react-xstate
Connecting react components with xstate state machine library.
Why?
react-xstate gives you easy access to xstate in the react world! ;)
Xstate allows you to improve state handling of your components by applying formal definition of a state machine including states and transitions. This allows you to better separate business logic from state handling and separate them into different files. You can use react-xstate to transition your UI-programming to model-driven-development which besides better code structure removes major error source and enables visual documentation.
The xstate library:
This library bases on the xstate by David Khourshid
- 📖 Read the documentation!
- Get inspired by 📽 the slides (🎥 video)
- Statecharts - A Visual Formalism for Complex Systems by David Harel
- Checkout xstate visualizer for graph generation by David Khourshid
React-xstate deepdive:
The xstate library implements the formal processing of state machines and leaves handling transitions, updating state and reducing actions to the user. This is where react-xstate comes into play and integrates state and transition handling directly into your react components, only by applying a state machine and action reducers and returning a xstate prop and a transition function. It also implements transition queueing to be able to fire transitions within action reducers.
Installation
npm install react-xstate --saveimport { mountXstate } from 'react-xstate'
Usage
Mount the xstate machine to your component by applying a machine definition and at least one actionReducer to your component.
AppExample
This simple state machine implements an easy to use statechart that transitions between ping and pong and when you click in state ping you will trigger the consoleLog action.
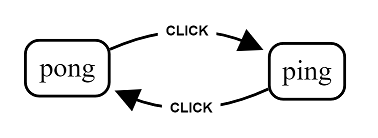
State Machine
const appMachine = initial: 'pending' states: ping: on: CLICK: pong: actions: 'consoleLog' pong: on: CLICK: 'ping' Action Reducer
const appReducer = { ifaction === 'consoleLog' console }Stateful Component
{ superprops; thishandleSubmit = thishandleSubmit; } { // See transition definition prop below thisprops } { const xstate: value: state = thisprops console return <button onClick=thishandleSubmit>Click</button> ; } appMachine appReducerAppAPI
withXstate(statechart, [actionReducer])(Component)
The withXstate higher-order component takes a statechart definition (see xstate), an array of actionReducers and a component.
It adds and exposes two new props to your component: transition and xstate.
actionReducer(action, event, xstate)
ActionReducers are functions that are mounted onto the state machine and called upon every action execution. Return should be an object that is passed through as additional state onto the xstate prop.
| Arg | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| action | string | Returns the current action called. |
| event | object | Additional payload of the transition triggering the action. |
| xstate | object | Access the xstate component itself to e.g. call transition from action. |
const reducer = { const transition = xstate ifaction === 'loadData' return loading: true }Props
transition(event): function
This function is hooked onto your components props and fires events towards your state machine. Expects an object with the event type and optionally and additional action payload that can be used by actionReducers to update the state.
{ thisprops}Queueing transitions
To enable transition chains by calling transition in action reducers we included a queued transition handling that queues transitions while there is already one transition happening.
xstate: object
This object exposes the state of the state machine, including action reduced state, to enable the user to build stateful component logic.
{ const xstate: value: state = thisprops return <div> <button>Send</button> state === 'loading' && <div>Loading...</div> </div> ;}