integrate-adaptive-simpson
Compute a definite integral of one variable using Simpson's Rule with adaptive quadrature
Introduction
This module computes the definite integral
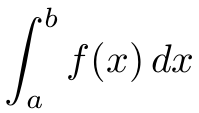
Install
$ npm install integrate-adaptive-simpsonExample
To compute the definite integral
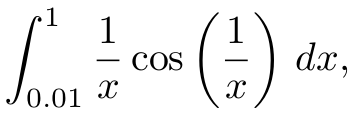
var integrate = ; { return Math / x);} ;// => -0.3425527480294604To integrate a vector function, you may import the vectorized version. To compute a contour integral of, say, ![]() about
about ![]() , that is,
, that is,
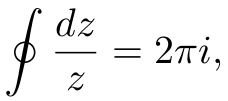
var integrate = ; ; // => [ 0, 6.283185307179586 ]API
require('integrate-adaptive-simpson')( f, a, b [, tol, maxdepth]] )
Compute the definite integral of scalar function f from a to b.
Arguments:
f: The function to be integrated. A function of one variable that returns a value.a: The lower limit of integration,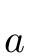 .
.b: The upper limit of integration,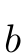 .
.tol: The relative error required for an interval to be subdivided, based on Richardson extraplation. Default tolerance is1e-8. Be careful—the total accumulated error may be significantly less and result in more function evaluations than necessary.maxdepth: The maximum recursion depth. Default depth is20. If reached, computation continues and a warning is output to the console.
Returns: The computed value of the definite integral.
require('integrate-adaptive-simpson/vector')( f, a, b [, tol, maxdepth]] )
Compute the definite integral of vector function f from a to b.
Arguments:
f: The function to be integrated. The first argument is an array of lengthninto which the output must be written. The second argument is the scalar value of the independent variable.a: The lower limit of integration,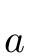 .
.b: The upper limit of integration,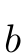 .
.tol: The relative error required for an interval to be subdivided, based on Richardson extraplation. Default tolerance is1e-8.maxdepth: The maximum recursion depth. Default depth is20. If reached, computation continues and a warning is output to the console.
Returns: An Array representing The computed value of the definite integral.
References
Colins, C., Romberg Integration and Adaptive Quadrature Course Notes.
License
(c) 2015 Scijs Authors. MIT License.

