Checkscripts
Half checklist, half script. Incremental automation of repetitive tasks made easy.
About
Inspired by Dan Slimmon's idea of "Do-nothing scripting", checkscripts allow you to programatically document a process. This gives the benefit of making the process easier to follow while allowing developers to incrementally automate it over time.
Getting Started
Install checkscripts as an npm module:
npm install -s checkscriptsExamples
Running a Checkscript
import { checkscript, step } from "checkscripts";
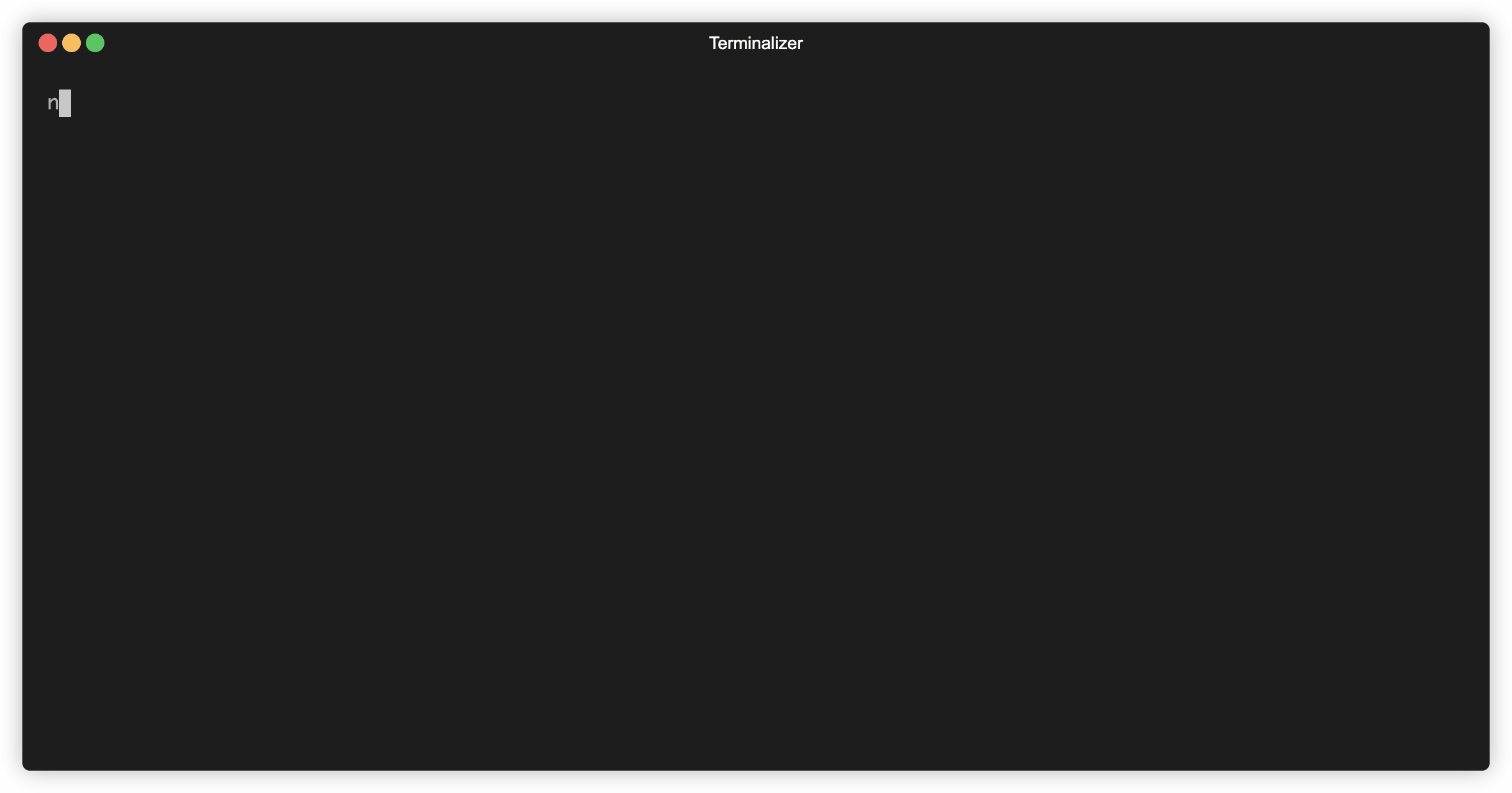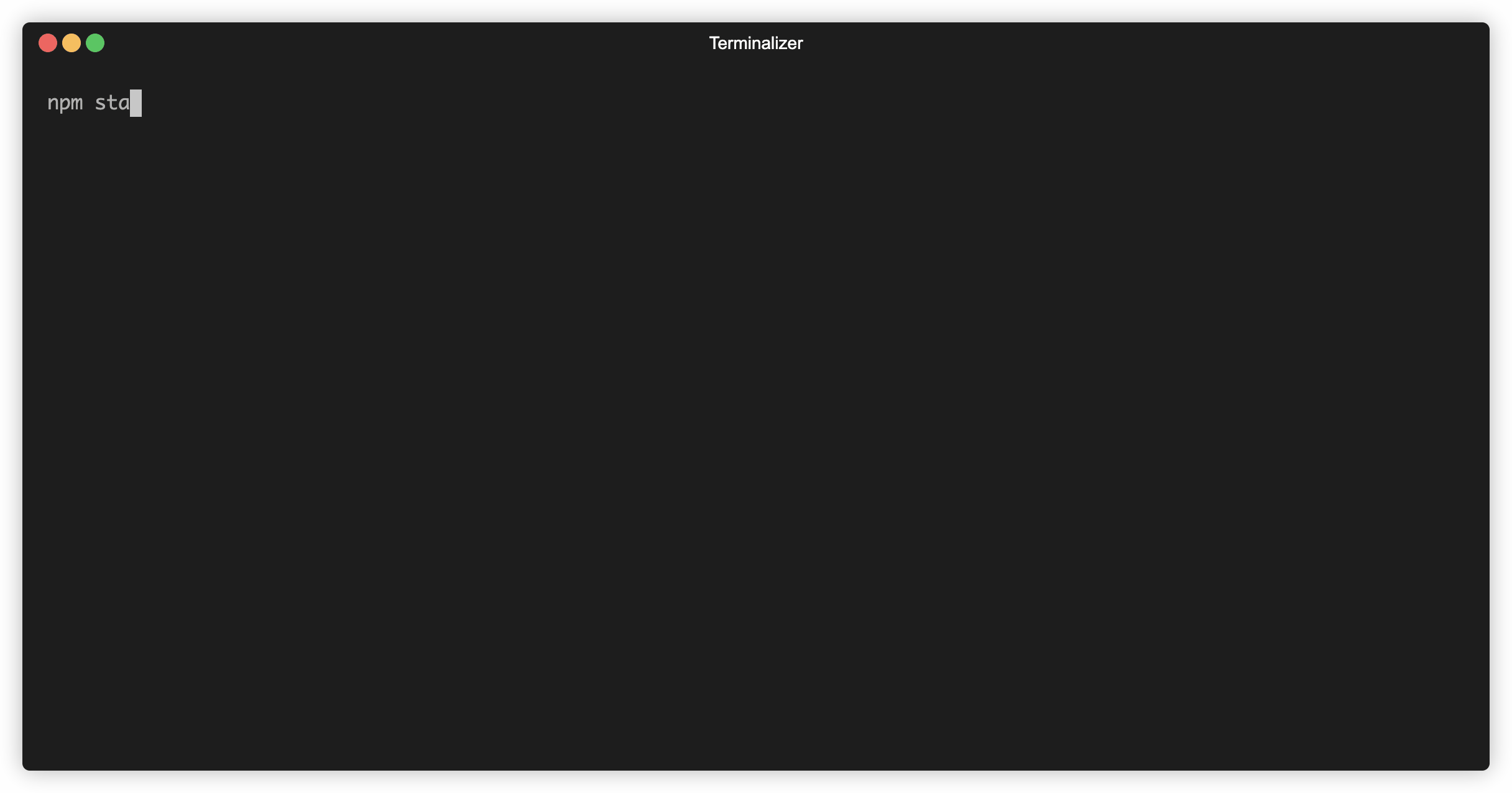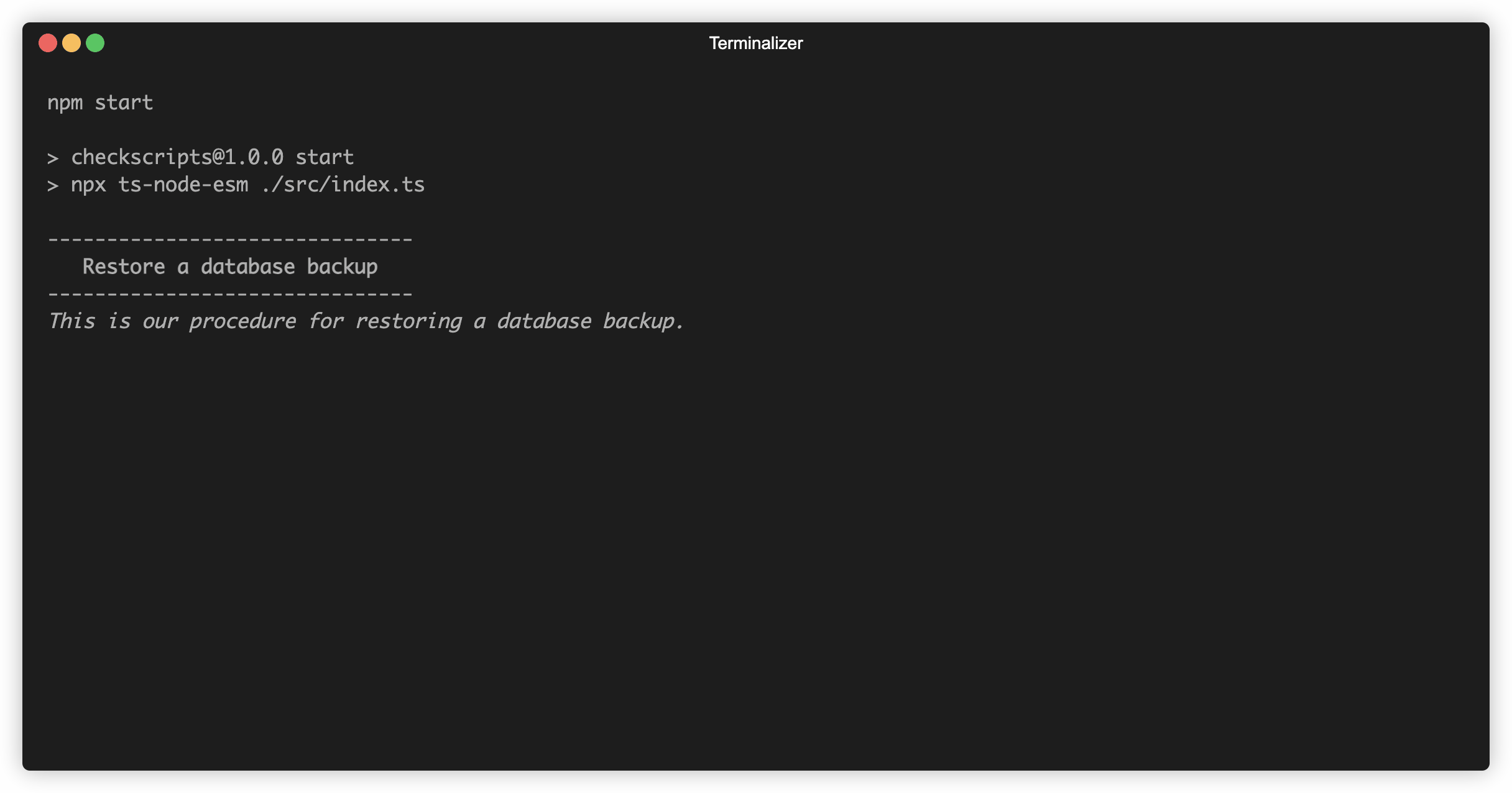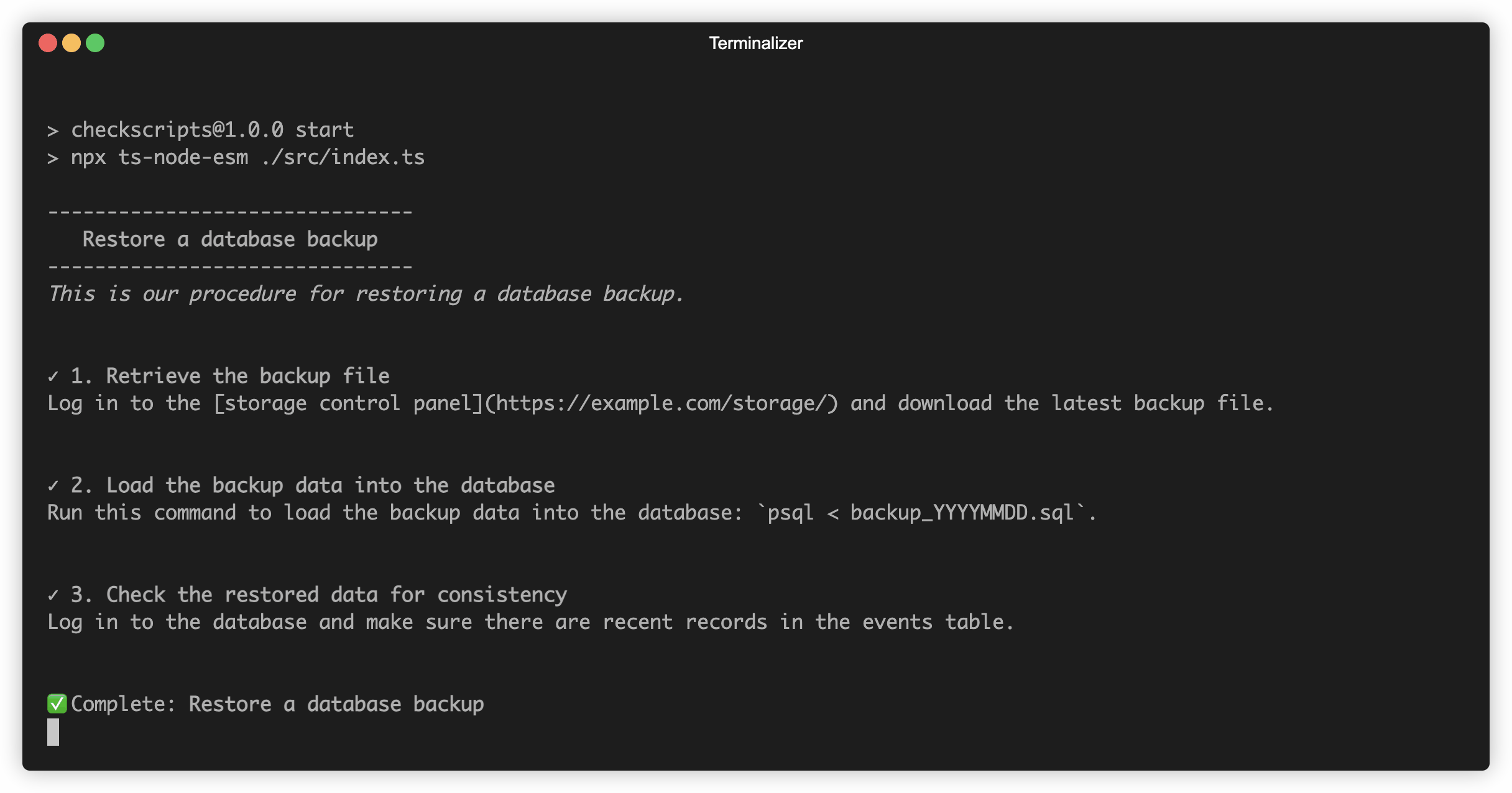
checkscript(
"Restore a database backup",
"This is our procedure for restoring a database backup."
)
.steps(
step(
"Retrieve the backup file",
"Log in to the [storage control panel](https://example.com/storage/) and download the latest backup file."
),
step(
"Load the backup data into the database",
"Run this command to load the backup data into the database: `psql < backup_YYYYMMDD.sql`."
),
step(
"Check the restored data for consistency",
"Log in to the database and make sure there are recent records in the events table."
),
)
.run();Running this looks like:
Once a step has been automated, it can be turned into a function:
import { checkscript, step } from "checkscripts";
interface ExampleContext {
backupFilePath: string | undefined;
}
checkscript<ExampleContext>(
"Restore a database backup",
"This is our procedure for restoring a database backup."
)
.steps(
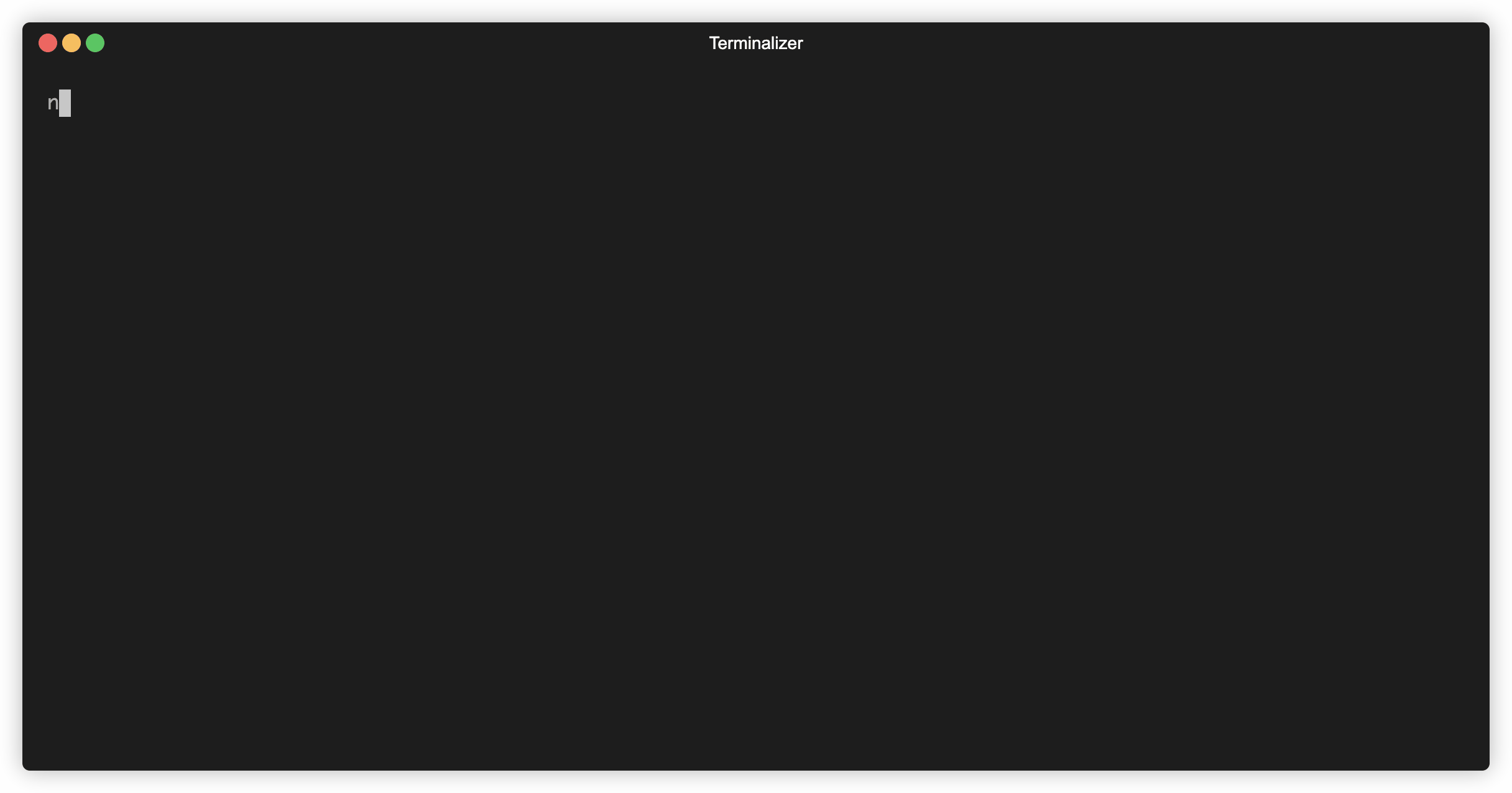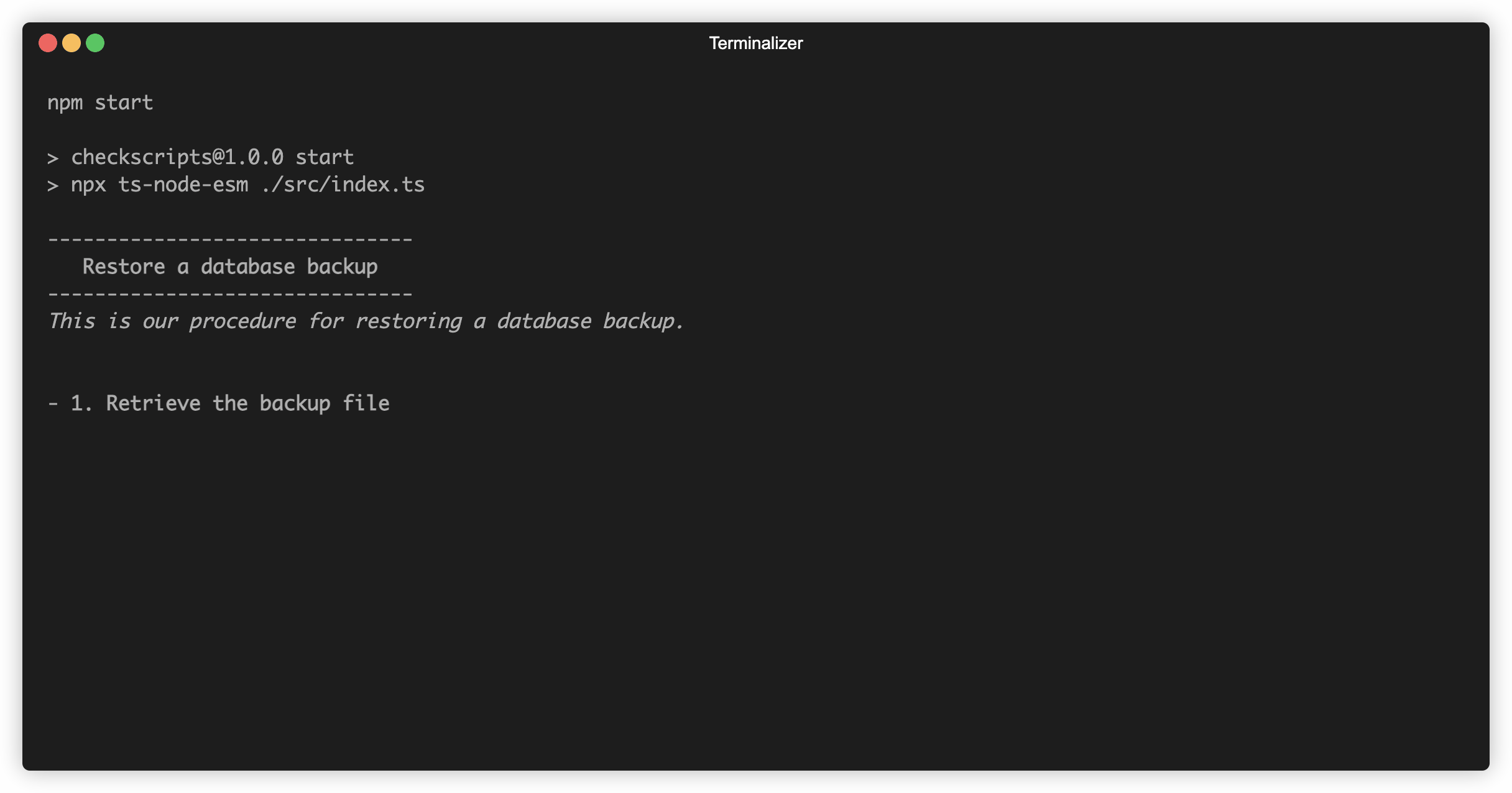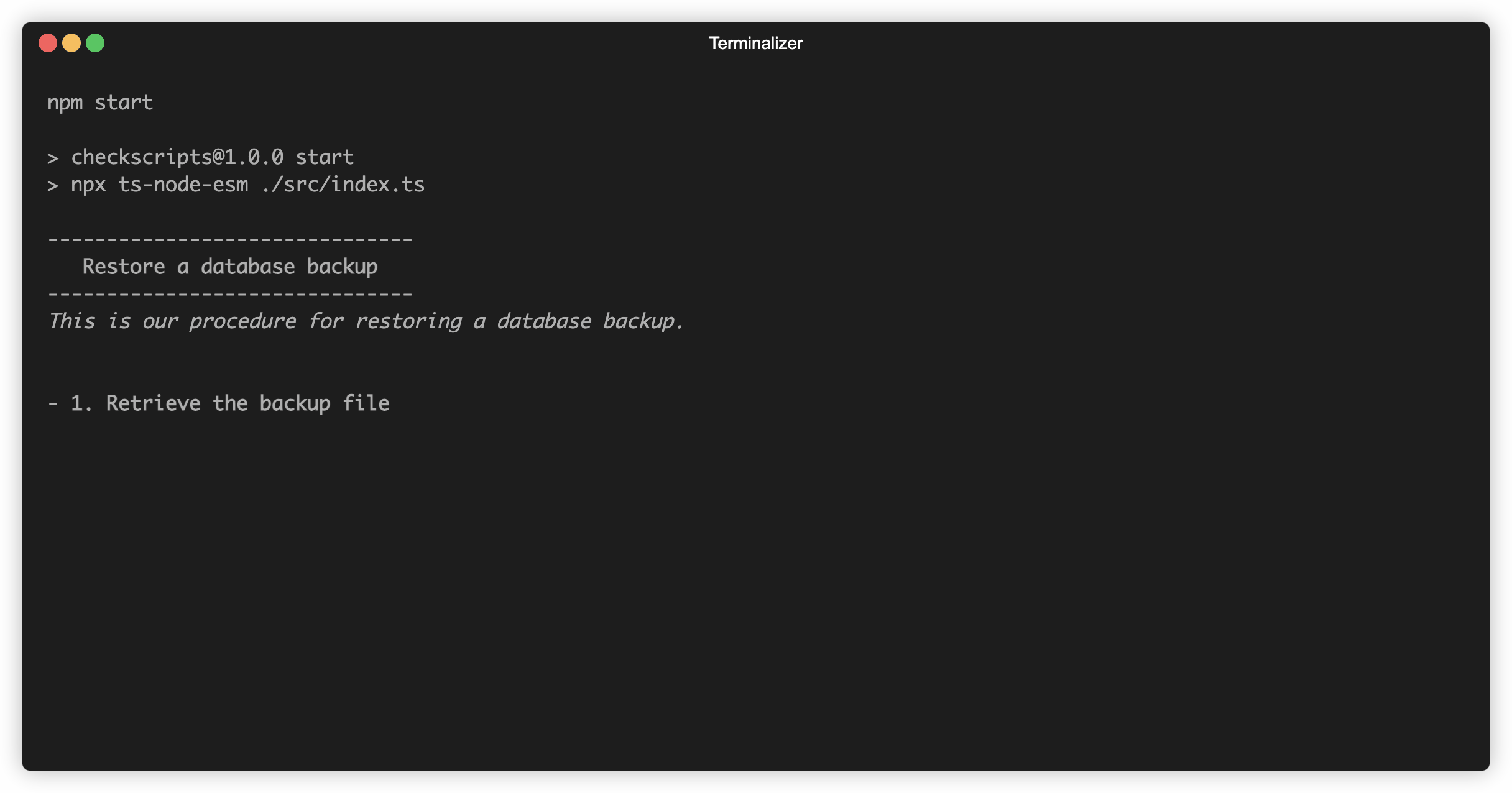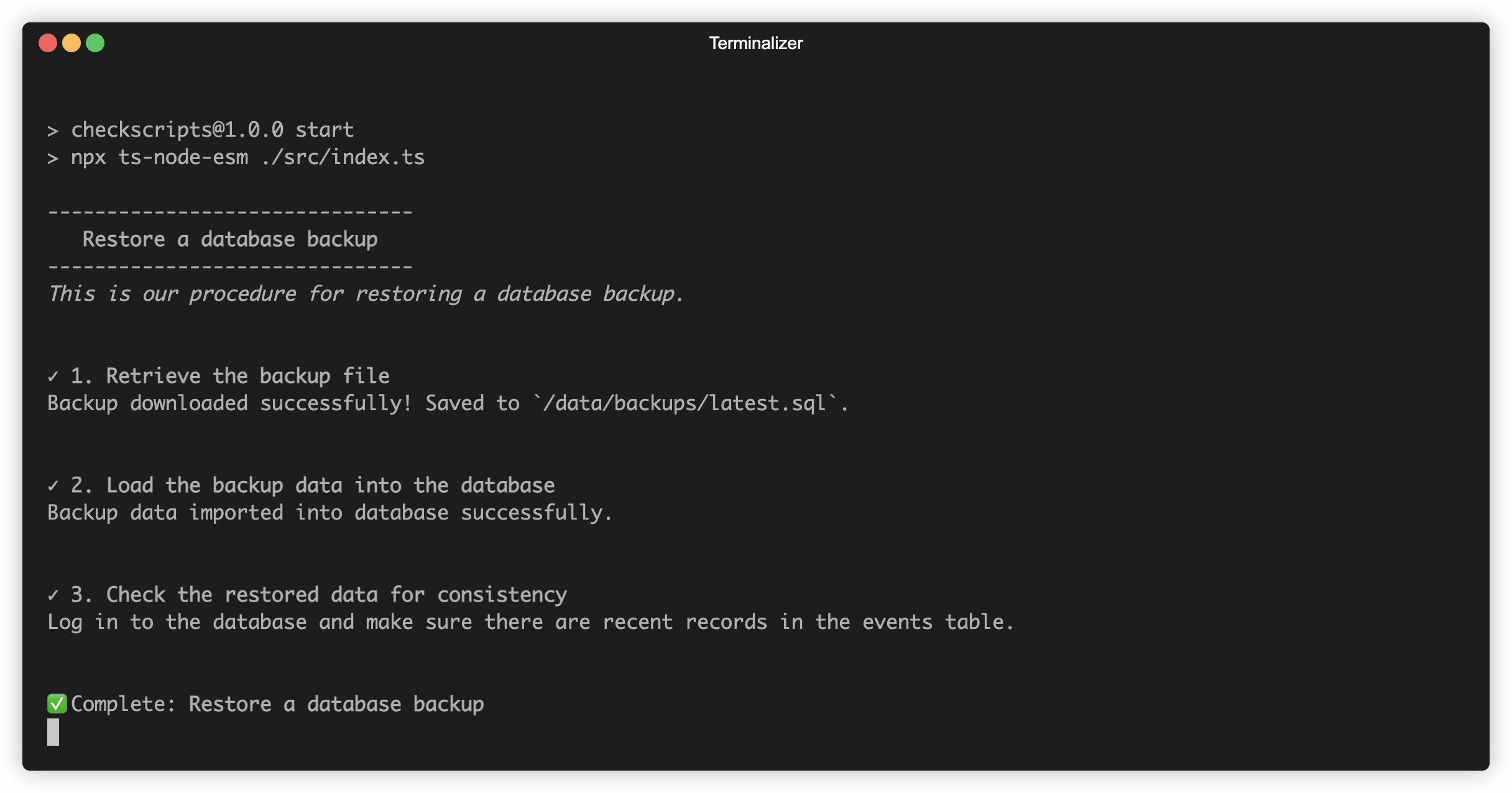
step("Retrieve the backup file", async (context) => {
const file = await fakeApiCall();
const path = await saveFile(file);
context.backupFilePath = path;
return `Backup downloaded successfully! Saved to \`${context.backupFilePath}\`.`;
}),
step("Load the backup data into the database", async (context) => {
if (!context.backupFilePath) throw new Error("No backup file found");
await importDataFromFile(context.backupFilePath);
return "Backup data imported into database successfully.";
}),
step(
"Check the restored data for consistency",
"Log in to the database and make sure there are recent records in the events table."
)
)
.run();and when this is run:
Documenting a Checkscript
A checkscript can be output as markdown, by calling document() instead of run(). Demonstrated with the original example:
import { checkscript, step } from "checkscripts";
checkscript(
"Restore a database backup",
"This is our procedure for restoring a database backup."
)
.steps(
step(
"Retrieve the backup file",
"Log in to the [storage control panel](https://example.com/storage/) and download the latest backup file."
),
step(
"Load the backup data into the database",
"Run this command to load the backup data into the database: `psql < backup_YYYYMMDD.sql`."
),
step(
"Check the restored data for consistency",
"Log in to the database and make sure there are recent records in the events table."
),
)
.document();The output will be:
# Restore a database backup
_This is our procedure for restoring a database backup._
## 1. Retrieve the backup file
Log in to the [storage control panel](https://example.com/storage/) and download the latest backup file.
## 2. Load the backup data into the database
Run this command to load the backup data into the database: `psql < backup_YYYYMMDD.sql`.
## 3. Check the restored data for consistency
Log in to the database and make sure there are recent records in the events table.
---
_This document is a [checkscript](https://github.com/gbannerman/checkscripts). It can be run using JavaScript._