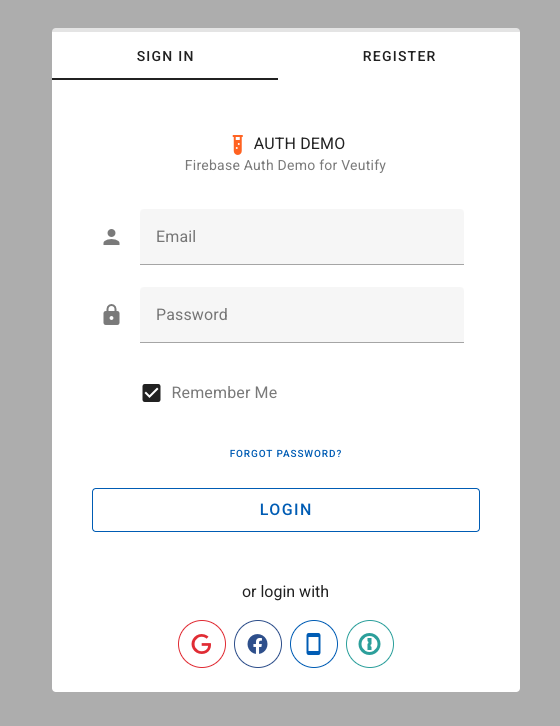
Accelerate your Vue 3 and Vuetify 3 application development with a ready-to-use Firebase authentication solution.
@nerd305/firebase-vuetify-auth provides a seamless integration of Firebase Authentication with beautiful Vuetify 3 components. This package is designed to save you significant development time by offering pre-built UI and logic for common authentication flows, allowing you to focus on your application's core features.
If you're building a Vue 3 application with Vuetify 3 and need robust user authentication without the boilerplate, this package is for you. Get your users signing in, registering, and managing their accounts quickly and easily.
- Rapid Integration: Drop in a complete authentication system in minutes.
- Time-Saving: Avoid building common authentication UI and logic from scratch.
- Vuetify 3 Native: Components are built with Vuetify 3, ensuring a consistent look and feel with your application.
- Firebase Powered: Leverages the security and scalability of Firebase Authentication.
- Feature-Rich: Supports email/password, social logins (Google, Facebook), phone authentication, SAML, and email verification.
- Customizable: Configure various authentication methods and UI aspects to suit your needs.
This package provides out-of-the-box solutions for:
- User Sign-In: A ready-to-use, Vuetify-styled login form.
- User Registration: Secure new user account creation.
- Email Verification: Optional, configurable email verification flow to ensure valid user emails.
- Password Reset: "Forgot Password" functionality.
-
Third-Party Logins: Easy integration for:
- Google Sign-In
- Facebook Sign-In
- Phone Number (Text Message/SMS) Authentication
- SAML-based Single Sign-On (SSO)
- Route Protection: Middleware to easily protect your application's routes.
- Reactive State Management: Built with Pinia for a clear and maintainable auth state.
Current master branch supports Vue 3 application. For Vue 2 please see vue2 branch.
Note: This package is compatible only with Pinia versions 3 and above.
This package assumes your VUE project is already integrated with Firebase & Vuetify. Example integration:
The Firebase config file, example: ./src/middleware/firebase is created to initiate Firebase Modular v9 SDK
example:
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app"
const config = {
appId: process.env.VITE_APP_FIREBASE_APP_ID,
apiKey: process.env.VITE_APP_FIREBASE_APIKEY,
authDomain: process.env.VITE_APP_FIREBASE_AUTH,
databaseURL: process.env.VITE_APP_FIREBASE_DATABASE,
projectId: process.env.VITE_APP_FIREBASE_PROJECT,
storageBucket: process.env.VITE_APP_FIREBASE_STORAGE,
messagingSenderId: process.env.VITE_APP_FIREBASE_MESSAGING,
measurementId: process.env.VITE_APP_FIREBASE_MEASUREMENT_ID,
}
const app = initializeApp(config)
export default appAdditionally, please ensure that you have installed the mdi/fonts package.
example of integration:
import "@mdi/font/css/materialdesignicons.css"add this into your vuetify.js
npm i @nerd305/firebase-vuetify-authIntegrating @nerd305/firebase-vuetify-auth into your Vue 3 and Vuetify 3 project is straightforward. If you've met the prerequisites outlined in the "Requirements" section, you can get up and running by following these three simple steps:
-
STEP 1: Update your
main.jsapp file to initialize the AuthGuard plugin. -
STEP 2: Add the
<AuthenticationGuard />component to your mainApp.vuetemplate. -
STEP 3: Update your Vue Router configuration to use the
AuthMiddlewarefor protecting routes.
This example assumes that you're using vue-router and pinia packages with your app, so we initialize VUE class by passing in router, store & vuetify objects.
import { createApp } from "vue"
import { createPinia } from "pinia"
import App from "@/App" // Your root App component
import router from "@/router" // Your Vue Router instance
import vuetify from "@/plugins/vuetify" // Your Vuetify instance
import AuthGuard from "@nerd305/firebase-vuetify-auth"
import firebaseApp from "@/middleware/firebase" // Your initialized Firebase app instance
const authGuardSettings = {
debug: true, // enable debug messages in console log
session: "local", // Default session persistence for all auth methods.
// Options:
// "local": Persists session across browser closures (user stays logged in).
// "browser" (or "session"): Session lasts only as long as the browser tab/window is open.
// "none": Session is in memory only, lost on page refresh/tab close (Firebase interprets this as browserSessionPersistence).
// The "Remember me" checkbox in the email/password form overrides this setting specifically for email/password logins.
router, // Your Vue Router instance
firebase: firebaseApp, // Your initialized Firebase app instance
saml: false, // allow authentication with SAML
saml_text: "Login with OKTA", // text for large login button if SAML is the only 3rd party provider
saml_provider_id: "saml.okta", // firebase provider ID for SAML
email: true, // allow authentication with email
phone: false, // allow authentication with phone
google: true, // allow authentication with gmail account
facebook: false, // allow authentication with facebook account
verification: false, // require user email to be verified before granting access.
// Can be true (for all) or an array of domains (e.g., ['example.com']).
registration: true, // allow new user registrations
// Optional UI Customizations
// title: "My App Authentication",
// subtitle: "Please sign in to continue",
// icon: "mdi-lock",
// iconColor: "blue"
}
const app = createApp(App)
app.use(createPinia())
app.use(router)
app.use(vuetify)
app.use(AuthGuard, authGuardSettings) // Initialize AuthGuard plugin
app.mount("#app")Update your App.vue to include global AuthGuard component.
This component will monitor Firebase user auth state and open a fullscreen modal dialog with login screen if user is not autthenticated.
<!-- App.vue -->
<template>
<v-app>
<v-main>
<router-view />
</v-main>
<!-- Required for phone authentication if enabled -->
<!-- <div id="recaptcha-container"></div> -->
<AuthenticationGuard /> {/* Add this component */}
</v-app>
</template>
<script setup>
// No specific script needed for basic integration here
</script>Example of router.js implementation.
import { createWebHistory, createRouter } from "vue-router"
import { AuthMiddleware } from "@nerd305/firebase-vuetify-auth" // Import the middleware
const routes = [
{
name: "Home",
path: "/",
component: () => import("@/views/HomePage.vue"),
meta: { requiresAuth: true }, // Protected route
},
{
name: "Public",
path: "/public",
component: () => import("@/views/PublicRoute.vue"),
// No meta.requiresAuth - this route is public
},
{
name: "Protected",
path: "/protected",
component: () => import("@/views/ProtectedRoute.vue"),
meta: { requiresAuth: true }, // Protected route
},
// ... other routes
];
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(),
routes,
});
// Apply the AuthMiddleware globally
router.beforeEach(AuthMiddleware);
export default router;add meta: { requiresAuth: true } for any route that would require authentication.
This section provides an overview of the internal mechanism of the firebase-vuetify-auth package.
When you install the plugin using app.use(AuthGuard, authGuardSettings):
- The
authGuardSettingsare merged with default settings and stored in the Pinia store (useAuthStore). - Firebase Authentication is initialized (
getAuth). - The default session persistence (e.g., "local", "browser") is set on the Firebase
authobject based on thesessionproperty inauthGuardSettings. This default applies to all sign-in methods unless overridden (e.g., by the "Remember me" checkbox for email/password). - An
onAuthStateChangedlistener is attached to Firebase. This listener is crucial for reacting to changes in the user's authentication state.
- This component should be added to your main
App.vue. - It renders the main authentication dialog (
v-dialog). - The visibility of this dialog (
is_authguard_dialog_shownstate in Pinia) is controlled by the authentication logic. - The dialog contains tabs for Sign In, Register, Reset Password, and also houses the Email Verification screen.
- Its internal state (like active tab) and the display of different forms (login, register, phone, email verification) are managed by the Pinia store.
A dedicated Pinia store (useAuthStore) is the central hub for authentication-related state:
-
config: Stores theauthGuardSettingsprovided during initialization. -
current_user: Holds the Firebase user object when a user is authenticated. -
is_loading,error: Manage loading states for asynchronous operations (like login attempts) and store any errors that occur. -
UI States:
-
is_authguard_dialog_shown: Boolean, controls the visibility of the main authentication dialog. -
is_authguard_dialog_persistent: Boolean, determines if the dialog can be closed by clicking outside or pressing Escape. -
is_email_verification_screen_shown: Boolean, controls the visibility of the email verification prompt. -
tab: Number, manages the active tab within the authentication dialog (Sign In, Register, Reset Password). - Other states related to phone login steps, password reset confirmation, etc.
-
-
Actions:
- Functions like
loginWithEmail,registerUser,signOut,loginWithGoogle, etc. - These actions typically call the corresponding Firebase SDK methods to perform authentication operations.
- They update
is_loadinganderrorstates and, upon success, Firebase'sonAuthStateChangedlistener (see below) will update thecurrent_user.
- Functions like
- Set up in
src/wrapper.js. - This listener fires whenever a user signs in or out of Firebase.
-
Primary Action: It updates the
authStore.current_userwith the new Firebase user object (ornullif signed out). -
Triggers
authcheck(): After updating the user state, it calls theauthcheck()function (see below) to re-evaluate route access permissions and dialog visibility based on the new authentication status. - Email Verification Check: If a user is authenticated but their email is not verified (and email verification is required by the configuration), this listener also sets up an interval to periodically reload the user's Firebase profile to check if their email has been verified. If verification occurs, the page is reloaded.
- This middleware is intended to be registered globally with Vue Router using
router.beforeEach(AuthMiddleware). -
On Each Navigation:
- It inspects the target route (
to) to see if it requires authentication (viato.meta.requiresAuth: true). - It determines if the navigation is from a public route to a protected route.
- It updates two key states in the Pinia store:
-
is_route_public: Set totrueif the target route does not require authentication,falseotherwise. -
is_from_public_to_auth: Set totrueif navigating from a public page to a protected one,falseotherwise. This influences dialog persistence.
-
-
Calls
authcheck(): After updating these store states, it calls theauthcheck()function to make the final decision on allowing or blocking the navigation.
- It inspects the target route (
This function is the heart of the access control and dialog management logic. It is called in two main scenarios:
- By the
AuthMiddlewareduring every route navigation. - By the
onAuthStateChangedlistener whenever the Firebase authentication state changes.
authcheck() performs the following checks:
-
Is the route public? (
store.is_route_public): If yes, access is allowed, and the auth dialog is hidden. -
Is the user authenticated? (checks
firebase.auth().currentUser):- If not authenticated and trying to access a protected route:
- The auth dialog (
is_authguard_dialog_shown) is shown. - If navigating from a public route (
store.is_from_public_to_authis true), the dialog is made non-persistent (is_authguard_dialog_persistent = false), allowing the user to close it and stay on the public page. - Otherwise (e.g., initial load on a protected route), the dialog is persistent.
- Navigation is blocked.
- The auth dialog (
- If authenticated:
-
Email Verification Check:
- It checks
currentUser.emailVerifiedagainst theconfig.verificationrules (is verification required for all, or for specific domains?). - If verification is required and the user's email is not verified:
- Access to the protected route is blocked.
- The auth dialog is shown and made persistent.
- The specific email verification screen is displayed (
is_email_verification_screen_shown = true).
- If email is verified, or verification is not required for this user:
- Access to the protected route is allowed.
- The auth dialog is hidden.
- It checks
-
Email Verification Check:
- If not authenticated and trying to access a protected route:
- Anonymous Users: If email verification is active, anonymous users are generally blocked from protected resources that would require a verified email, as they cannot verify an email.
-
Returns:
trueif navigation/access is allowed,falseotherwise. TheAuthMiddlewareuses this return value to callnext()ornext(false).
- If
authGuardSettings.verificationis enabled (eithertruefor all or an array of domains):- When an authenticated but unverified user (matching the verification rules) attempts to access a protected route,
authcheck()will:- Block access.
- Show the auth dialog (
is_authguard_dialog_shown = true). - Make the dialog persistent (
is_authguard_dialog_persistent = true). - Display the email verification screen (
is_email_verification_screen_shown = true) within the dialog. This screen prompts the user to check their email and provides an option to resend the verification email.
- The
onAuthStateChangedlistener insrc/wrapper.jsincludes logic to periodically reload the user's Firebase profile. IfcurrentUser.emailVerifiedbecomestrue, it reloads the entire page to reflect the verified state and grant access.
- When an authenticated but unverified user (matching the verification rules) attempts to access a protected route,
The authentication dialog's persistence (whether it can be closed by clicking outside or pressing Escape) is dynamically managed:
-
Persistent:
- Typically when the user initially lands on a protected route and is not authenticated.
- When email verification is required and the user's email is not yet verified.
-
Non-Persistent (Closable):
- When a user navigates from a public page to a protected page. This allows them to close the dialog and remain on the public page if they choose not to sign in.
This mechanism ensures that users are appropriately prompted for authentication or verification while providing a user-friendly experience for different navigation scenarios.
For detailed examples of expected behavior under various conditions (user signed off, signed in with unconfirmed email, different verification settings, etc.), please refer to the manual test scenarios outlined in:
src/tests/README.md
This document provides a structured way to test the core functionalities and edge cases of the package.
If you enable phone authentication (phone: true in authGuardSettings), Firebase requires a reCAPTCHA verifier. You must include an empty div with the ID recaptcha-container in your main application template (e.g., App.vue or wherever the AuthenticationGuard component is rendered). This div is used by Firebase to render the reCAPTCHA element (it's usually invisible).
Example in App.vue:
<template>
<v-app>
<!-- ... your app layout ... -->
<!-- This div is used by Firebase for reCAPTCHA. It can be empty. -->
<div id="recaptcha-container"></div>
<AuthenticationGuard />
</v-app>
</template>Ensure this div is present in the DOM when phone authentication is attempted.
This package facilitates client-side authentication flows with Firebase. It is crucial to understand that client-side code, including Firebase API keys and configuration, is publicly accessible.
True security for your application's data and backend resources must be enforced through Firebase Security Rules (for Firestore, Realtime Database, and Cloud Storage) and by correctly configuring your Firebase Authentication providers in the Firebase console. This package helps manage the user's authentication state on the client but does not, by itself, secure your backend. Always ensure your Firebase Security Rules are robust and properly tested.
After following implementation instruction requests to protected views, should render a login / registration view, unless user is already logged into the application.
For more usage examples (how to log in/sign out and so on) please check the package source code
| Prop | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
router |
Vue Router Instance | null |
Required. Your Vue Router instance. |
firebase |
Firebase App Instance | null |
Required. Your initialized Firebase app instance. |
session |
String | "local" |
Default Firebase auth state session persistence for all auth methods. Options: "local", "browser" (or "session"), "none". The "Remember me" checkbox for email/password login overrides this for that specific login. See Firebase Docs. |
verification |
Boolean or Array | false |
Requires email verification. true for all new accounts, or an array of specific email domains (e.g., ['yourdomain.com']) to target. |
registration |
Boolean | true |
true to allow new user registrations through the UI, false to disable. |
debug |
Boolean | false |
true to enable verbose console logging from the package, false to disable. |
email |
Boolean | true |
true to enable email/password authentication method. |
phone |
Boolean | false |
true to enable phone number authentication method. (Requires reCAPTCHA setup, see above). |
google |
Boolean | true |
true to enable Google Sign-In authentication method. |
facebook |
Boolean | false |
true to enable Facebook Sign-In authentication method. |
saml |
Boolean | false |
true to enable SAML-based authentication. |
saml_text |
String | "Login with OKTA" |
Custom text for the SAML login button (if saml is true and it's the only 3rd party provider). |
saml_provider_id |
String | "saml.okta" |
Your Firebase SAML Provider ID (e.g., "saml.myprovider") (if saml is true). |
title |
String | "Authenticate" |
Title displayed on the authentication dialog. |
subtitle |
String | "Firebase Vuetify Authentication NPM package" |
Subtitle displayed on the authentication dialog. |
icon |
String | "mdi-brightness-7" |
MDI icon class for the icon displayed on the authentication dialog. |
iconColor |
String | "orange" |
Color of the icon on the authentication dialog. |