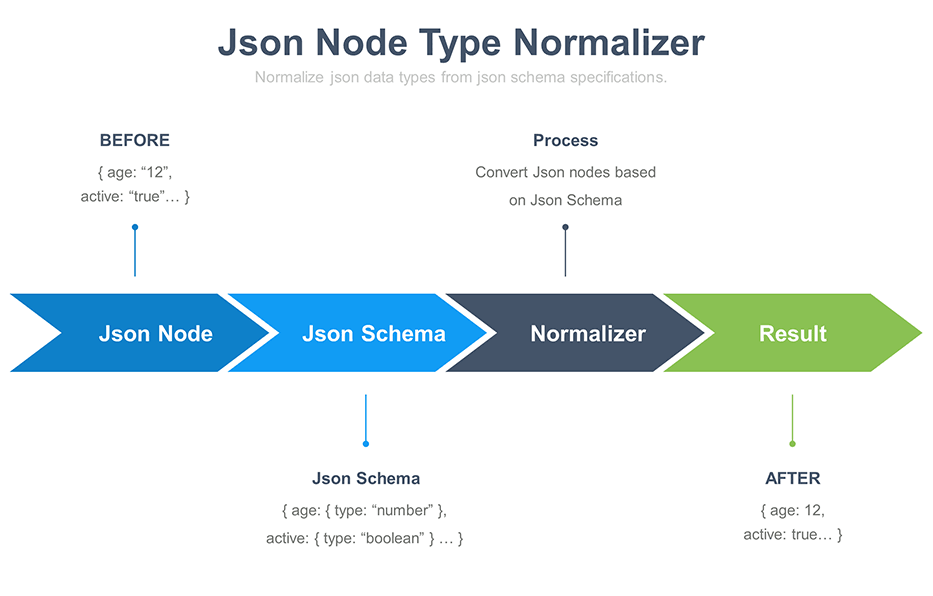
Json-Node-Normalizer
NodeJS module that normalize json data types from json schema specifications.
Features
- Convert / Cast Json Node type to another type :
- From Json Schema Specifications
- From Json Path
- Supported types :
string-
number,integer arraybooleannull
- Json Schema $Ref / Definitions support
Installation
Add the latest version of json-node-normalizer to your package.json:
npm install json-node-normalizer --saveNode.js Usage
const JsonNodeNormalizer = require('json-node-normalizer');
const normalizedJson = await JsonNodeNormalizer.normalize(jsonData, jsonSchema);Use case
We have a json object with incorrect type formats :
const jsonData = {
"fields":{
"id": 123, // Must be a string
"name":"my_name",
"firstName":"firstName",
"age": "31", // Must be a number
"phone": "33600000010", // Must be a number
"orders": [{
// Must contain a "label" fields with default value
"articles": { // Must be an array
"price": "15.4"
}
}],
"externalData": {
"id": "1234"
}, // Must be a null
"active": "true" // Must be a boolean
}
}We want to normalize json object to match with a Json Schema :
const jsonSchema = {
"fields":{
"type":"object",
"properties":{
"id":{
"type": "string"
},
"name":{
"type": "string"
},
"firstName":{
"type": "string"
},
"age":{
"type": "number"
},
"phone":{
"type": "integer"
},
"orders":{
"type": "array",
"items":{
"label":{
"type": "string",
"default": "Empty order"
},
"articles": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"price": { "type": "string" }
}
}
}
},
"externalData": {
"type": "null"
},
"active":{
"type": "boolean"
}
}
}
}We can use JsonNodeNormalizer to normalize our json data :
const JsonNodeNormalizer = require('json-node-normalizer');
const result = await JsonNodeNormalizer.normalize(jsonData, jsonSchema);Result :
result = {
"fields":{
"id": "123",
"name": "my_name",
"firstName": "firstName",
"age": 31,
"phone": 33600000010,
"orders":[{
"label": "Empty order",
"articles": [{
"price": "15.4"
}]
}],
"externalData": null,
"active": true
}
}Other Example
Code sample :
// Given
const dataToNormalize = {
data: {
enable: 'true' // MUST BE CONVERTED TO BOOLEAN
}
};
const jsonSchema = {
data: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
enable: {
type: 'boolean'
}
}
}
};
const result = await JsonNodeNormalizer.normalize(dataToNormalize, jsonSchema);Result :
result = {
"data":{
"enable": true
}
}You can find some other examples in 'tests' project folder.
Normalize node(s) from path (Without Json-Schema)
You can also use normalizePaths method if you do not want to use the schema json.
const { JsonNodeNormalizer, NodeTypes } = require('json-node-normalizer');
let normalizedJson = JsonNodeNormalizer.normalizePaths({ jsonNode: jsonData, paths: ['.fields.id'], type: NodeTypes.NUMBER_TYPE });
normalizedJson = JsonNodeNormalizer.normalizePaths({ jsonNode: jsonData, paths: ['.fields.orders'], type: NodeTypes.ARRAY_TYPE });
normalizedJson = JsonNodeNormalizer.normalizePaths({ jsonNode: jsonData, paths: ['.fields.orders[*].label'], type: NodeTypes.STRING_TYPE });
// You can also normalize each element with name 'active' for example...
normalizedJson = JsonNodeNormalizer.normalizePaths({ jsonNode: jsonData, paths: ['..active'], type: NodeTypes.BOOLEAN_TYPE });Set default node(s) value from path (Without Json-Schema)
You can also use normalizePaths method to set default value (if value doesn't exist).
const { JsonNodeNormalizer, NodeTypes } = require('json-node-normalizer');
let normalizedJson = JsonNodeNormalizer.normalizePaths({ jsonNode: jsonData, paths: ['.fields.orders[*].label'], type: NodeTypes.STRING_TYPE, defaultValue: 'Empty Order' });Play with Swagger 2 & Openapi 3 specification
In Swagger 2 and Openapi 3 specification, you can use $ref, allOf, anyOf, oneOf in definition of objects
If you want use a definition of object with this key words, you need flatter the definition like this:
const openapi_spec_flattered = JsonNodeNormalizer.oasFlatten(openapi_spec);
Example with a Swagger 2 specification:
cont openapi_spec = require('./docs/my-swagger.json');
openapi_spec_flattered = JsonNodeNormalizer.oasFlatten(openapi_spec);
...
jsonData = {
id: 1
name: 'Rex',
color: 'brown chocolate'
}
...
const normalizedJson = await JsonNodeNormalizer.normalize(jsonData, openapi_spec_flattered.definitions.Pet);
...
JsonPath Documentation
See https://github.com/json-path/JsonPath for more information about JsonPath expressions.
Logging Level
Logging is disabled by default (since 1.0.10).
To enable logging, you must define the JSON_NODE_NORMALIZER_DEBUG environment to true.
Log events can have different severity levels - in some cases, you just want to log events with at least a warning level, sometimes log lines have to be more verbose.
Each level is given a specific integer priority. The higher the priority the more important the message is considered to be.
| Level | Priority |
|---|---|
| debug | 4 |
| info (default) | 2 |
| error | 0 |
By default the logging level is set to 'info'.
You can override the logging level by setting the JSON_NODE_NORMALIZER_LOGGING_LEVEL environment variable.
JsonNodeNormalizer Configuration
For more specific usages, you can specify some configuration parameters when you use 'normalize' method :
Normalization type field name
Could be used in case that you want to use other field than 'type' to specify the target normalization type.
Code sample :
// Given
const dataToNormalize = {
data: {
enable: 'true' // MUST BE CONVERTED TO BOOLEAN
}
};
const jsonSchema = {
data: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
enable: {
normalization_type: 'boolean' // 'type' by default but in that case we want to use 'normalization_type'
}
}
}
};
const config = {
fieldNames: {
type: 'normalization_type' // Configure target normalization field name here !
}
};
const result = await JsonNodeNormalizer.normalize(dataToNormalize, jsonSchema, config);Result :
result = {
"data":{
"enable": true
}
}Exclude some fields
If you need to exclude some fields to be normalized, you can use the configuration variable excludePaths
Code sample :
// Given
const dataToNormalize = {
data: {
enable: 'true',
count: '72',
other: '12',
foo: 5414325,
},
};
const jsonSchema = {
data: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
enable: {
type: 'boolean',
},
count: {
type: 'number',
},
other: {
type: 'number',
},
foo: {
type: 'string',
format: 'date-time',
},
},
},
};
const config = {
excludePaths: [
{
path: '$.data.enable', // Exclude by field path
},
{
type: 'number', // Exclude by type
},
{
type: 'string', // Exclude by both type and format
format: 'date-time',
},
],
};
const result = await JsonNodeNormalizer.normalize(dataToNormalize, jsonSchema, config);Result :
result = {
data: {
enable: 'true',
count: '72',
other: '12',
foo: 5414325,
},
};Cache to increase performance
If your schema doesn't change between calls, you can enable cache to reduce process time.
Configuration variables :
{
useCache: true,
cacheId: "schemaId", // Schema identifier used to put/get schema from cache.
cacheDuration: 60000 // Cache duration in milliseconds
}Code sample :
// Given
const dataToNormalize = {
data: {
enable: 'true' // MUST BE CONVERTED TO BOOLEAN
}
};
const jsonSchema = {
schemaName: "mySchema",
data: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
enable: {
normalization_type: 'boolean' // 'type' by default but in that case we want to use 'normalization_type'
}
}
}
};
const config = {
fieldNames: {
useCache: true,
cacheId: "mySampleSchema",
cacheDuration: 60000 // 60 seconds
}
};
const result = await JsonNodeNormalizer.normalize(dataToNormalize, jsonSchema, config);Result :
result = {
"data":{
"enable": true
}
}Note :
You can use JsonNodeNormalizer.clearCache() to manually reset the library cache.