controlable-stream
Controlable Stream for NodeJS
What controllable-stream can do
- It is possible to measure the speed of the readable stream
- Speed of writable stream can be adjusted
- The strictness of the speed limit can be adjusted
Installation
npm i controlable-streamUsage example
- Base
import { ControlableStream } from 'controlable-stream'
readableStream
.pipe(new ControlableStream(100, 10))
// 100 - 100byte/sec
// 10 - Transmits 10 times per second
.pipe(writableStream)- Print every second
import { Readable } from 'stream'
import { ControlableStream } from 'controlable-stream'
Readable.from('abcdefghijk').pipe(new ControlableStream(1, 1)).pipe(process.stdout)
// a.. b.. c.. d.. ..... k- Read file and print
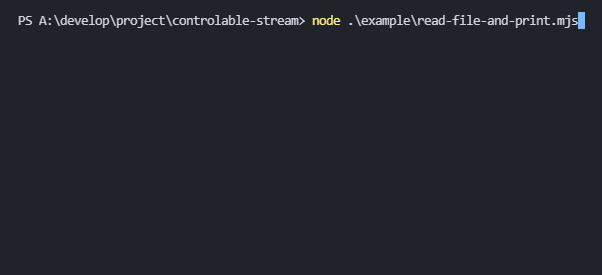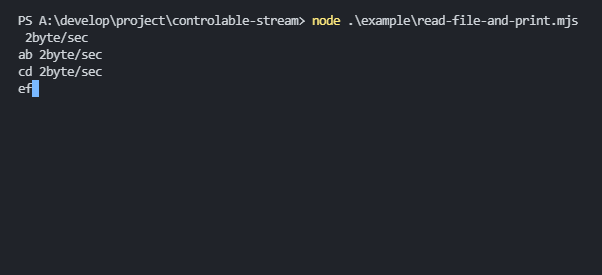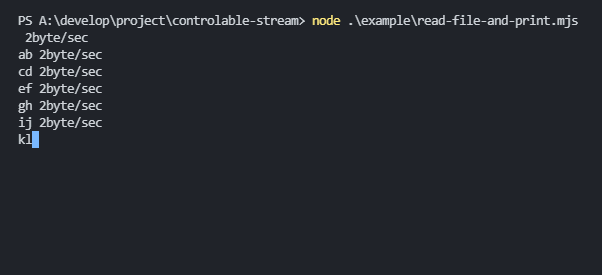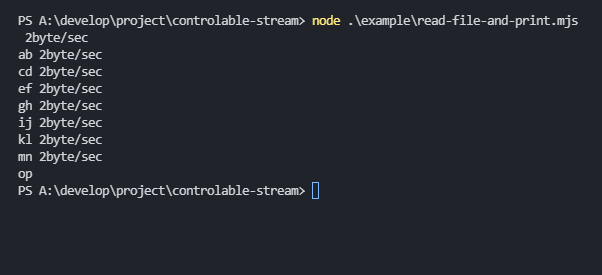
abcdefghijklmnopimport { ControlableStream } from "controlable-stream";
import { createReadStream } from "fs";
const cstream = new ControlableStream(2, 1)
cstream.setOnAddHistory((speed) => console.log(` ${speed}byte/sec`))
createReadStream('./example/test.txt').pipe(cstream).pipe(process.stdout)
// 2byte/sec
// ab 2byte/sec
// cd 2byte/sec
// ef 2byte/sec
// gh 2byte/sec
// ij 2byte/sec
// kl 2byte/sec
// mn 2byte/sec
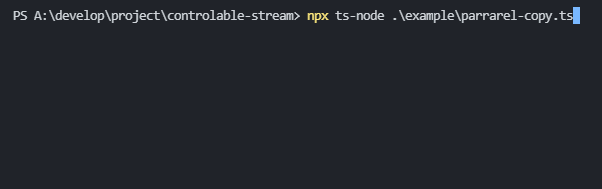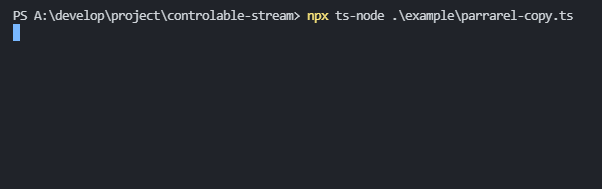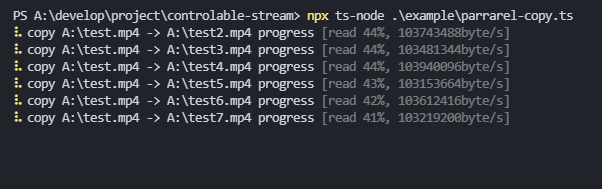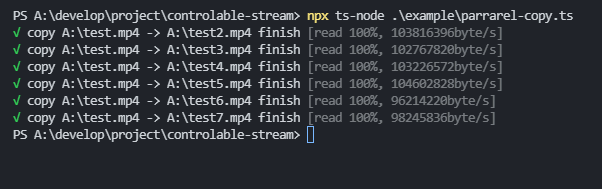
// op- parrarel copy
import { constants } from 'fs';
import { access, stat } from 'fs/promises';
import { createReadStream, createWriteStream } from 'fs';
import { finished } from 'stream/promises';
import { ControlableStream } from 'controlable-stream';
import task from 'tasuku';
function getFileStat(filePath: string) {
return access(filePath, constants.F_OK | constants.R_OK)
.then(() => stat(filePath))
.catch(() => null);
}
export function copy(filePath: string, destPath: string) {
const taskTitle = `copy ${filePath} -> ${destPath}`;
let percentage = 0;
return task(
`${taskTitle} start`,
async ({ setTitle, setStatus, setError }) => {
setTitle(`${taskTitle} progress`);
const fileStat = await getFileStat(filePath);
if (fileStat === null) {
return setError(`not accessable file = ${filePath}`);
}
const rStream = createReadStream(filePath);
const cStream = new ControlableStream(Infinity, 100); // no limit
const wStream = createWriteStream(destPath);
setStatus(`read ${percentage}%`);
cStream.setOnAddHistory((speed, historys) => {
const h = historys.at(-1);
const nowPercentage = Math.floor(
(cStream.getTotalByte() / fileStat.size) * 100
);
if (percentage !== nowPercentage) {
percentage = nowPercentage;
setStatus(`read ${percentage}%, ${speed}byte/s`);
}
});
rStream.pipe(cStream).pipe(wStream);
await finished(wStream).then(() => {
setTitle(`${taskTitle} finish`);
});
}
);
}
copy(`A:\\test.mp4`, `A:\\test2.mp4`);
copy(`A:\\test.mp4`, `A:\\test3.mp4`);
copy(`A:\\test.mp4`, `A:\\test4.mp4`);
copy(`A:\\test.mp4`, `A:\\test5.mp4`);
copy(`A:\\test.mp4`, `A:\\test6.mp4`);
copy(`A:\\test.mp4`, `A:\\test7.mp4`);API
Initialize the ControlableStream
const cStream = new ControlableStream(bytePerSec, numOfSendPerSec, limitStrict, transformOption)`Contructor Arguments
- bytePerSec: (0 ~ infinity)
- numOfSendPerSec: (0 < numOfSendPerSec < 1000), (numOfSendPerSec < bytePerSec)
- limitStrict: 0(never) | 1(seldom) | 2(rarely)
- transformOption: TransformOptions
ControlableStream.setOnSpeedChange(fn: OnSpeedChange | null): void
Execute OnSpeedChange function whenever speed changes
ControlableStream.setOnSpeedChange(fn)ControlableStream.setOnAddHistory(fn: onAddHistory | null): void
Executes onAddHistory function whenever a value is sent to the writable stream
ControlableStream.setOnAddHistory(fn: onAddHistory)ControlableStream.setBytePerSec(bytePerSec: number): void
ControlableStream.setBytePerSec(1000)ControlableStream.setNumOfSendPerSec(numOfSendPerSec: number): void
ControlableStream.setNumOfSendPerSec(100)ControlableStream.setLimitStrict(limitStrict: 0 | 1 | 2): void
ControlableStream.setLimitStrict(2)ControlableStream.calcByteForSend(): number
Calculate the number of bytes that can be transmitted at one time
ControlableStream.calcByteForSend()ControlableStream.calcTimeToSpend(length: number): number
Waiting time after sending to the writable stream at the currently limited speed
ControlableStream.calcTimeToSpend(buf.length)ControlableStream.getSpeed(): number
get last speed
ControlableStream.getSpeed()ControlableStream.getTotalByte(): number
total bytes read
ControlableStream.getTotalByte()License
MIT. Copyright (c) bishil06