[!NOTE] This is one of 192 standalone projects, maintained as part of the @thi.ng/umbrella monorepo and anti-framework.
🚀 Please help me to work full-time on these projects by sponsoring me on GitHub. Thank you! ❤️
Datetime types, relative dates, math, iterators, composable formatters, locales.
STABLE - used in production
Search or submit any issues for this package
yarn add @thi.ng/dateESM import:
import * as date from "@thi.ng/date";Browser ESM import:
<script type="module" src="https://esm.run/@thi.ng/date"></script>For Node.js REPL:
const date = await import("@thi.ng/date");Package sizes (brotli'd, pre-treeshake): ESM: 5.43 KB
Several projects in this repo's /examples directory are using this package:
| Screenshot | Description | Live demo | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Heatmap visualization of this mono-repo's commits | Source | |
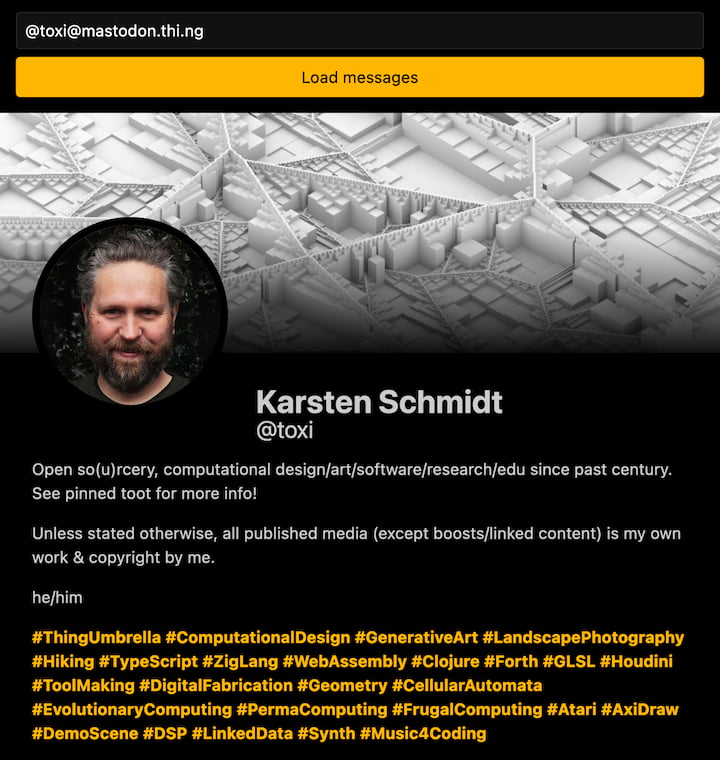 |
Mastodon API feed reader with support for different media types, fullscreen media modal, HTML rewriting | Demo | Source |
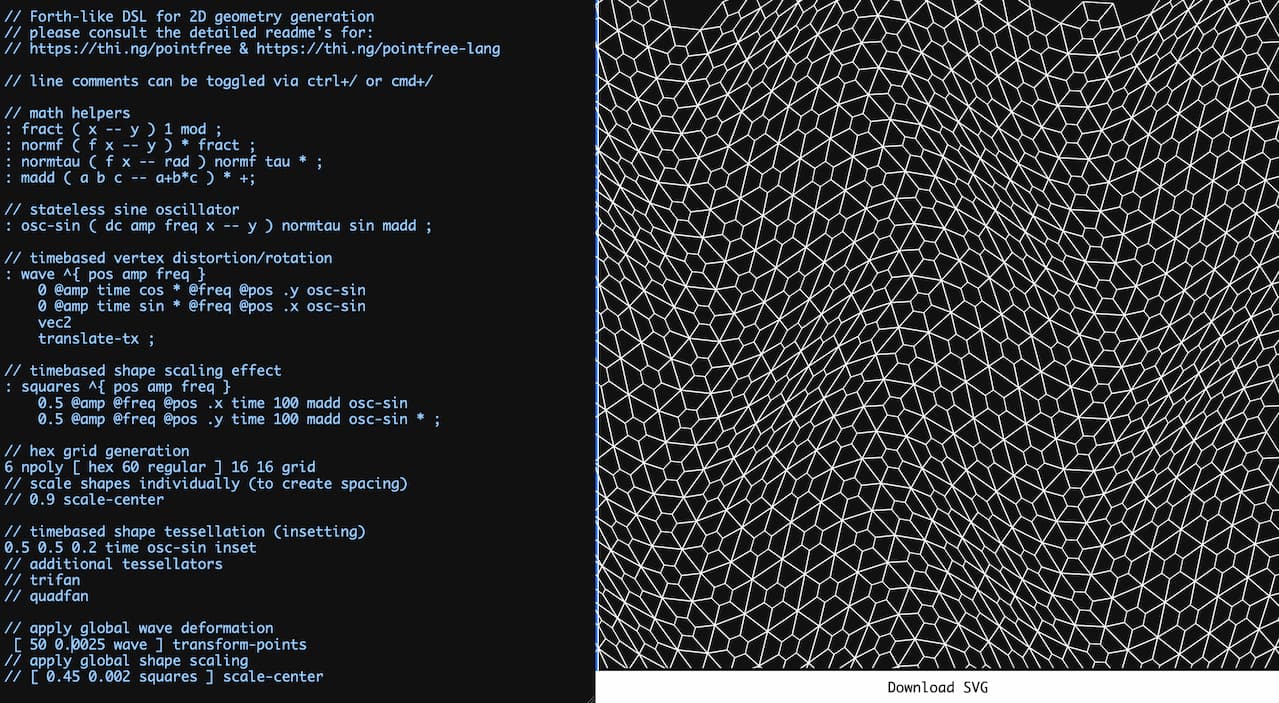 |
Live coding playground for 2D geometry generation using @thi.ng/pointfree-lang | Demo | Source |
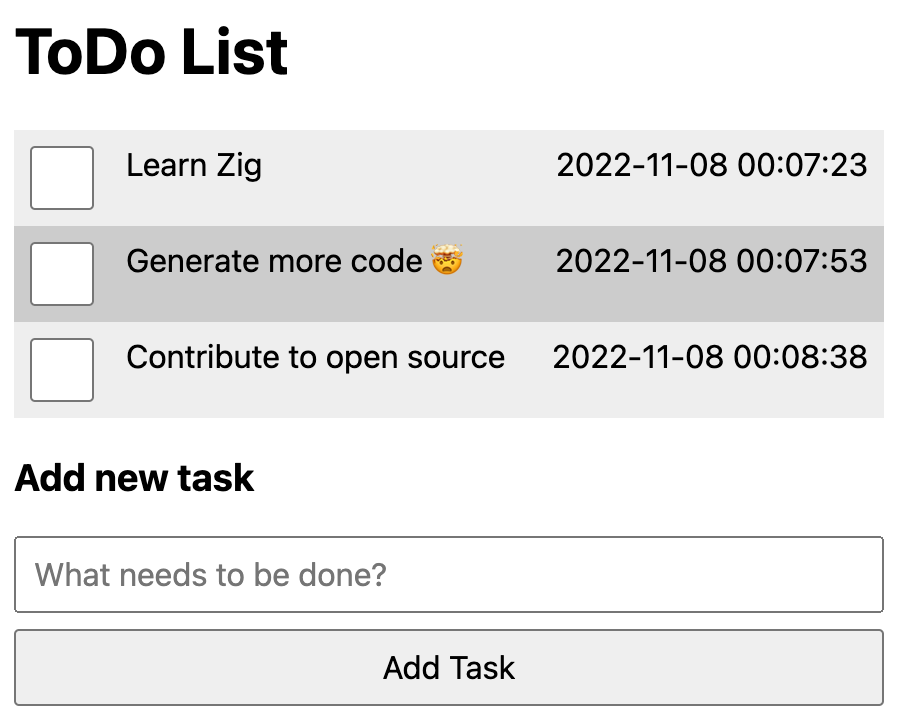 |
Zig-based To-Do list, DOM creation, local storage task persistence | Demo | Source |
TODO - Please see tests and doc strings in source for now...
The DateTime class acts as a thin wrapper around UTC epochs/timestamps,
with the constructor supporting coercions and varying granularity/precision
(from years to milliseconds). Default precision is milliseconds.
| Key | Precision |
|---|---|
y |
Year |
M |
Month |
d |
Day |
h |
Hour |
m |
Minute |
s |
Second |
t |
Millisecond |
Note: DateTime instances also define the above keys as properties, plus
getters for week-in-year (.w) and quarter (.q).
import { dateTime } from "@thi.ng/date";
// create w/ current date (or pass epoch, string, Date or DateTime instances)
const a = dateTime();
// DateTime { y: 2020, M: 8, d: 19, h: 12, m: 17, s: 16, t: 884 }
// provide additional precision (here year only)
const b = dateTime(a, "y");
// or
const b = a.withPrecision("y")
// DateTime { y: 2020, M: 0, d: 1, h: 0, m: 0, s: 0, t: 0 }
a.toString();
// Sat Sep 19 2020 12:17:16 GMT'
a.toISOString()
// '2020-09-19T12:17:16.884Z'
b.toISOString();
// 2020-01-01T00:00:00.000Z
a.isLeapYear()
// true
a.daysInMonth()
// 30
a.dayInYear()
// 263
a.weekInYear()
// 38
a.isAfter(b)
// true\
b.isBefore(a)
// trueDateTime instances support basic math to derive future/past instances, given an
offset period. Period identifiers are any Precision ID (see above) or w
(week, aka 7 days) or q (quarter, aka 3 months):
import { dateTime, difference, absDifference, asDays } from "@thi.ng/date";
const a = dateTime();
// DateTime { y: 2020, M: 8, d: 19, h: 12, m: 17, s: 16, t: 884 }
// create new instance 61 seconds in the future
// any `Period` ID can be used
a.add(61, "s")
// DateTime { y: 2020, M: 8, d: 19, h: 12, m: 18, s: 17, t: 884 }
// ...or 90 days ago
a.add(-90, "d")
// DateTime { y: 2020, M: 5, d: 21, h: 12, m: 17, s: 16, t: 884 }
// ...or 2 quarters (aka 2x 3 months) ahead of time
a.add(2, "q").toISOString()
// "2021-03-19T12:17:16.884Z"
// check for equivalence
a.equiv("2020-09-19T12:17:16.884Z")
// true
// are dates equal (with tolerance of ±100 ms)
a.eqDelta(a.add(99, "t"), 100)
// true
a.compare(a.add(1, "s"))
// -1000
// compute (signed) difference between dates (in milliseconds)
difference(a, "1970-01-01") === a.getTime()
// true
// difference = a - b
difference("2020-02", "2021-02")
// -31622400000
// always produces unsigned result
absDifference("2020-02", "2021-02")
// 31622400000
// compute abs difference in days
asDays(absDifference("2020-02", "2021-02"))
// 366 (because 2020 was a leap year)Several iterators are provided to produce timestamps of various granularities between two given dates. Originally, these were intended for visualization purposes (i.e. as axis tick label generators for @thi.ng/viz).
years()querters()months()weeks()days()hours()minutes()seconds()milliseconds()
import { months, FMT_yyyyMMdd } from "@thi.ng/date";
[...months("2021-01-03", "2021-07-16")]
// [
// 1609459200000,
// 1612137600000,
// 1614556800000,
// 1617235200000,
// 1619827200000,
// 1622505600000,
// 1625097600000
// ]
[...months("2021-01-03", "2021-07-16")].map((x) => FMT_yyyyMMdd(x))
// [
// '2021-02-01',
// '2021-03-01',
// '2021-04-01',
// '2021-05-01',
// '2021-06-01',
// '2021-07-01'
// ]Relative dates can be obtained via
parseRelative()
or relative().
import { dateTime, parseRelative } from "@thi.ng/date";
const now = dateTime();
// DateTime { y: 2021, M: 2, d: 21, h: 14, m: 26, s: 0, t: 661 }
// see the linked documentation for all supported formats
parseRelative("2 weeks ago", now);
// DateTime { y: 2021, M: 2, d: 7, h: 14, m: 26, s: 0, t: 661 }
parseRelative("an hour", now);
// DateTime { y: 2021, M: 2, d: 21, h: 15, m: 26, s: 0, t: 661 }
parseRelative("tomorrow", now);
// DateTime { y: 2021, M: 2, d: 22, h: 14, m: 26, s: 0, t: 661 }
parseRelative("-1 month", now)
// DateTime { y: 2021, M: 1, d: 21, h: 14, m: 26, s: 0, t: 661 }Dates can be formatted as relative descriptions using
formatRelative()
and
formatRelativeParts().
Both functions use the currently active locale and accept an
optional reference date (default: now()).
import {
setLocale, withLocale, DE_LONG, EN_LONG,
formatRelative, formatRelativeParts, formatDuration,
decomposeDifference
} from "@thi.ng/date";
setLocale(EN_LONG);
formatRelative("2020-06-01", "2021-07-01")
// "1 year ago"
formatRelative("2020-08-01", "2021-07-01")
// "11 months ago"
formatRelative("2021-07-01 13:45", "2021-07-01 12:05")
// "in 2 hours"
formatRelative("2021-07-01 12:23:24", "2021-07-01 12:05")
// "in 18 minutes"
// with default precision (seconds)
formatRelativeParts("2012-12-25 17:59:34", "2021-07-16 12:05")
// "8 years, 6 months, 21 days, 17 hours, 5 minutes, 26 seconds ago"
// with day precision
formatRelativeParts("2012-12-25 17:59:34", "2021-07-16 12:05", "d")
// "8 years, 6 months, 22 days ago"
// with month precision
formatRelativeParts("2012-12-25 17:59:34", "2021-07-16 12:05", "M")
// "8 years, 7 months ago"
formatRelativeParts("2021-07-16", "2021-01-01", "y")
// "in less than 1 year"
// with locale DE_LONG
withLocale(DE_LONG, () => formatRelativeParts("2020-01-01 12:34"))
// "vor 1 Jahr, 6 Monaten, 15 Tagen, 23 Stunden, 38 Minuten, 9 Sekunden"
// obtain the relative parts in raw form
// returns tuple of: [sign, years, months, days, hours, mins, secs, millis]
decomposeDifference("2020-01-01 12:34", Date.now())
// [-1, 1, 6, 15, 23, 38, 9, 703]
// format a duration (in ms), optionally with given precision
formatDuration(45296000)
// "12 h, 34 min, 56 s"
formatDuration(45296000, "h")
// "13 h"
formatDuration(45296000,"d")
// "< 1 d"Custom date/time formatters can be assembled via
defFormat(),
using the following partial format identifiers. The MMM and E formatters use
the currently active locale. To escape a formatter and use as a
string literal, prefix the term with \\.
| ID | Description |
|---|---|
yy |
Short year (2 digits) |
yyyy |
Full year (4 digits) |
M |
Unpadded month |
MM |
Zero-padded 2-digit month |
MMM |
Month name in current locale (e.g. Feb) |
d |
Unpadded day of month |
dd |
Zero-padded 2-digit day of month |
E |
Weekday name in current locale (e.g. Mon) |
w |
Unpadded week-in-year (ISO8601) |
ww |
Zero-padded 2-digit week-in-year (ISO8601) |
q |
Unpadded quarter |
H |
Unpadded hour of day (0-23) |
HH |
Zero-padded 2-digit hour of day (0-23) |
h |
Unpadded hour of day (1-12) |
m |
Unpadded minute of hour |
mm |
Zero-padded 2-digit minute of hour |
s |
Unpadded second of minute |
ss |
Zero-padded 2-digit second of minute |
S |
Unpadded millisecond of second |
SS |
Zero-padded 3-digit millisecond of second |
A |
12-hour AM/PM marker (uppercase) |
a |
12-hour am/pm marker (lowercase) |
Z |
Timezone offset in signed ±HH:mm format |
ZZ |
Same as Z, but special handling for UTC |
/ED |
Locale-specific weekday-day separator |
/DM |
Locale-specific day-month separator |
/MY |
Locale-specific month-year separator |
/HM |
Locale-specific hour-minute separator |
(Format IDs somewhat based on Java's SimpleDateFormat)
The following preset formatters are available:
-
FMT_ISO-"2020-09-13T21:42:07.123Z" -
FMT_ISO_SHORT-"2020-09-13T21:42:07Z" -
FMT_yyyyMMdd-"2020-09-13" -
FMT_yyyyMMdd_ALT-"20200913" -
FMT_Mdyyyy-"9/13/2020" -
FMT_MMMdyyyy-"Sep 13 2020" -
FMT_dMyyyy-"13/9/2020" -
FMT_dMMMyyyy-"13 Sep 2020" -
FMT_yyyyMMdd_HHmmss-20200913-214207 -
FMT_HHmm-"21:42" -
FMT_hm-"9:42 PM" -
FMT_HHmmss-"21:42:07" -
FMT_HHmmss_ALT-"214207" -
FMT_hms-"9:42:07 PM" -
FMT_yyyy-"2020"(4 digit year) -
FMT_MM-"12"(2 digit month) -
FMT_ww-"52"(2 digit week) -
FMT_dd-"28"(2 digit day in month) -
FMT_HH-"23"(2 digit hour, 24h system) -
FMT_mm-"59"(2 digit minute) -
FMT_ss-"01"(2 digit second)
All formatters are fully composable/nestable, i.e. new formats can be created using existing formats like so:
import { defFormat, FMT_HHmmss, FMT_yyyyMMdd } from "@thi.ng/date";
defFormat([FMT_yyyyMMdd, " @ ", FMT_HHmmss])();
// "2024-02-28 @ 12:05:47"For timebased media applications, the higher-order defTimecode() can be used
to create a formatter for a given FPS (frames / second, in [1..1000] range),
e.g. HH:mm:ss:ff. The returned function takes a single arg (time in
milliseconds) and returns formatted string.
The timecode considers days too, but only includes them in the result if the day
part is non-zero. The 4 separators between each field can be customized via 2nd
arg (default: all :).
import { defTimecode, DAY, HOUR, MINUTE, SECOND } from "@thi.ng/date";
const a = defTimecode(30);
a(1*HOUR + 2*MINUTE + 3*SECOND + 4*1000/30)
// "01:02:03:04"
a(DAY);
// "01:00:00:00:00"
const b = defTimecode(30, ["d ", "h ", "' ", '" ']);
b(DAY + HOUR + 2*MINUTE + 3*SECOND + 999)
// "01d 01h 02' 03" 29"The following locale presets are available by default:
| Preset | Example |
|---|---|
DE_SHORT |
29.6.2021 @ 5:48 |
DE_LONG |
Dienstag, 29. Juni 2021 @ 5:48 |
EN_SHORT |
29/06/2021 @ 5.48 am |
EN_LONG |
Tuesday 29 June 2021 @ 5.48 am |
ES_LONG |
martes 29 junio 2021 @ 5:48 |
FR_LONG |
mardi 29 juin 2021 @ 5h 48 |
IT_LONG |
martedì 29 giugno 2021 @ 5.48 |
The MMM (month) and E (weekday) formatters make use of the strings provided
by the current LOCALE (default: EN_SHORT) and can be set/changed via the
setLocale() function:
import {
dateTime, defFormat, setLocale,
EN_SHORT, EN_LONG
} from "@thi.ng/date";
const fmt = defFormat(["E", " ", "d", " ", "MMM", " ", "yyyy"]);
setLocale(EN_SHORT); // also the default
// {
// months: [
// 'Jan', 'Feb', 'Mar', 'Apr', 'May', 'Jun',
// 'Jul', 'Aug', 'Sep', 'Oct', 'Nov', 'Dec'
// ],
// days: [ 'Sun', 'Mon', 'Tue', 'Wed', 'Thu', 'Fri', 'Sat' ]
// }
fmt(dateTime());
// Sat 19 Sep 2020
setLocale(EN_LONG);
fmt(dateTime());
// Saturday 19 September 2020Use withLocale()
to only temporarily set a locale and execute a function with it, then
automatically restoring the currently active locale.
import { dateTime, withLocale, FR_LONG } from "@thi.ng/date";
fmt(dateTime());
// 'Fri 16 Jul 2021'
withLocale(FR_LONG, () => fmt(dateTime()));
// 'vendredi 16 juillet 2021'
fmt(dateTime());
// 'Fri 16 Jul 2021'If this project contributes to an academic publication, please cite it as:
@misc{thing-date,
title = "@thi.ng/date",
author = "Karsten Schmidt",
note = "https://thi.ng/date",
year = 2020
}© 2020 - 2024 Karsten Schmidt // Apache License 2.0




