multigame
Multigame is a library, or perhaps more of a framework, to help you manage and build JavaScript multiplayer games. It takes care of connecting players and viewers (=spectators) to games and handles the communication between them. It runs on node.js.
There is a server part and a client part of the library. The client part exposes an object that acts a bit like a proxy for the game that runs on the server, that the client is connected to.
A multigame server can handle many games instances, of different game types, simultaneously. The WebSocket protocol is used to communicate between server and clients.
Games must be built using the framework to be able to be hosted on a multigame server.
Install
You need Node.js on your machine, then do:
npm install multigame --saveand in the client code:
The gameProxy.js file can be found under ./lib.
Usage
Writing a game
When writing a game, using this framework, you create a Rules object to be placed on the server. It shall implement the multigame's Rules interface and this is a place to put game logic. You should only need one Rules object for all your game instances (if they are of the same type that is). A Rule object should be stateless.
You will need a client part of your game too. The client part has access to a game proxy object, that is part of the framework. It takes care of the communication with the server. You decide where you want to put the game logic, server and/or client side.
Multigame Game and Player objects have a property called 'state'. It is empty from the start. A Game's 'state' is what is sent to all who are connected to a Game when there has been an update to the game's state (the notify() method has been called). If the client is a player it will also receive the state of the player object, that resides on the server and is associated with the client/socket.
You yourself fill the state properties with whatever that is relevant for your game. You can also add whatever you need to a Game or Player object (properties and methods), just remember that it is the 'state'-properties that are sent to clients.
A game that uses the framework is Tricker.
Setting up a multigame server
var http = ; // Get the multigame server "factory" functionvar GameServer = Server; // Get the verifyer objectvar verifyer = verifyer; // Create a HTTP servervar server = http;server; // Register domains from which connections should be acceptedverifyer; // Create a new multigame server using the "factory" functionvar multiServer = ;Setting up a new game
// Get the Manager "singleton"var Manager = Manager; // Get the Game constructor functionvar Game = Game; // Get a Rules object for the type of game you want to createvar TrickerRules = Rules; // Create a new game and register it with the Manager objectManager;Creating a player for a game
// Get the Player constructor functionvar Player = Player; // Create a Player objectvar player = socket; // Register the Player object with the gamegame;You might want to add additional properties and methods to the Player object.
Retrieving a specific game
// Get the Manager "singleton"var Manager = Manager; var game = Manager;Connect to a game
In the client code, you first need to register an object as an observer to the GameProxy object to receive server updates. The GameProxy object expects the object to have an update(state) method.
// Register the tricker client as an observer to GameProxy eventsGameProxy;Then connect to a game on the server:
// Connecting to a gameGameProxy;Overview
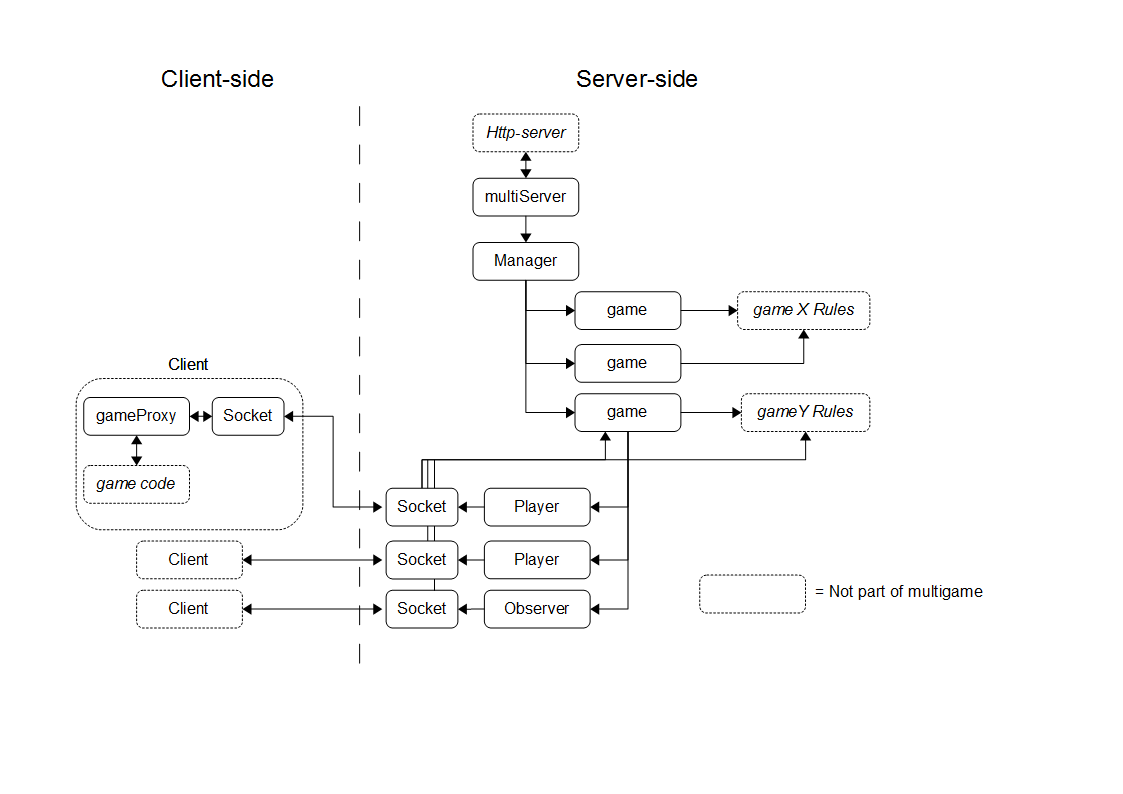
Protocol between server and client
Client generated events
- connection
- disconnect
- error (data: error)
- game_connect (data: game id)
- add_player
- add_observer
- msg (data: game specific event data)
Server generated events
- connect
- connect_error (data: error)
- error (data: error)
- disconnect (data: disconnect reason)
- state (data: game and possibly player state)
TODO
These are things that should be addressed:
- Remove socket.io dependency
- Be able to connect to a db for players/observers (?!)
- A better way to handle game and player states