Jupyter devinstall tool
Utility designed to simplify the installation of a Jupyter/IPython development environment.
Installation
Make sure you have iojs (and npm, which is included) installed on your machine, then run:
npm install -g jupyter-devinstall
(you may need to prefix the line with sudo)
Usage
Usage: jupyter-devinstall [options] <githubName> <installdir>
Options:
-h, --help output usage information
-P, --skip-pip skip pip projects
-N, --skip-npm skip npm projects
-r, --reinstall reinstall existing repositories, without recloning
--python [string] path of the python executable [python]
-o, --overwrite overwrite existing directories
-u, --upstream [string] name of the non-origin git remote [upstream]
-g, --global global install
-n, --no-install don't install
-U, --upstream-origin set the origin to point to upstream
-S, --ssh use SSH (git protocol) when setting up remotes
-s, --silent don't prompt the user for anything
-V, --version output the version number
Example for GitHub username jdfreder installed to the HOME directory:
jupyter-devinstall jdfreder ~/
Notes
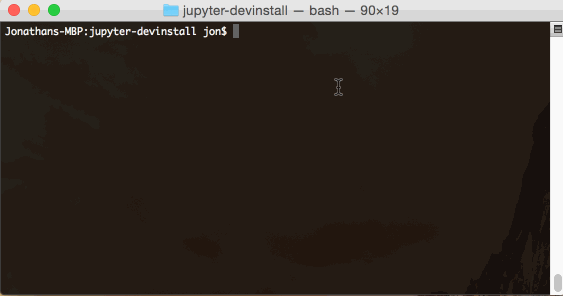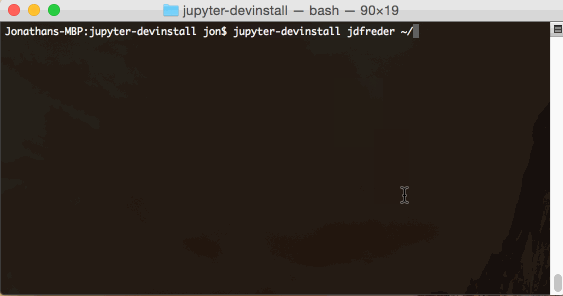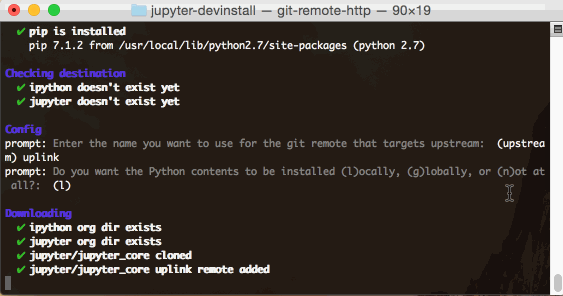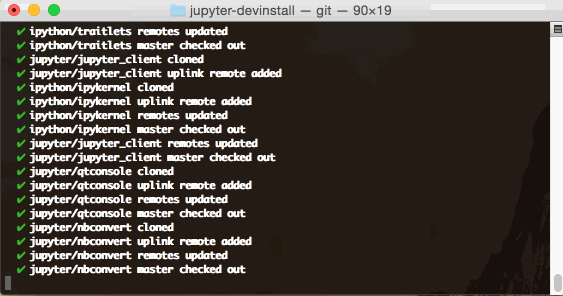
If you have not specified the --silent (-s for short) flag, part way through
the tool will behave like a wizard, prompting you for input.
The tool will ask you if you want to install locally, globally, or not at all:
- locally - pip install each repository
- globally - pip install each repository with the
-gflag. This may require sudo, which may have undesired side effects. - not at all - doesn't pip/npm install anything
Default workflow
The default workflow installed by this tool is that origin points to your fork
of the upstream repository. You can change this behavior by using the -U flag,
to force origin to point to the upstream repo. For example,
jupyter-devinstall jdfreder ~/ -U -u me
will setup the clones so origin points to the upstream repo and me points to
the forked repo (in the example this is in jdfreder).