v-rule
Light and flexible validation rules for form
Advantages:
- Limited API, save you from complicated configuration
- Quite flexible, able to compose any validation rule
- Small library with no dependence
Core API
- when(key: string, assert?: func)
- whenNot(key: string, assert?: func)
- expect(desc: string, assert?: func)
- validate(key: string)
Install
npm i -S v-ruleExample - Order beer in restaurant
1
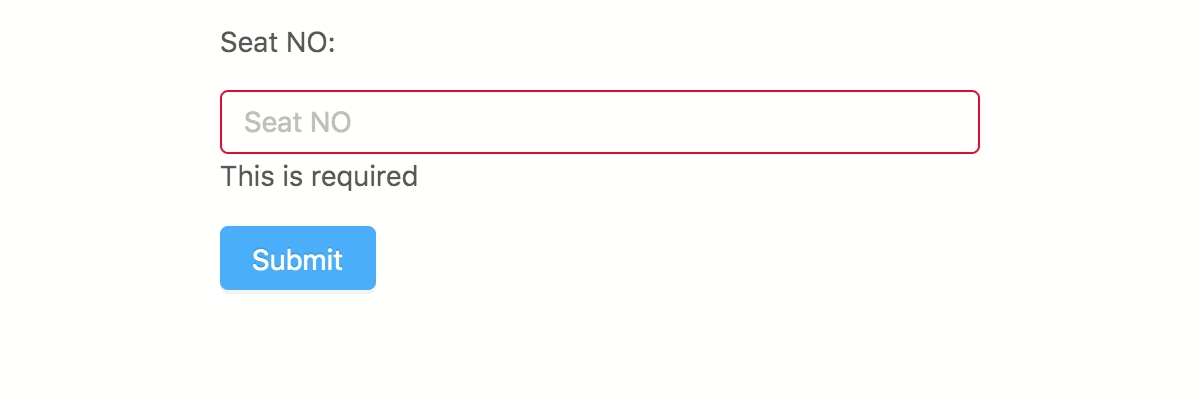
import v from 'v-rule' const validation = vconst result = validation// => { pass: false, messages: { seat: 'This is required' } }2
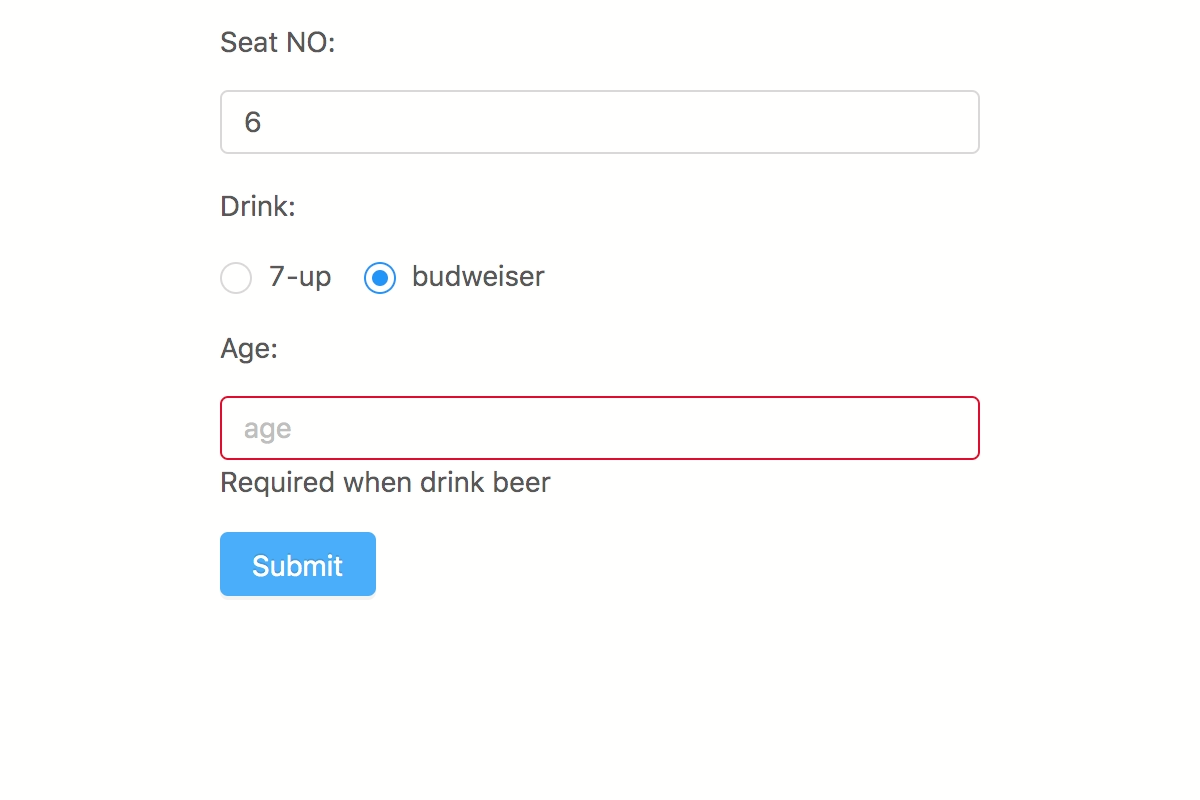
import v from 'v-rule' const validation = vconst result = validation// => { pass: false, messages: { age: 'Required when drink beer' } }3
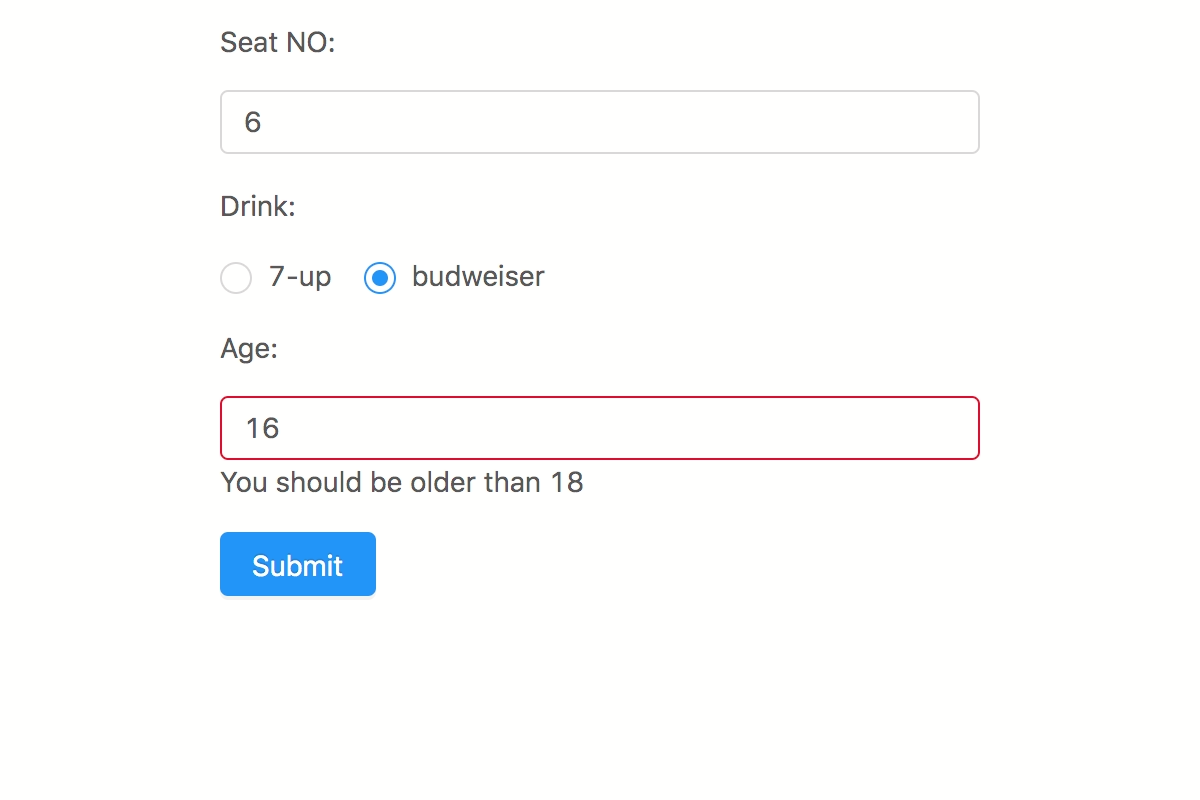
import v from 'v-rule' const validation = vconst result = validation// => { pass: false, messages: { age: 'You should be older than 18' } }4
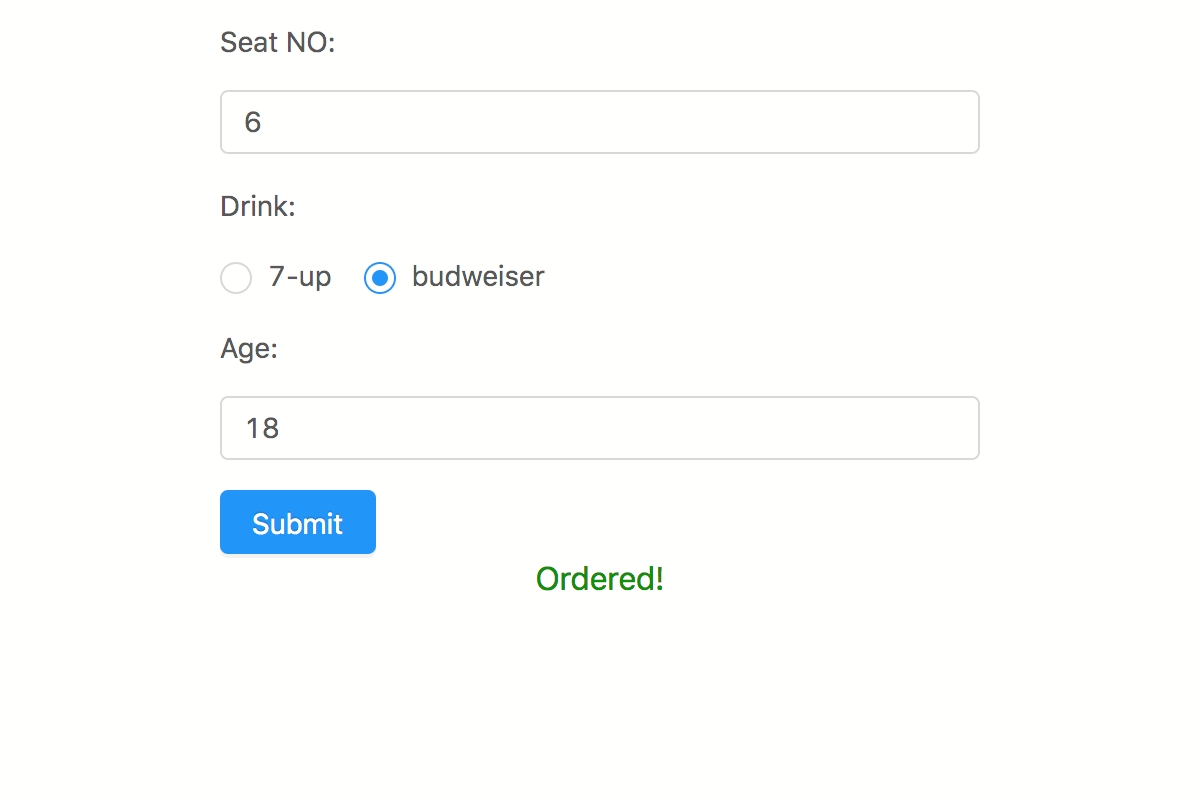
import v from 'v-rule' const validation = vconst result = validation// => { pass: true, messages: {} }Usage
Preset
import preset from 'v-rule' const v = const validation = vMulti rules
const validation = v const result = validation// => r { pass: false, messages: { age: 'should between min and max' } }Trigger another rule
const validation = v const context = age: '17'const result = validation// => { pass: false, messages: { age: 'age should be greater than 18' } }Test all rules
v.test only tests with available values in obj whereas testAllRules will default unavailable value to {key: undefined} and test against all rules. Use v.testAllRules when submit form.
const validation = vlet r = validation// => { pass: false, messages: { name: '', pwd: 'required' } }